Translate this page into:
Peripheral neuritis: Tuberculosis as a rare diagnostic contender
Corresponding author: Dr. Swastika Suvirya, Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy, King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. swastika.p@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Tripathi S, Tyagi V, Rawat D, Srivastava A, Malhotra KP, Bajaj DK, et al. Peripheral neuritis: Tuberculosis as a rare diagnostic contender. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_811_2024
Dear Editor,
A 52-year-old woman presented with progressive nodular swellings over her right wrist joint accompanied by mild pain for a year. She was in good nutritional health, did not smoke or drink, and had no family history of leprosy or tuberculosis. As an accredited social health activist in her village, she had been engaged in identifying and providing directly observed treatment for tuberculosis patients during the last decade.
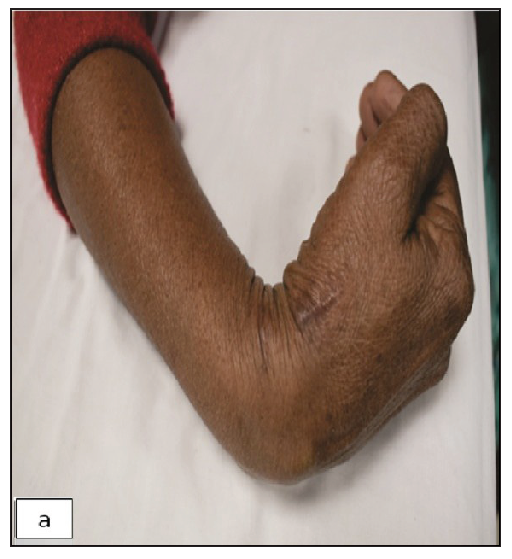
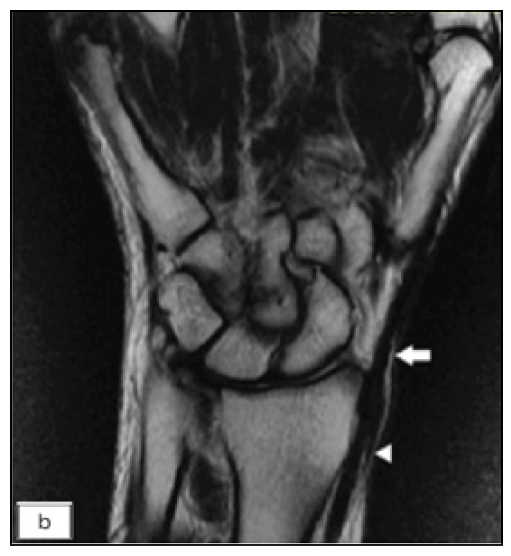
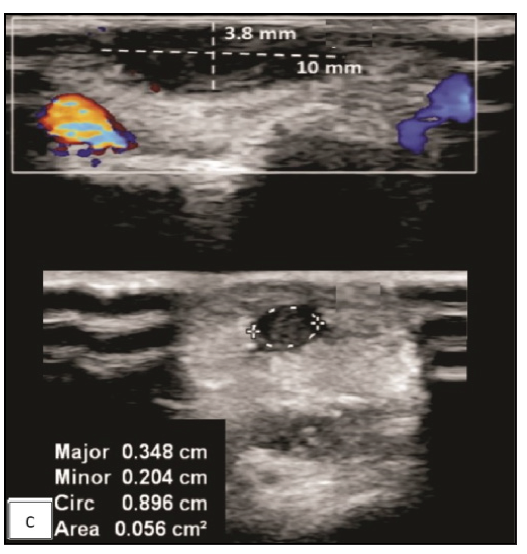
Physical examination revealed three non-compressible, ill-defined swellings around the right wrist, extending above and below the joint. One of these swellings had crusting and ulceration from a previous attempted incision and drainage performed outside our institute [Figure 1a]. The superficial branch of the right radial nerve was grossly thickened as compared to the contralateral side, but there was no sensory loss. Range of motion was normal at small joints of the right hand. The differential diagnoses considered at this point of time were leprosy, sporotrichosis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, trauma-related causes, diabetic complications, and connective tissue diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 30mm/hour and the Mantoux test showed a positive induration of around 25mm. The nerve conduction study was normal and the slit-skin smear was negative. X-ray of the wrist did not reveal any bony erosions. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the right wrist joint revealed tenosynovitis of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons [Figure1b and 1c]. A high-resolution ultrasound was also conducted to evaluate further and monitor any changes in the size of the peripheral nerve during follow-up. It showed three hypoechoic lesions, with the largest measuring 18 × 13 mm, and thickening of the superficial branch of the radial nerve (cross-sectional area of 0.47 cm2 vs 0.026 cm2 of the left) in close approximation to the largest swelling. The size of other swellings as appreciated on high-resolution ultrasound was 17 × 6 mm (over the dorsal aspect of the first metacarpal) and 14 × 7 mm (over the lateral aspect of the wrist) [Figure 2a].Histopathological analysis confirmed granulomatous inflammation in both the nodule and nerve samples [Figure 2b]. Ziehl-Neelsen and Wade-Fite staining showed no acid-fast bacilli. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA. was negative in both samples. Cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification testing (CBNAAT) with the Xpert® Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin assay kit (Cepheid Inc, U.S.A.) yielded a positive result from the nodule but was negative in the nerve. Cultures for Mycobacterium tuberculosis were negative in both samples. A final diagnosis of tubercular tenosynovitis with neuritis was made.
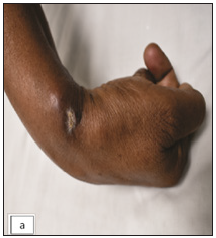
- Three nodules proximal and distal to the wrist joint, the middle one showing crusting at the site of attempted incision and drainage done outside our institute.
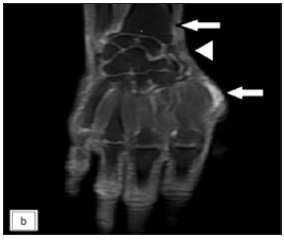
- Coronal post contrast T1-weighted MRI of right hand showing two focal enhancing thickening of the synovial sheath of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis tendons at the lateral aspect of the wrist and the level of the first metacarpal head (white arrows -first and third nodules). The thickening is also noted extending to involve the adjacent superficial branch of the radial nerve (white arrow head).
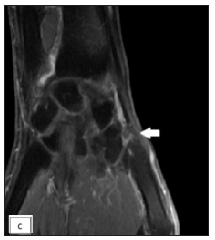
- Coronal post contrast T1-weighted MRI of right hand showing another focal enhancing thickening of the synovial sheath of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis tendons at the level of first metacarpal base (white arrow-second nodule).
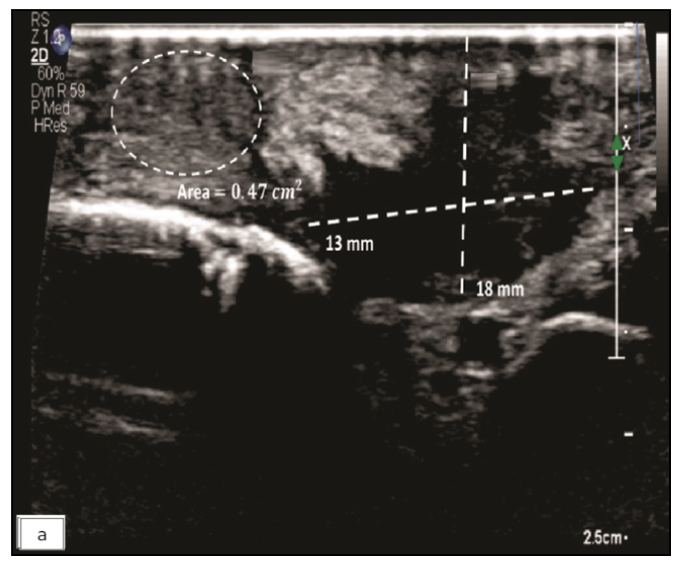
- Greyscale high-resolution ultrasound image of right hand showing a heterogeneous hypoechoic lesion in the skin and subcutaneous tissue (dotted lines) over the cubital fossa with thickened and heterogeneous superficial branch of the radial nerve (dotted circle) which is involved by the lesion.
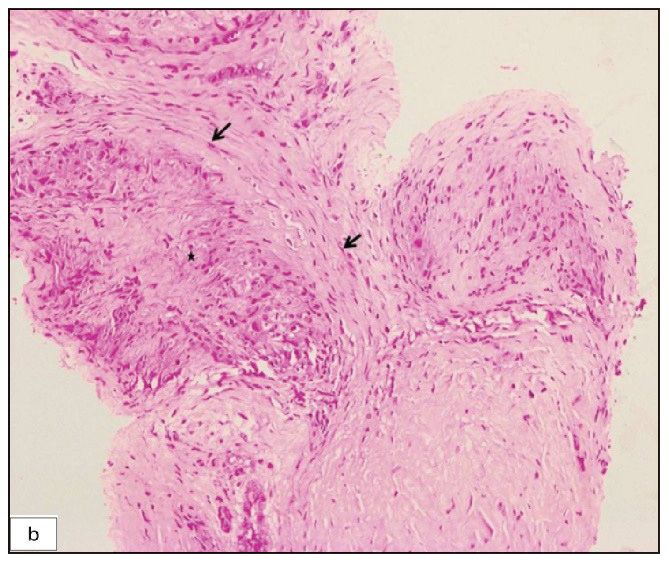
- Biopsy of the superficial branch of radial nerve depicting nerve bundles (black arrows) and an eccentric granuloma (asterisk) (Haematoxylin & eosin, 200x).
The patient was prescribed anti-tubercular therapy of intensive phase for two months and continuation for another 16 months owing to her reluctance to undergo surgery. At the six-month follow-up, complete resolution of the distal nodule on the lateral side of the wrist was observed, along with a partial reduction in the size of the other two nodules and the nerve. Following 18 months of anti-tubercular therapy, the nodules had resolved completely and the nerve size had returned to normal, both clinically and on radiological examination [Figures 3a, 3b, and 3c].
- Completely resolved nodules post anti-tubercular therapy at 18 months with a longitudinal scar at the site of biopsy.
- Coronal T2-weighted MRI of the right hand, post 18 months of anti-tubercular therapy, shows complete resolution of synovial thickening along the tendons (white arrow)and normalisation of thecalibre of the superficial branch of the radial nerve (white arrow head).
- Nine-month follow-up Greyscale high-resolution ultrasound image of the right hand showing significant reduction in the size and vascularity of the cutaneous lesion in the skin and subcutaneous tissue (dotted lines) at the cubital fossa with a reduction in the size of the superficial branch of the radial nerve (dotted circle).
In the index case, a 25mm induration on the Mantoux test, exceeding the 10mm threshold for high-risk occupational exposure (or even 15mm for healthy individuals) per Centers for disease control and prevention guidelines, along with a CBNAAT-positive nodule and response to anti-tubercular therapy, further supports the diagnosis as an inflammatory process attributable to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.1
Primary tuberculous tenosynovitis predominantly affects the wrist and volar aspect of the hand, representing approximately 5% of osteoarticular tuberculosis cases.2 While tuberculosis-induced neuritis is rare, it has been documented in isolated instances, affecting areas such as the phrenic and optic nerves, often in cases of regional tuberculosis spread.3 Peripheral nerve involvement following regional tuberculous tenosynovitis has been infrequently reported.4
In a few cases, achieving desired results has been possible with extended courses of anti-tubercular therapy, often surpassing the recommended six-month duration,5 while surgery remains essential in others, with varying opinions on the extent of surgical debridement. This case is distinguished from others as we utilised molecular tests, specifically CBNAAT on the nodule and nerve tissue, providing greater insight into the exact pathogenesis of peripheral nerve involvement in tuberculosis cases. In our patient, neuritis preceded the anti-tubercular treatment. Neuropathy in tuberculosis patients is not always iatrogenic, and the potential for a primary effect on nerves subsequent to tuberculosis should be acknowledged. Immune-mediated mechanisms, granuloma in nerve, deposition disease, compression effect due to vertebral collapse, granulomatous tissue, or cold abscess are putative mechanisms of neuropathy in tuberculosis cases.6
Tuberculosis-related neuropathy is also linked to comorbidities like the human immunodeficiency virus, diabetes, malnutrition, hypothyroidism, and alcoholism. Familiarity with the tubercular aetiology of neuritis is crucial for dermatologists, as it closely resembles leprosy, where peripheral nerve thickening with swelling is often misconstrued as a manifestation of the latter.7 Early recognition of tubercular neuropathy will allow early treatment and prevent permanent and irreversible consequences.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of AI-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Nationwide shortage of tuberculin skin test antigens: CDC recommendations for patient care and public health practice. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:552-3.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- An uncommon occupational accident: Tuberculous tenosynovitis of the extensor tendons of the hand. Chir Main. 1999;18:309-12.
- [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubercular neuritis: A new manifestation of an ancient disease. Australas Med J. 2011;4:674-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical spectrum of tuberculous optic neuropathy. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2012;2:183-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Tuberculous tenosynovitis of the Flexor Tendons of the hand and wrist: A case report and mini-review. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020;57:249-52.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Peripheral neuropathy in persons with tuberculosis. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2015;2:5-11.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Epidemiology of peripheral neuropathy: An Indian perspective. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2017;20:173-84.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]





