Translate this page into:
Cutaneous cholesterol embolization syndrome
2 Department of Medicine, Ryukyu University School of Medicine, Okinawa, Japan
Correspondence Address:
Naohiko Imai
Department of Medicine, St. Marianna University School of Medicine, Kanagawa
Japan
| How to cite this article: Imai N, Zamami R, Kimura K. Cutaneous cholesterol embolization syndrome. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2015;81:388 |
A 67-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Six weeks later, bluish reticulated patches were observed on the tips of his toes and an ulcer was noted on his right toe [Figure - 1]a. Laboratory tests showed eosinophilia, an elevated serum creatinine level and an elevated lactate dehydrogenase level. Skin biopsy showed the presence of cholesterol clefts in the lumen of a vessel [Figure - 1]b]. His kidney function continued to deteriorate and reached end-stage renal disease in 3 months. Cholesterol embolization syndrome is caused by embolization of cholesterol crystals and is commonly associated with iatrogenic manipulations. Skin biopsy is diagnostic and the needle-shaped spaces noted within the lumen of arterioles of the affected skin are characteristic.
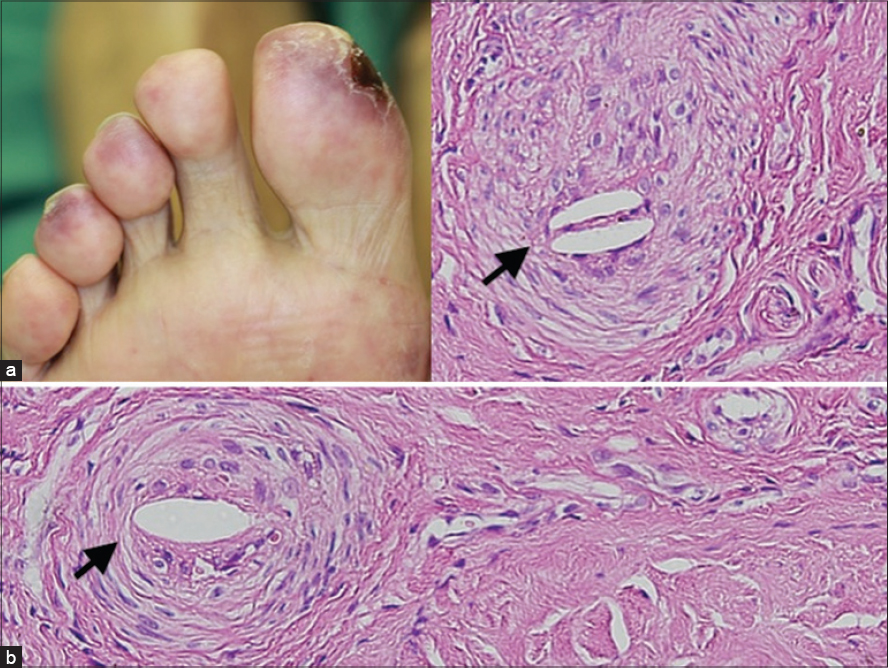 |
| Figure 1: (a) Bluish reticulated patches were observed on the tips of the patient's toes and an ulcer was noted on his right toe; (b) skin biopsy showed the presence of cholesterol clefts in the lumen of a vessel |
Fulltext Views
2,546
PDF downloads
2,534





