Translate this page into:
Cydnidae bug pigmentation mimicking dermatitis artefacta
Corresponding author: Dr. Manju Daroach, Dermatology, AIIMS Bilaspur, India. daroachmanju@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Dhiman A, Chauhan P, Daroach M. Cydnidae bug pigmentation mimicking dermatitis artefacta. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:136. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_623_2023
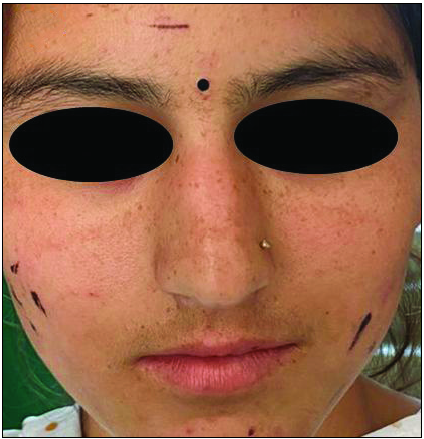
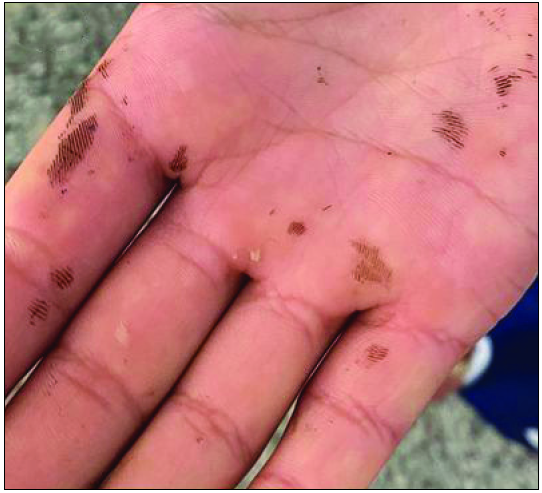
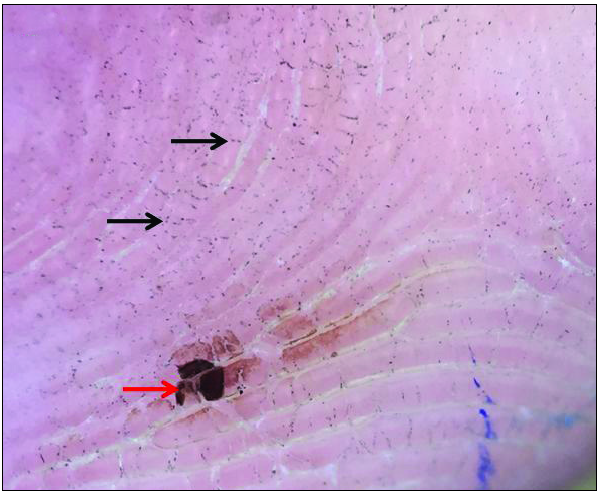
An 18-year-old girl presented with asymptomatic pigmentation on her face and palm that appeared suddenly the previous night, resembling ink-like markings. The lesions were non-blanchable and attempts to rub them off with acetone/alcohol were unsuccessful. There were no systemic symptoms or any psychiatric co-morbidity. She had a history of outdoor activity the previous day. A physical examination revealed multiple, black-brown streaky macules over the face [Figures 1 and 2] and blotchy brown pigmentation over the palms [Figure 3]. Dermoscopy of the finger lesion revealed brown blotchy pigmentation and micropigmentation in the surrounding areas. [Figure 4] Other mucocutaneous sites were uninvolved. A diagnosis of Cydnidae (Burrowing Bug) pigmentation was made. Cydnidae bugs, when in contact with human skin, release an odorous substance from the special glands in their thorax as a self-defense mechanism, causing macular pigmentation that persist for around 10–15 days. These glands can be actively expressed or squeezed out by pressure on the insect. History of outdoor activity before the development of lesions is characteristic in such cases. It improves spontaneously, hence awareness of this uncommon cause of pigmentation is essential to alleviate anxiety and avoid unnecessary investigations and treatment. Most cases documented in the literature reportedly affect palms and soles. However, an uncommon location and streaky pigmentation was observed in the present case. This distinctive presentation could be potentially misdiagnosed as dermatitis artefacta.
-
Multiple linear black macules over the face.

-
Multiple linear black macules with surrounding erythema over the right cheek.
-
Brownish pigmented macules over the palm.
-
Dermoscopic examination (using Dermlite DL3 10X) polarized mode of finger revealed brown blotchy pigmentation (red arrow) along with micropigmentation in surrounding areas (black arrow).
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.





