Translate this page into:
Therapeutic potential of biosimilars in dermatology
Correspondence Address:
Binod K Khaitan
Department of Dermatology and Venereology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110 029
India
| How to cite this article: Gupta V, Khaitan BK. Therapeutic potential of biosimilars in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2015;81:451-456 |
Abstract
The introduction of biologic therapy has revolutionized the treatment of many chronic diseases, including several dermatological disorders. Biological agents promise to satisfy medical needs previously unmet by conventional medicines. Unfortunately, these agents are expensive and out of reach for the majority of patients who need them. Biosimilars are copies of the innovator biological agents and represent an important advance in the field of biological therapeutics. Although they are similar to the original biologic, differences in terms of structure, efficacy, safety and immunogenicity remain a concern. Thus, biosimilars cannot be regarded as bio-generics. Awareness of the key differences between a biosimilar and its reference biological agent is essential for optimal treatment and safety of patients. The increasing availability of biosimilars provides patients and doctors with less expensive alternatives and increases the accessibility of biologic therapy to needy patients. In this review, we discuss the concept of biosimilars, the need for appropriate regulatory pathways and their current status in dermatology.INTRODUCTION
The introduction of biologics has produced a paradigm shift in the management of many chronic skin diseases. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Centre for Biologics Evaluation and Research defines "biologics" as therapeutic agents derived from any living material (microbe, plant, animal or human) which mimic or block the function of naturally occurring proteins. [1] Advances in the understanding of the basis of several recalcitrant dermatologic diseases have led to the successful use of many biologics such as etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, rituximab and interleukins in these conditions. Although biologic agents have proven to be effective when conventional treatments fail or cannot be given, their high cost has so far limited access. Thus, there is a need for less expensive biological agents, and this has led to the development of "biosimilars."
What are Biosimilars?
The term "biosimilar" has been defined by various agencies [Table - 1]. [2],[3],[4] Essentially, a "biosimilar" is a biological agent similar to an already approved or licensed-for-use biological medicine, also known as the "reference product." By definition, a biosimilar will have a similar safety and efficacy profile as its reference product and is generally used to treat the same conditions. Biosimilars are also known as "follow-on biologics" in the USA and "subsequent entry biologics" in Canada. [5],[6]

Biosimilar or Biogeneric?
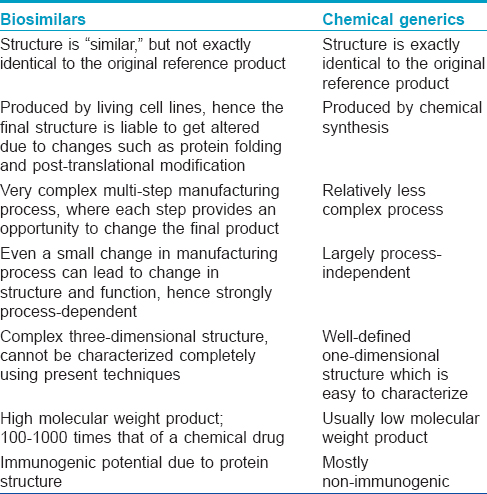
Generic drugs are a copy of the original molecule. By the same analogy, biosimilars may be considered as biogenerics, as they are copies of the original biological agent. However, unlike chemical generics, biosimilars are only similar to, but not an exact replica of the original drug. The manufacture of biologics and biosimilars is very complex, with many steps being involved. Slight variations in the manufacturing process during the production of biosimilars may create a final product not exactly identical to the biologic. [7] Every step of the manufacturing process, from the selection of host cell lines to purification systems, protein sequencing and post-translational modifications may change the structure of the biosimilar relative to the original biologic. [8] Thus, even though biosimilars may be regarded as the biological equivalent of chemical generic drugs, differences exist, and these are summarized in [Table - 2].
Regulatory Framework concerning Biosimilars
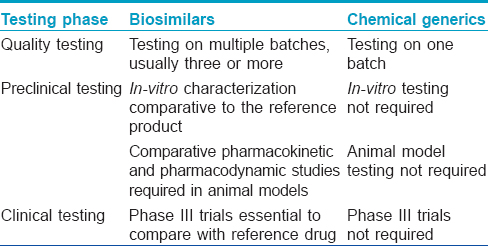
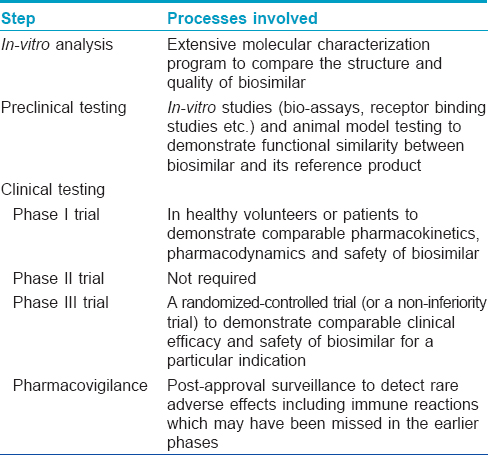
The European Medicines Agency was the first regulatory agency to enunciate guidelines for biosimilars in 2005. The first biosimilars to enter the market were Omnitrope (biosimilar to Genotropin) and Valtropin (biosimilar to Humatrope) in 2006, both were recombinant human growth hormone (somatropin). [7] As of February 2015, of the 21 biosimilars approved by the European Medical Agency, 2 have been withdrawn (Filgrastim ratiopharm in 2011, and Valtropin in 2012), leaving 19 biosimilars approved for use in the European market. [9] The European Medical Agency guidelines on biosimilars are widely regarded as the gold standard and many countries including Australia, Canada and Japan have adopted them without making major changes. [7],[10] The World Health Organisation (WHO) released a set of standards in 2009 assuring the safety, efficacy and quality of biosimilars aimed at providing a consistent scientific standard across the globe. [11] This has been adopted as a reference by some nations to formulate their own set of approval pathways. India announced its biosimilar guidelines in 2012. [12] Interestingly, while the European Union with its European Medicines Agency has been a pioneer in the regulations on biosimilars, the USFDA has only recently, in May 2014, released its first draft of guidelines on "follow-on biologics." On March 6, 2015, Zarxio (filgrastim-sndz) became the first biosimilar to be approved by the US-FDA. [13] Although the requirements for approval of biosimilars are more stringent than that for licensing of simpler generic drugs [Table - 3], [5],[8] the process is much shorter and less tedious compared to the original biologic. [10] The makers of biosimilars are required only to demonstrate a certain degree of similarity, both structurally and functionally with the original biologic along with safety in a step-wise process [Table - 4]. The major issues addressed by the European Medical Agency guidelines are degree of similarity, safety, immunogenicity and extrapolation of indications. [10]
Degree of similarity
The European Medicines Agency guidelines recognize the fact that biologicals cannot simply be copied and therefore accept minor differences in the active substance, such as variability in post-translational modifications. [7] The structural similarity between a biosimilar and the original agent can be demonstrated using invitro preclinical analytical techniques such as chromatography, protein sequencing, mass spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Strictly speaking, even the manufacturers of the licensed biopharmaceuticals produce a "biosimilar" of their own agent with every new batch or changes in the manufacturing process. Hence, these analytical methods are used to compare various batches of already approved biologics, too. However, it is important to note that all the potential differences between biopharmaceuticals may not be identified by analytical methods. [14] Thus, it becomes mandatory to demonstrate similar clinical efficacy, in addition to structural similarity with the comparator biologic. This is accomplished through pre-clinical and clinical studies comparing the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the biosimilar with the original biologic in healthy volunteers or patients. The maximum allowable difference between a biosimilar and the innovator molecule profile has been considered to be 15%. [6] The objective of the biosimilar guidelines is not to re-establish patient benefit but to demonstrate high similarity with the reference biological agent. Thus, traditional phase II trials are not needed to evaluate biosimilars, paving the way for abbreviated pathways for biosimilar approval. This also means that the clinical comparisons of biosimilar and reference product can use a different study design, sample population and endpoints from those used to establish the therapeutic benefit of the original product. [15] Both European Medicines Agency and US-FDA require at least one clinical trial, of sufficient size and power, to demonstrate clinical equivalence or non-inferiority for each available formulation. [16] However, because a biosimilar, by definition, has to be "similar" to the original innovator drug and cannot be either "superior" or "inferior," concerns have been raised regarding the suitability of a non-inferiority trial to establish biosimilarity as it cannot exclude superior efficacy of the biosimilar to the innovator. [14] Although these stringent requirements are in place to ensure good quality control of biosimilars, they may lead to higher costs and limit commercialization of these agents thus restricting availability to patients with limited means. [14]
Safety and immunogenicity
As the technology for manufacturing the original biopharmaceutical is a closely guarded trade secret, biosimilars are produced using processes independent of their reference products. This may cause structural differences which might translate into functional differences, raising concerns regarding the safety of biosimilars. [10]
"Immunogenicity" is a safety issue unique to biologics. Like all proteins, biologics too have the potential to induce antibody responses. In most instances the immune reactions are not of clinical significance, but occasionally, such reactions may be life-threatening. Unfortunately, immunogenicity in animals is not predictive in humans, and hence the immunogenic potential of biosimilars cannot be fully predicted using pre-clinical studies alone. Even clinical studies (owing to limited sample size) may not always reveal the differences, especially when the biosimilar differs from the reference product mostly with regard to safety, immunogenicity or rare adverse events. [16] This is best illustrated by the example of pure red cell aplasia arising as a complication of epoetin therapy. [17],[18] Instead of improving anemia of chronic kidney disease, it led to severe epoetin-resistant anemia requiring blood transfusions, immunosuppressive treatment and eventually kidney transplantation. Though not fully understood, substitution of polysorbate 80 in the epoetin formulation and subcutaneous route of its administration were thought to be responsible for the immune response against both recombinant epoetin and endogenous erythropoietin. Recently, leachates released by contact between polysorbate 80 and the uncoated rubber stoppers of pre-filled syringes were also hypothesized to act as adjuvants to the immune response. [19]
An effective pharmacovigilance program is important in identifying such rare adverse events. Manufacturers must have a robust system in place to record hitherto unreported adverse events. [6] Pharmacovigilance should also ensure the traceability of the products. This is complicated if biosimilars have the same international non-proprietary name as the innovator. Currently, the WHO is deciding whether biosimilars should be assigned a different international non-proprietary name to that of the original biologic. [20] Moreover, the practice of reporting drug adverse effects varies widely from place-to-place and is dependent on the local regulatory authorities.
Another hurdle in an effective pharmacovigilance program is the "interchangeablity" or "automatic substitution" of biosimilars i.e., the substitution of a drug at the pharmacy. [8] Chemical generics are usually considered to be interchangeable; the risk of substitution is expected to be low as they are an exact copy of the original drug. However, since biosimilars cannot be exactly identical, the same substitution rules cannot be applied. [7] The European Medical Agency guidelines are silent on this important matter and thus each European Union member state decides on its own. [6] The US-FDA, on the other hand, can designate a biosimilar as interchangeable with its reference product. This allows the pharmacist to dispense either the original biological agent or its biosimilar version without the knowledge of the prescribing physician, preventing traceability of the drug, and thus hindering the pharmacovigilance program. There are also concerns that repeated switching might increase immunogenicity. [21]
Extrapolation of indications
A biosimilar can be used for all indications approved for the innovator drug and there is no need for independent clinical studies. However, the final decision rests with the regulatory authorities. [6]
Current Status in India
Although biosimilars have been marketed in India for many years, comprehensive regulatory guidelines governing their approval were announced only in June 2012. The regulatory bodies responsible for approval of "similar biologics" in India are the Department of Biotechnology (under the Ministry of Science and Technology), through its Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare). [12] The guidelines outline a simple abridged procedure for evaluation of "similar biologics" which have been approved and marketed in India, Europe or USA for more than 4 years. Before these regulations came into effect on September 15, 2012, many biosimilars had already been approved for use in India under an ad-hoc abbreviated pathway. However, these "alternative" biologicals cannot be compared to those approved in the European Union which are subject to rigorous comparability exercises and cannot be regarded as a "true" biosimilar and thus cannot be licensed in the European Union or North America. Nonetheless, recent reports suggest that an agreement in June 2012 between Dr. Reddy′s Laboratories (India) and Merck Serono (Germany) will allow Dr. Reddy′s Laboratories to market its product in Europe. [22] The various biosimilars used in dermatological diseases available in India, as well as their global counterparts are summarized in [Table - 5].
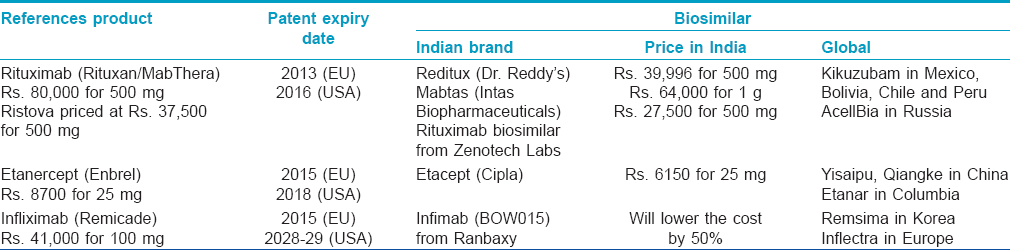
Roche′s rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, was licensed in the USA as Rituxan and in the European Union as MabThera. It is distributed in India as Ristova, in partnership with Emcure pharmaceuticals. Its patent expired in the European Union in November 2013 and in the USA, it is due to expire in September 2016. Since April 2007, Dr. Reddy′s has marketed Reditux, a rituximab biosimilar, in India, Bolivia, Chile and Peru. So far, the only data supporting its efficacy and safety is on 17 patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, published as an abstract. [23] In May 2006, Dr. Reddy′s launched an initiative called Sparsh, through which all oncology brands of Dr. Reddy′s are given free to patients suffering from cancer. [24] Unfortunately there is no such scheme for patients with pemphigus and other dermatologic conditions. However, the authors are informed by the representatives of the company that it provides a vial free on purchase of one vial to poor patients on the request of the treating doctor, thus effectively halving the cost of the treatment course. The other recently developed rituximab similar biologics available in India are Mabtas (Intas Biopharmaceuticals) and another developed by Zenotech Labs. Our limited experience in using rituximab biosimilars (Reditux and Mabtas) in pemphigus patients has been satisfactory with no major adverse events so far.
On April 17, 2013, Cipla launched the first biosimilar of etanercept (Enbrel, Pfizer/Amgen) in India, called Etacept which is expected to be about 30% cheaper as compared to Enbrel. [25],[26] It is manufactured by a China-based company Shanghai CP Guojian Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and will be marketed by Cipla in India. Since its launch in 2006 in China, over 50,000 patients have been treated with Etacept. However, it is understood that like Reditux, Etacept is also not developed in accordance with the global guidelines.
In December 2014 Ranbaxy′s Infimab (formerly known as BOW015) became India′s first infliximab biosimilar to be approved by the Drug Controller General of India. Infimab has been developed for the Indian market in accordance with the country′s 2012 biosimilar guidelines. It is marketed under a licensing partnership with Boston-based EPIRUS Biopharmaceuticals and will be manufactured by Reliance Life Sciences at a facility in Mumbai, India. [27] In a phase III trial on 189 rheumatoid arthritis patients, Infimab has been demonstrated to have a similar efficacy, safety and immunogenicity as the innovator molecule (infliximab, Remicade). [28]
SUMMARY
Biosimilars may be regarded as the biological equivalent of a chemical generic drug. They are similar, but not exactly identical, to the original innovator biological agent. It is important to be aware of the differences between original biotechnological medicines and biosimilars for patient safety; however, this should not deter a physician from using the less expensive biosimilars. Clinicians are often unaware that even original molecules can undergo modifications in manufacturing after approval from regulatory agencies, thus effectively becoming a biosimilar in itself.
Biosimilars represent important innovations that are less expensive and hence offer the potential to deliver benefit to a number of patients who may not currently be able to access these therapies. In addition, since the biosimilar is being produced years after the introduction of the innovator, biosimilar manufacturers may take advantage of advances in biopharmaceutical production that can yield cost savings compared to the original production processes. Awareness about biosimilars and biological agents along with consistent pharmacovigilance will allow treating clinicians to be more confident in its use.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
| 1. |
Krueger JG. The immunologic basis for the treatment of psoriasis with new biologic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002;46:1-23.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Expert Committee on Biological Standardization. Guidelines on Evaluation of Similar Biotherapeutic Products (SBPs). World Health Organization. October 23, 2009. Available from http://www.who.int/biologicals/areas/biological_therapeutics/BIOTHERAPEUTICS_FOR_WEB_22APRIL2010.pdf. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 22].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Draft overarching guidelines on biosimilars: Guideline on Similar Biological Medicinal Products (Reference number: CHMP/437/04 Rev 1). European Medicines Agency. May 22, 2013. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_ library/Scientific_guideline/2013/05/WC500142978.pdf. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 20].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Quality considerations in demonstration biosimilarity to a reference protein product. Washington, DC: U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2012.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Ranjan N, Mahajan VK, Misra M. Biosimilars: The "future" of biologic therapy? J Dermatol Treat. 2011;22:319-22.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 6. |
Puig L. Biosimilars in dermatology: Starting with infliximab. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas 2013;104:175-80.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 7. |
Nowicki M. Basic facts about biosimilars. Kidney Blood Press Res 2007;30:267-72.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 8. |
Strober BE, Armour K, Romiti R, Smith C, Tebbey PW, Menter A, et al. Biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars in psoriasis: What the dermatologist needs to know. J Am Acad Dermatol 2012;66:317-22.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 9. |
Biosimilars approved in Europe. Available from: http://www.gabionline.net/Biosimilars/General/Biosimilars-approved-in-Europe. [Last accessed on 2015 Jul 17].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 10. |
Dranitsaris G, Amir E, Dorward K. Biosimilars of biological drug therapies: Regulatory, clinical and commercial considerations. Drugs 2011;71:1527-36.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 11. |
Bogaert P, Lietzan E, Sim L. Biosimilar regulation: Important considerations and global developments. Cross-border Life Sciences Handbook. UK: Practical Law Company; 2011
[Google Scholar]
|
| 12. |
Guidelines on similar biologics: Regulatory requirements for marketing authorization in India Available from: Dbtbiosafety.nic.in/Files\CDSCO-DBT Similar Biologicsfinal.pdf [Last accessed on 2015 May 25].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 13. |
Press Announcements - FDA approves first biosimilar product Zarxio. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm436648.htm [Last accessed on 2015 Jul 17].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 14. |
Vital EM, Kay J, Emery P. Rituximab biosimilars. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2013;13:1049-62.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 15. |
What are biosimilars and are they important? Drug Ther Bull 2013;51:57-60.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 16. |
Fiorino G, Girolomoni G, Lapadula G, Orlando A, Danese S, Olivieri I, et al. The use of biosimilars in immune-mediated disease: A joint Italian Society of Rheumatology (SIR), Italian Society of Dermatology (SIDeMaST), and Italian Group of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IG-IBD) position paper. Autoimmun Rev 2014;13:751-55.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 17. |
Mellstedt H, Niederwieser D, Ludwig H. The challenge of biosimilars. Ann Oncol 2008;19:411-19.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 18. |
Kuhlmann M, Marre M. Lessons learned from biosimilar epoetins and insulins. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis 2010;10:90-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 19. |
Locatelli F, Del Vecchio L, Pozzoni P. Pure red-cell aplasia "epidemic"- -mystery completely revealed? Perit Dial Int 2007;27 Suppl 2:S303-307.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 20. |
Available from: http://www.ebe- biopharma.org/docs/pdf/Biosims_EBEEFPIAPosition_Naming_7July2006.pdf. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 23].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 21. |
Kessler M, Goldsmith D, Schellekens H. Immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006;21 Suppl 5:v9-12.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 22. |
Biosimilar News. Dr. Reddy′s and Merck Serono to develop and commercialise biosimilars. Available from: http://www.biosimilarnews.com/dr-reddys-and-merck-seronoto- develop-and-commercialise-biosimilars. [Last accessed on 2015 Jul 17].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 23. |
Viswabandya A, Prashanthi PV, Raju CN, Rajsekhar R, Mathews V, Madki S, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of a biosimilar rituximab in newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Treated with R-CHOP (Rituximab, Cyclophosphamide, Adriamycin, Vincristine, Prednisolone). Blood 2007;110:4491. [ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 2007 November 16].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 24. |
Reditux, An Affordable Biosimilar Monoclonal Antibody. 5 December, 2008. Available from: http://www.biospectrumindia.com/biospecindia/news/158720/reditux-affordable-biosimilar-monoclonal-antibody. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 23].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 25. |
Cipla launches first etanercept "similar biologic" in India. April 2013. Available from: http://www.gabionline.net/Biosimilars/News/Cipla-launches- first-etanercept -similar-biologic-in-India. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 23].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 26. |
Jayaraman K. India′s Cipla sets sights on Avastin, Herceptin and Enbrel. Nat Biotechnol 2010;28:883-84.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 27. |
Malkhed VK. Ranbaxy launches first biosimilar infliximab in India. Available from: http://www.biosimilar news.com/ranbaxy-launches- first- biosimilar- infliximab- in-india. [Last accessed on 2015 Apr 02].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 28. |
BOW015, a Biosimilar Infliximab, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis on Stable Methotrexate Doses: 54-Week Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Active Comparator Study. ACR Abstracts. Available from: http://acrabstracts.org/abstracts/bow015-a-biosimilar-infliximab-in-patients-with- active-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-stable- methotrexate -doses-54- week-results-of-a-randomized-double-blind- active- comparator-study/ [Last accessed on 2015 Apr 02].
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
5,900
PDF downloads
3,075





