Translate this page into:
Comparative efficacy and therapeutic positioning of biologics in hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomised trials
Corresponding author: Dr. Husein Husein-ElAhmed, Department of Dermatology, Hospital de Baza, Granada, Spain. huseinelahmed@hotmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Husein-ElAhmed H, Husein-ElAhmed S. Comparative efficacy and therapeutic positioning of biologics in hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomised trials. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:302-10. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_665_2023
Abstract
Background
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a challenging inflammatory skin condition. Recently, many different biologics have been tested for HS, but the paucity of head-to-head comparative trials makes it difficult to determine the real value of each biological intervention. We aimed to determine the relative efficacy among biologics in treating moderate-to-severe HS throughout a network meta-analysis (NMA) and, to identify which pathogenetic pathways may be the most appropriate to target.
Methods
We comprehensively identified studies in 3 databases and clinicaltrials.gov. The eligibility criteria included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) reporting data on the efficacy of moderate-to-severe HS.
Results
The NMA comprised 13 studies comprising 14 interventions on 2,748 participants in the network. The NMA showed the odds of achieving the clinical response were significantly superior with adalimumab (RR: 0.37, 95% CI = 0.06–0.63), adalimumab QW (RR: 0.63, 95% CI = 0.43–0.87), MAB1p (RR: 1.33, 95% CI = 0.03–3.12), secukinumab (RR: 0.25, 95% CI = 0.11–0.47) and secukinumabQ2W (RR: 0.24, 95% CI = 0.1–0.46) compared to placebo.
Conclusion
Based on the NMA, inhibiting tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a with adalimumab appears to be the best strategy, followed by the blockade of IL--17 with secukinumab. Data for bimekizumab and CJM112 are promising. Infliximab has inconsistent clinical response, and more data are necessary to confirm this molecule as a potential third-line therapy in HS. The blockade of IL-23 and CD5a pathways is not relevant, or at least the current evidence is insufficient to recommend further investigation of guselkumab, risankizumab, and vilobelimab in phase III trials.
Keywords
Hidradenitis suppurativa
network meta-analysis
biologics
efficacy
treatment
WHAT’S ALREADY KNOWN ABOUT THIS TOPIC?
-
-
Many different biologics have been tested for hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), but head-to-head comparative trials are lacking.
WHAT DOES THIS STUDY ADD?
-
-
Adalimumab is the best strategy, followed by the blockade of IL-17 with secukinumab.
-
-
Data for bimekizumab and CJM112 are promising
-
-
Infliximab has inconsistent clinical response, and more data are necessary to confirm this molecule as a potential third-line of therapy in HS.
-
-
The blockade of IL-23 and CD5a pathways is not relevant, or at least the current evidence is insufficient to recommend further investigation of guselkumab, risankizumab, and vilobelimab in phase III trials.
Introduction
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by recurrent painful subcutaneous nodules, abscesses, and draining sinuses that can progress to scarring.1 Lesions of HS typically affect flexural sites such as the axillae and groins in a recurrent pattern. These lesions, along with the pain, pus, and odour, significantly impact patients’ quality of life.2 The complex multifactorial pathogenesis of this condition is not fully understood yet. Mutations of nicastrin and g-secretase genes, elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a, interleukin (IL)-1b, IL-17, IL-23, and interferon (IFN)- g and altered microbiome are vital factors that contribute to the development of HS.3
Non-surgical interventions for HS comprise a wide range of treatments, such as topical therapies, systemic antibiotics, retinoids, biologics, immunomodulatory oral therapies, and lasers.4 However, decision-making should ideally be based on high-certainty evidence (particularly randomised clinical trials), which is scarce. In conjunction with the unpredictable response to therapy, this fact increases the challenge of HS treatment, particularly in severe cases. Current treatment guidelines recommend biologics for cases of moderate-to-severe HS that have failed systemic therapies, with adalimumab being recommended as the first-line biologic.5–8 Recently, many different drug- and class-specific biologics have been tested for treating this challenging condition. However, the paucity of head-to-head comparative trials makes it difficult to establish the real value of each biological intervention.7
Hence, in this study, we aimed to determine the relative efficacy of biologics in treating moderate-to-severe HS throughout a network meta-analysis (NMA) and identify which pathogenetic pathways may be the most appropriate to target.
Material and Method
Protocol, search and eligibility
This review was carried out per the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA),9 and was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42023389081). We comprehensively identified English-language studies in Pubmed, EMBASE, Scopus, and clinicaltrial.gov from inception to February 2023 using the MeSH terms or key words “hidradenitis suppurativa” AND “biologics”. The detailed searching role of each author has been published previously elsewhere.10 The eligibility criteria included studies with randomised controlled trials (RCTs) design reporting efficacy data specifically for individuals with moderate-to-severe HS. Studies reporting post-hoc analysis and open-label studies were ineligible. Since the core outcome sets (COSs) for HS were not set up until a few years ago,11 we did not specify an explicit endpoint a priori in the eligibility criteria. Consequently, we did not expect most retrieved trials to have endpoints in common.
Statistical analysis and quality assessment
The detailed protocol of the statistical analysis to conduct this NMA has been published previously elsewhere.10 Quality of evidence was assessed independently by the authors with the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool.12
Results
Study selection and characteristics
The PRISMA study flow is presented in Supplementary file 1. Our search identified 823 records from databases and 28 records registered in clinicaltrials.gov, with 86 screened for the titles and abstracts. The full text of 17 reports was assessed for eligibility, culminating in 13 studies eligible for inclusion 13–24 and four studies excluded for insufficient data25,26 and post-hoc analysis 27,28. Basic study characteristics are presented in Table 1. All of the included papers were placebo-controlled randomised double-blinded trials; hence, they were rated with a low risk of bias in all domains. The NMA comprised 14 interventions involving 2,748 patients in the network [Figure 1].
|
Study Country* |
Trial Registration number |
Type of design |
Treatment Arms |
N |
Disease severity Primary endpoint |
Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- Bechara, 2021 - America & Europe |
- SHARPS - NCT02808975 |
R, DB, PC, Phase IV |
- ADA40Q2W - Placebo |
- 103 - 103 |
- Hurley II- or III HS - HiSCR |
Week 12 |
|
- Glatt, 2021 - America, Asia & Europe |
- NCT03248531 |
R, DB, PC, Phase II |
- BIMEK - ADA40Q2W - Placebo |
- 46 - 22 - 22 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 12 |
|
- Grant, 2010 - America |
- HS2006 - NCT00795574 |
R, DB, PC, Phase II |
- IFX - Placebo |
- 15 - 23 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HSSI50 |
Week 8 |
|
- Kanni, 2018 - America & Europe |
- NCT02643654 |
R, DB, PC, Phase II |
- MABp1 - Placebo |
- 10 - 10 |
- Hurley II- or III HS - HiSCR |
Week 12 |
|
- Kimball, 2012 - America |
- NCT00918255 |
R, DB, PC, Phase II |
- ADA40Q2W - ADA40QW - Placebo |
- 52 - 51 - 51 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HS-PGA |
Week 16 |
|
- Kimball, 2016 - America & Europe |
- PIONEER I & II - NCT01468207 & NCT01468233 |
R, DB, PC Phase III |
- ADA40Q2W - ADA40QW - Placebo |
- - 316 - 317 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 12/24 |
|
- Kimball, 2022 - America & Europe |
- NCT02421172 |
R, DB, PC Phase II |
- CJM112 - Placebo |
- 33 - 33 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HS-PGA |
Week 16 |
|
- Tzanetakou, 2016 - America & Europe |
- NCT01558375 |
R, DB, PC Phase II |
- ANAK - Placebo |
- 10 - 10 |
- Hurley II- or III HS - HiSCR |
Week 24 |
|
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals - America, Asia & Europe |
- SUNRISE - NCT03713632 |
R, DB, PC Phase III |
- SECQ2W - SECQ4W - Placebo |
- 180 - 180 - 183 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 16 |
|
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals - America, Asia & Europe |
- SUNSHINE - NCT03713619 |
R, DB, PC Phase III |
- SECQ2W - SECQ4W - Placebo |
- 181 - 180 - 180 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 16 |
|
- Janssen Research & Development - America & Europe |
- NOVA - NCT03628924 |
R, DB, PC Phase II |
- GUS - Placebo |
- 59 - 62 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 16 |
|
- AbbVie - America, Australia & Europe |
- DETERMINED 1 - NCT03926169 |
R, DB, PC Phase II |
- RISAN180 - RISAN360 - Placebo |
- 80 - 81 - 82 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 12 |
|
- InflaRx GmbH - America & Europe |
- SHINE - NCT03487276 |
R, DB, PC Phase II |
- VILOB - Placebo |
- 36 - 37 |
- Moderate-to-severe HS - HiSCR |
Week 16 |
HiSCR: Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response. HSSI50: a decrease of at least 50% from baseline in the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Index. HS-PGA: a Hidradenitis Suppurativa Physician’s Global Assessment score of clear, minimal, or mild with at least a 2-grade improvement relative to baseline score. R, DB, PC: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled. * Multicenter study would be presented with the continent instead of the country. ADA40Q2W: adalimumab injection of 80 mg given at baseline followed by 40 mg every 2 weeks starting week 1. ADA40QW: 160 mg of adalimumab at week 0 and 80 mg at week 2, followed by 40 mg weekly starting at week 4. ANAK: 100 mg of anakinra injected subcutaneously daily for 12 weeks. BIMEK: 320 mg of bimekizumab every 2 weeks after a 640 mg loading dose at baseline. CJM112: a subcutaneous injection weekly for 5 doses followed by bi-weekly for 5 doses for 10 doses. IFX: infliximab is given intravenously and continuously at 5 mg/kg doses at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and every 8 weeks. GUS: guselkumab 100 mg subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 4, and once every 8 weeks. MABp1: 7.5 mg/kg of MABp1 infusion every 14 days for a maximum of seven infusions. SECQ2W: secukinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks. SECQ4W: secukinumab 300 mg every 4 weeks. RISAN180: risankizumab 180 mg via subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 4, and 12. RISAN360: risankizumab 360 mg via subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 4, and 12. VILOB: 1,200 mg of vilobelimab given intravenously every other week.

- Network of interventions with the 14 interventions for clinical response in hidradenitis suppurativa.
Analyses of convergence and inconsistency
Examination of the deviance information criterion (DIC) indicated that the fixed-effect model was more suitable to fit the data than the random-effect model (DIC: 58.15 vs 59.16 Supplementary file 2). In the convergence assessment, we obtained an overall Potential Scale Reduction Factor (PSRF) of 1.004, indicating an adequate convergence of our network model. The trace and density plots are depicted in Supplementary File 3, while the Gelman-Rubin-Brooks plot is presented in Supplementary File 4. The inconsistency test of the optimised MCMC model with at least 5,000 adaptation iterations and 100,000 stimulation iterations determined a feasible applicability of the NMA results.
Clinical efficacy and ranking of interventions by relative efficacy
The NMA showed the odds of achieving the clinical response were significantly superior with adalimumab (RR: 0.37, 95% CI = 0.06–0.63), adalimumabQW (RR: 0.63, 95% CI = 0.43–0.87), MAB1p (RR: 1.33, 95% CI = 0.03–3.12), secukinumab (RR: 0.25, 95% CI = 0.11–0.47) and secukinumabQ2W (RR: 0.24, 95% CI = 0.1–0.46) compared to the treatment of reference (placebo). Anakinra (RR: –1.62, 95% CI = –4.81–0.25), bimekizumab (RR: 0.38, 95% CI = –0.01–0.89), CJM112 (RR: 0.76, 95% CI = –0.24–1.82), guselkumab (RR: 0.24, 95% CI = –0.23–0.63), infliximab (RR: 0.77, 95% CI = –0.68–2.38) risankizumab180 (RR: 0.06, 95% CI = –0.31–0.43), risankizumab360 (RR: 0.01, 95% CI = –0.42–0.41) and vilobelimab (RR: –0.12, 95% CI = –0.68–0.45) demonstrated worse therapeutic effect compared with placebo. The higher statistically significant difference was obtained for adalimumabQW. The network estimates (pooled direct and indirect data) of each intervention compared with the treatment of reference are presented in a forest plot of logarithm scale in Figure 2.
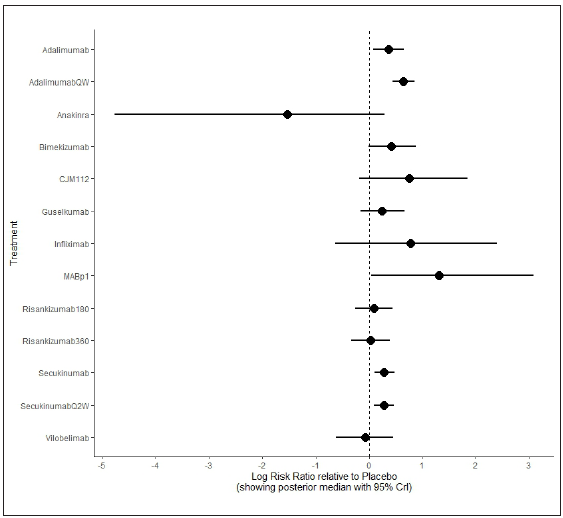
- Forest plot of primary endpoint (clinical response in hidradenitis suppurativa).
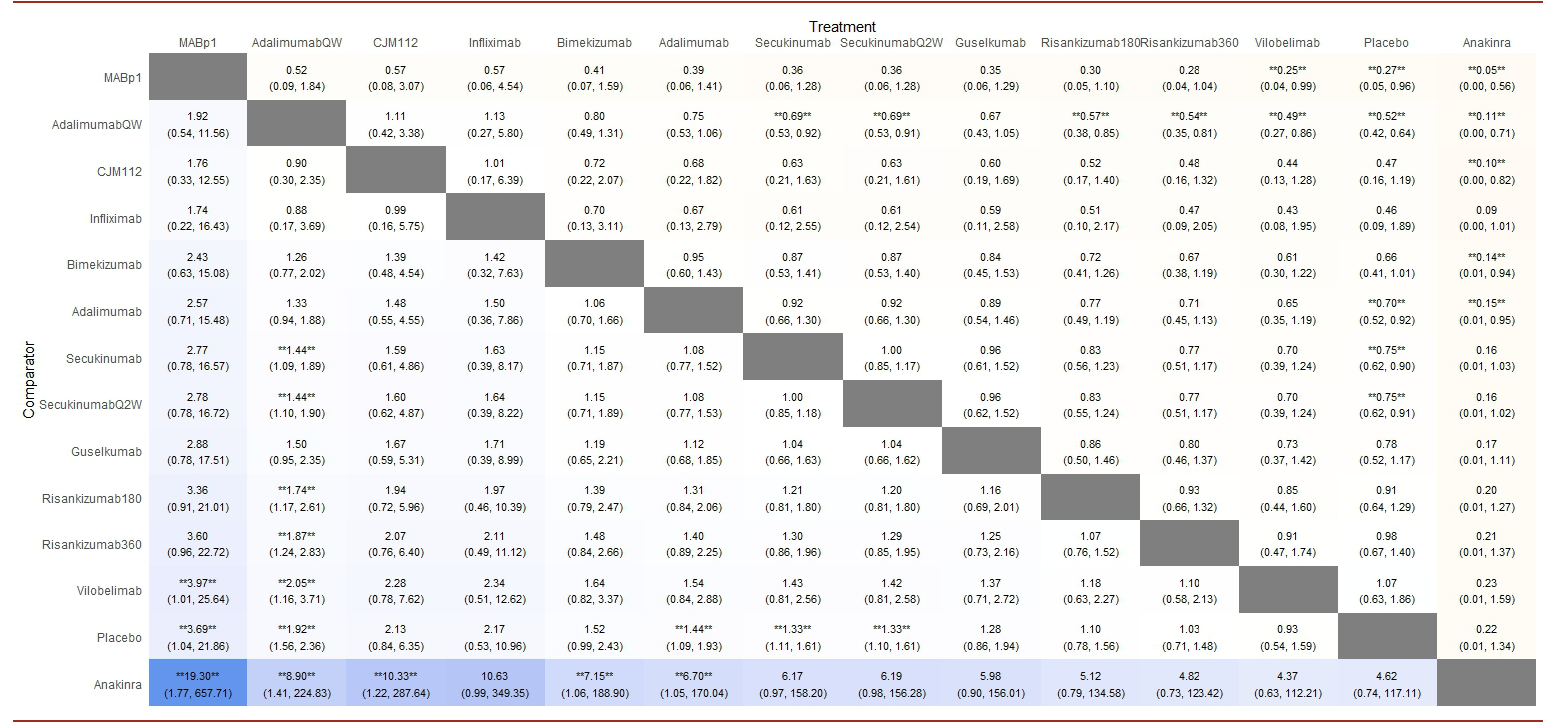
According to the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) [Figure 3], MABp1 had the highest probability of being the best treatment (0.954), followed by adalimumabQW (0.775), infliximab (0.752), CMJ112 (0.738), bimekizumab (0.660), adalimumab (0.591), guselkumab (0.479), secukinumab (0.476) and secukinumabQ2W (0.472). The remaining interventions yielded the following SUCRAs: risankizumab180 (0.330), risankizumab360 (0.267), vilobelimab (0.239), placebo (0.198) and anakinra (0.061). Table 2 summarises the results of relative efficacy in a league table.
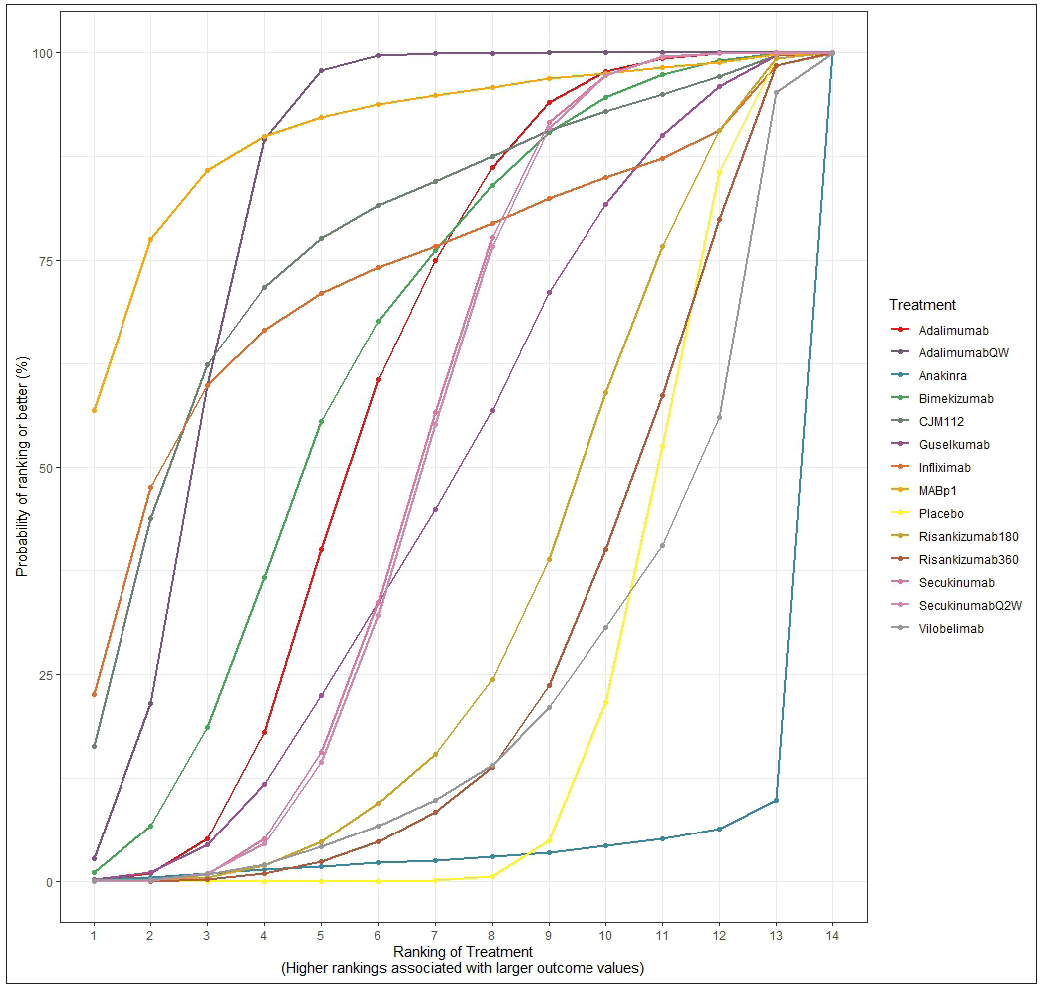
- The surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) shows the relative probability of being the best-ranked treatment in obtaining a clinical response.
Discussion
Despite the wide array of therapeutic approaches to HS, the evidence for the existing treatments is limited, indicating a particular need for more large clinical trials in HS.29 Furthermore, adalimumab, the biologic with the largest body of evidence, shows loss of efficacy in almost half of patients after 36 weeks of treatment,18 hence, other therapies with novel pathways of mechanisms are necessary.
This work reports the first biologic-specific NMA addressing their efficacy in HS. Our analysis included biologics targeting TNF (adalimumab and infliximab), IL-1 (anakinra and MABp1), IL-17 (bimekizumab, secukinumab and CJM112), IL-23 (risankizumab and guselkumab) and C5a receptor (vilobelimab). A recent NMA on the efficacy of biologics and small molecules has been recently published.30 In this article, authors concluded that adalimumab ranked first, followed by bimekizumab and secukinumab. Our results are consistent with these conclusions. Another novel NMA on the efficacy of non-surgical monotherapy for HS included other non-biologic treatments such as antibiotics and botulinum toxin type B.31 Notably, this article presented a heterogeneity in the disease severity of HS participants. Some trials comprised mild HS cases, and the largest network of this work comprised only 4 nodes. Consequently, this NMA fell into an intransitivity and incomparability among the interventions. Conversely, our NMA only included participants with moderate-to-severe HS treated with biologics in a parallel pattern with a placebo group. Thus, the transitivity and comparability of our network were warranted. Another advantage of our methodological approach is that it provides evidence of the mechanism of action at the molecular level.
Expectedly, adalimumab once a week presented with the most robust statistically significant difference against placebo with the narrowest confident interval. Additionally, it ranked at high positions in the SUCRA and league table. In one recent pair-wise meta-analysis involving 5 RCTs, adalimumab effectively achieved the clinical response and improved both symptoms and quality of life.32 However, the authors stated the certainty of evidence for adalimumab once weekly was still low, and more robust evidence was still necessary. Of note, infliximab, another anti-TNF drug of our NMA, obtained highly variable and unpredictable outcomes based on one RCT. Although encouraging, the accurate efficacy of infliximab should be further appraised.
Interleukin (IL)-1a and IL-1b are increased in the pus of the lesions from Hurley III-stage HS patients.33 MABp1 is the first-in-class human monoclonal antibody cloned from B lymphocytes that specifically neutralises IL-1a.16 According to our results, MABp1 was significantly superior to placebo and ranked as the best treatment in SUCRA and the league table. Conversely, we found that anakinra, a recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1R) that competitively prevents the effects of both IL-1a and IL-1b,34 was ranked as the worst choice. This striking finding indicates that the IL-1a pathway blockade (but not the IL-1b) may be considered an encouraging pathway to block in the future HS management that warrants further research.
The rationale for selecting IL-17 as a therapeutic target for HS is based on the evidence of the high expression of IL-17A, IL-17C, IL-17F, and IL-23 and the presence of IL-17-producing T cells in the cutaneous lesions of HS.35–37 Furthermore, a specific IL-17 signature and dysregulation of T-helper type 17 cytokines in HS lesional skin have been demonstrated.38
Consistent with these molecular findings, all the IL-17 antagonists analysed in our NMA showed a distinct superiority versus placebo. In the case of secukinumab, such superiority was statistically significant with a narrow confidence interval, indicating that the estimated relative risk is fairly accurate. Notably, we observed that clinical outcomes of secukinumab were independent of the dosage regimen, unlike adalimumab, for which the higher dosage regimen (once weekly) translated into better outcomes than the lower dosage regimen (q.2w.). This can be explained based on the pivotal role of IL-17 in the chronic inflammatory diseases of the skin,39 for which a much lower dose of an IL-17 antagonist than anti-TNFa drug is needed to get the desired anti-inflammatory effect. Once a threshold is reached, an overdosage of IL-17 antibodies would not translate into further anti-inflammatory response.
CJM112 is a novel fully human anti‐IL‐17A IgG1/k monoclonal antibody that binds with similar affinity to both IL‐17A and IL‐17AF. This molecule is structurally closely related to secukinumab and has shown even higher blockade potency than secukinumab.40 In our NMA, CJM112 showed a trend to statistically significant superiority to placebo, and it was ranked in third position in the league table and as the fourth best possible treatment according to SUCRA. These outcomes are based solely on one single phase II RCT, suggesting that CJM112 can be a promising candidate in the management of HS that certainly deserves deeper exploration with additional trials.
Regarding bimekizumab, another monoclonal antibody neutralising both IL‐17A and IL‐17F,14 we obtained similar clinical outcomes to CJM112. Remarkably, the trial design exploring bimekizumab in HS was unique as it used adalimumab as an active comparator and a third placebo arm. Bimekizumab achieved higher HiSCR and HiSCR scores than adalimumab.14
Among the three anti-IL-17s analysed in our study, secukinumab is the only molecule in phase III, which means it is the most advanced in clinical development for treating HS.21 This NMA confirms the promising clinical efficacy obtained in the previous trials. As reported by our results, we can propose secukinumab as second-line biologic therapy in patients with primary or secondary failure to adalimumab. Further evidence is required to make a similar recommendation for bimekizumab and CJM112.
IL-23 is a pro-inflammatory member of the IL-12 cytokine superfamily, with a potent ability to enhance the production of Th17 cells. However, this cytokine’s exact role in HS pathogenesis is not yet fully understood.41 As per our NMA, the IL-23 blockade pathway does not translate into a favourable clinical response: neither guselkumab nor risankizumab was superior to placebo and ranked low in SUCRA and the league table. A detailed view of the data and graphics shows that guselkumab yielded slightly better outcomes than risankizumab.
Along with the adaptive immune system, an upregulation of the innate immunity has also been described in HS lesions,42 and complement pathway activation with elevated levels of C5a and C5b-9 have been described in HS plasma.43 However, our results highlight that outcomes from vilobelimab, an anti-C5a antibody, are comparable to placebo; hence, the complement C5a pathway seems irrelevant for HS management.
One of the significant difficulties when measuring the clinical response to treatment in HS is selecting the most appropriate clinical outcome. Several scoring systems have been designed for this task, such as the Hurley staging system, the modified Sartorius score (MSS), the hidradenitis suppurativa physician global assessment (HS-PGA), and the hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR). The HiSCR has been proven to be a validated, FDA-supported primary efficacy endpoint with proper correlation analysis.44,45 In this aspect, our NMA is powered, whereas most included studies measured the clinical response with the HiSCR score. Furthermore, using a common comparator to which many interventions have not been compared may lead to wider confidence intervals and, hence, to less secure inferences than the data may warrant.46 In this way, we can state our outcomes are accurate since all the analysed interventions were primarily compared to a common comparator (placebo) in the RCTs.
The results of NMAs may be complicated to interpret for clinicians, especially when there are many alternative treatments and outcomes to consider.47 To address interpretation challenges, it has been proposed that NMA authors complement numerical data with graphical and ranking tools,48 bearing in mind that each tool has limitations and requires cautious interpretation.46 Hence, to avoid misleading and to promote the correct understanding of our NMA, we drew our conclusions based on the assessment of four criteria: 1) the statistical significance by forest plot, 2) the width of the confidence interval, 3) the SUCRA graphic and 4) the league table. For instance, according to the SUCRA and league table, MABp1 was the best possible treatment. Still, the large width of its confidence interval precludes us from accurately establishing the real effect size. Hence, we cannot recommend it before other more precise and robust alternatives, such as adalimumab or secukinumab.
This work is subject to certain limitations: First, long-term interpretations are limited since the mean follow-up period of the analysed studies is 15 weeks. To counteract this limitation, we collected data from the last reported time point in the trials. Second, nearly all included RCTs consisted of phase 2, except secukinumab and adalimumab, which were tested in large-scale phase 3 and 4 trials. Hence, more evidence is required for those phase 2 interventions. Third, we cannot predict whether the proposed ranking of biologics is equally effective in patients naïve to anti-TNF treatment and patients refractory to previous anti-TNF treatment with primary or secondary failure. Conclusions drawn from this NMA must be interpreted with these drawbacks in mind. These limitations illustrate the need for larger, longer studies that allow clinicians to make therapeutic decisions in HS care.
Conclusion
This study opens innovative insights into HS’s current and future management as it presents the first evidence-based comparison of biologics for HS treatment throughout an NMA. Our data highlight the IL-1a and IL-17 pathways represent two pathogenetic cascades whose activity should be therapeutically targeted and explored in future trials.
Based on the NMA, inhibiting tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a with adalimumab is the best strategy, followed by the blockade of IL-17 with secukinumab. Data for bimekizumab and CJM112 are promising, and these IL-17 blockers might be positioned at the same level as secukinumab if such data are confirmed in future research. This statement also applies to MABp1.
The inhibition of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a with infliximab has inconsistent clinical response. More RCTs on the exact efficacy of infliximab are necessary to confirm this molecule as a potential third-line of therapy in HS.
The blockade of IL-23 and CD5a pathways is not relevant, or at least the current evidence is deficient in recommending a further investigation of guselkumab, risankizumab, and vilobelimab in phase III trials. These drugs may comprise a fourth-line therapy for HS. Anakinra should only be used after failures of all other biological alternatives.
Acknowledgement
H. H-E. wrote the code used for the data analysis, and worked with S. H-E. to ensure the interpretation was correct. H. H-E. prepared the draft of the manuscript, coordinated the project team, and interpreted the procedure and results of the analysis. S. H-E. assisted with the data analysis and provided feedback on the draught to ensure that the analysis interpretation was clear. No drug manufacturing company was involved in the study design, data analysis, data interpretation, or manuscript writing. All data were collected from published articles in the public domain or clinicaltrials.gov (Accessed on February 5, 2023).
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa/acne inversa: Criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland). 2015;231:184-90.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quality of life and psychosocial implications in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland). 2016;232:687-91.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review integrating inflammatory pathways into a cohesive pathogenic model. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:2965.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-44.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- British association of dermatologists guidelines for the management of hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa) 2018. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:1009-17.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: Part II: Topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:91-101.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: A practical framework for treatment optimisation - Systematic review and recommendations from the HS ALLIANCE working group. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:19-31.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Consensus on the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa - Brazilian Society of Dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:7-19.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n160.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Bayesian network meta-analysis of head-to-head trials for complete resolution of nail psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol.. 2023;48:895-902.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A core domain set for hidradenitis suppurativa trial outcomes: An international Delphi process. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:642-50.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- The cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in conjunction with surgery in moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: The SHARPS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg. 2021;156:1001-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy and safety of bimekizumab in moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1279-88.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Infliximab therapy for patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:205-17.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MABp1 targeting IL-1a for moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa not eligible for adalimumab: A randomized study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:795-801.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adalimumab for the treatment of moderate to severe Hidradenitis suppurativa: A parallel randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:846-55.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Two phase 3 trials of adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:422-34.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IL-17A is a pertinent therapeutic target for moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Combined results from a pre-clinical and phase II proof-of-concept study. Exp Dermatol. 2022;31:1522-32.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Safety and efficacy of anakinra in severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:52-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMJ Dermatol. 2022;10[1]:40–43. DOI/10.33590/emjdermatol/10182311. https://doi.org/10.33590/emjdermatol/10182311.
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03628924 (Accessed February 5th 2023)
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03926169 (Accessed February 5th 2023)
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03487276 (Accessed February 5th 2023)
- Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with etanercept injection. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:501-4.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial of adalimumab in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165:391-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adalimumab treatment in women with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa from the placebo-controlled portion of a phase 2, randomized, double-blind study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1192-6.
- [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reduction in pain scores and improvement in depressive symptoms in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa treated with adalimumab in a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt38x5922j.
- [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;10:Cd010081.
- [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy and safety of biologics and small molecules for moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15:1351.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy of non-surgical monotherapies for hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review and network meta-analyses of randomized trials. J. Dermatol. Treat 2022:1-12.
- [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e26190.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Compartmentalized cytokine responses in hidradenitis suppurativa. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0130522.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Systematic review of safety and efficacy of IL-1-targeted biologics in treating immune-mediated disorders. Front Immunol. 2022;13:888392.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:790-98.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deficiency of IL-22 contributes to a chronic inflammatory disease: Pathogenetic mechanisms in acne inversa. J Immunol. 2011;186:1228-39.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interleukin 17C is elevated in lesional tissue of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:1045-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Dysregulated cytokine expression in lesional and nonlesional skin in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1431-39.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Psoriasis pathogenesis and the development of novel targeted immune therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:645-53.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ProvidedDocs/71/NCT02998671/Prot_000.pdf (Accessed February 5th 2023)
- Expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:790-98.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a interleukin (IL)-1b and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: A rationale for targeting TNF-a and IL-1b. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Complement activation in hidradenitis suppurativa: A new pathway of pathogenesis? Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:413-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New treatments and new assessment instruments for hidradenitis suppurativa. Exp Dermatol. 2022;31:33-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- HiSCR (Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response): A novel clinical endpoint to evaluate therapeutic outcomes in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa from the placebo-controlled portion of a phase 2 adalimumab study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:989-94.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Approaches to interpreting and choosing the best treatments in network meta-analyses. Syst Rev. 2017;6:79.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Reporting of results from network meta-analyses: Methodological systematic review. BMJ. 2014;348:g1741.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014;349:g5630.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






