Translate this page into:
A new occlusive patch test system comparable to IQ and Finn chambers
2 Department of Dermatology, CLAIMS Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3 Department of Pharmacy, CLAIMS Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Correspondence Address:
Shaziya Z Sajun Merchant
CLAIMS Pvt. Ltd., 4th Floor, B Wing, Modi House, C 10, Dalia Industrial Estate, New Link Road, Andheri (W), Mumbai - 400 058, Maharashtra
India
| How to cite this article: Sajun Merchant SZ, Vaidya AD, Salvi A, Joshi RS, Mohile RB. A new occlusive patch test system comparable to IQ and Finn chambers. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2014;80:291-295 |
Abstract
Background: A good patch test system should have good adhesion and contact, and minimal leakage; Finn and IQ patch test system have these properties but are expensive. Aims: To develop a new cost-effective occlusive patch test system that had good contact with the skin and was non-irritant. Methods: The system (designated Chamber X) was fabricated using a semi-permeable tape and a flexible virgin plastic chamber. Chamber X was developed by (i) selecting adhesive tape based on its non irritancy and adhesive potential (ii) testing plastic chamber material for its skin irritancy (iii) testing the assembled system against Finn, IQ and locally available chambers for irritancy, contact, leakage and occlusivity. Results: Chamber X showed better occlusion than IQ, Finn and locally available chambers and was comparable to, (P > 0.05) IQ and Finn in terms of irritancy, contact and leakage. Conclusions: The results demonstrate that the Chamber X offers a cost effective patch test system comparable to IQ and Finn chambers in terms of safety, adhesion, leakage and occlusivity.Introduction
Patch testing has, for many years, been used to make a diagnosis of and predict the potential for primary irritation and/or allergenicity of materials that come in contact with the skin. [1] Initially, an absorbent material containing the test product was attached to a variety of adhesive tapes and applied directly on the skin for testing. Many systems with better occlusivity and contact have since been developed.
We present data on safety, adhesion, leakage and occlusivity of a new system (designated Chamber X fabricated by C.L.A.I.M.S. Pvt. Ltd.) based on flexible virgin plastic chamber material in combination with an adhesive tape. Chamber X was developed by (i) selecting a non-irritant adhesive tape with good adhesion [1] (ii) testing the plastic chamber material for its skin irritancy, and (iii) testing the assembled system against Finn, IQ and locally available chambers for skin irritancy, contact, leakage and occlusivity.
METHODS
The study was monocentric, randomized and comparative. It was approved by an independent ethics committee after a review of the study documents and was registered under the CTRI (Clinical Trial Registry of India) prior to initiation. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS software version 10.0. The Students "t0" test and Mann-Whitney U test were used for statistical analysis of data to prove significance.
Materials
The Chamber X is made from two components:
- The adhesive tape
- The chamber material
The adhesive tape used was the semi-occlusive Micropore™ (3M) because of its good adhesion and low irritation potential. The chamber was made from grade 1070 LA 17 low density polyethylene (LDPE) supplied by Reliance Industries. This grade is virgin plastic without any plasticizer and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (India) for use in contact with food and beverages; it is quite flexible and can maintain good contact with the skin surface (http://plastics.ides.com/datasheet/e117557/relene-1070la17).
Adhesive tapes assessed during these experiments included Micropore (latex free hypoallergenic paper tape); Durapore (latex free silk like hypoallergenic tape), Transpore (clear, porous, latex free hypoallergenic plastic tape) and Surgical Paper tape (hypoallergenic paper tape) which were all obtained from 3M India Limited.
The Chamber X was compared with commercially available patch testing systems: Finn chambers (obtained from Smart Practice, Phoenix, Arizona, USA), IQ chambers (from Chemotechnique Diagnostics, Sweden) and locally available aluminium chambers (purchased from Systopic Laboratories, New Delhi, India).
A Spectrophotometer (CM 2600 D, Konica Minolta) was used to assess erythema and a Moisturemeter SC, (Delfin Technologies) was used to measure the occlusive properties of the chambers during the study.
Methods
Testing of adhesive tape
Adhesion and irritancy of the following tapes were assessed in order to select the appropriate tape for making Chamber X: Micropore, Durapore, Transpore, Surgical Paper tape and tapes of IQ chambers.
Bare patches of different tapes were applied on the upper inner forearm of 32 volunteers (this site was preferred over the back as pressure on the back during rest or sleep could alter evaluation of adhesion giving false positive results). Six test sites (3 × 3 cm 2 ) were marked on the upper arms of the volunteers for application of five different tapes and one site (without any application) was the control. The patches were applied in 3 layers: adhesive surgical tape (Micropore/Durapore/Transpore/1 × 1 cm 2 ) patches was first applied and covered by 2 × 2 cm 2 gauze sheet, and followed by 3 × 3 cm 2 patches of Micropore/Durapore/Transpore. Scoring for adhesiveness was performed at 24 hours after removing the tapes, and irritancy scoring was done at 48 hours.
Patches were analysed for irritancy and adhesion (using irritancy and adhesion scales described below). The innermost 1 × 1 tape was a measure for irritancy and the outermost 3 × 3 tape was a measure of adhesion and irritancy.
Draize scale for irritancy
Score for erythema
0=No reaction
1=Very slight erythema/glaze/wrinkles
2=Slight erythema/glaze/wrinkles
3=Moderate erythema/glaze/wrinkles
4=Severe erythema/glaze/wrinkles
Score for oedema (O)
0=No reaction
1=Very slight oedema
2=Slight oedema
3=Moderate oedema
4=Severe oedema
As per Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) guidelines for safety evaluation of cosmetics, with reference to IS 4011:1997 Amendment No. 2, September 2004, the product is classified as non-irritant if the mean score is 2; mildly irritant if score is up to 4 and irritant if it scores above 4. [2]
Adhesion scale [3]
0= >/=90% adhered (essentially no lift off of the skin)
1= >/=75% to < 90% adhered (some edges only lifting off of the skin)
2= >/=50% to < 75% adhered (less than half of the system lifting off of the skin)
3= <50% adhered but not detached (more than half the system lifting off of the skin without falling off)
4= patch detached (patch completely off the skin).
Testing Chamber X material
An empty Chamber X in the reversed position was applied on the back in order to maximize skin contact and to check safety of Chamber X material. The results were evaluated using the Draize scale and spectrophotometric "a" value readings (erythema).
Method for testing chamber irritancy and contact
Patches were applied on the back of 30 healthy volunteers using Chamber X, Finn chambers, IQ chambers and local aluminium chambers.
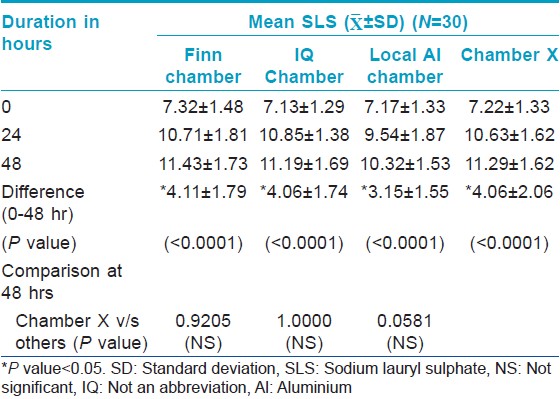
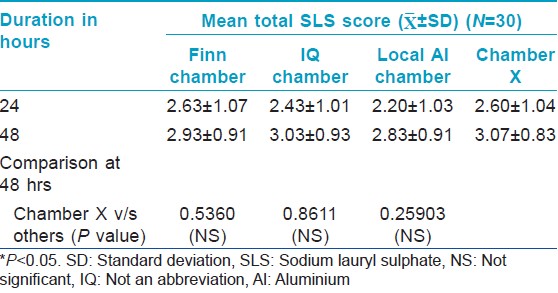
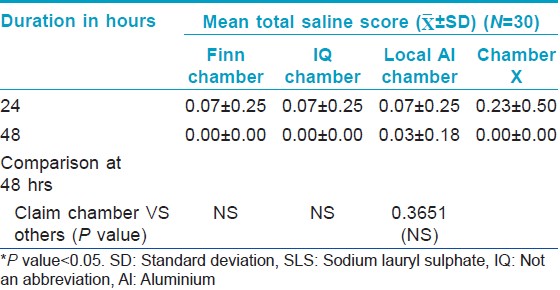
For the irritancy test, each patch contained two chambers: One filled with 1% sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and the other filled with 0.9% saline (negative control). The Chamber X material was stuck on the tape selected from study 1, while the other chambers were on their original tape. Thus, four patches were randomly applied on the back, each containing 2 chambers. The SLS bearing test area should give a definite reaction so as to prove proper contact of the chambers with the skin.
Evaluation of irritancy
The results for irritancy were evaluated using:
- Draize scale and
- Spectrophotometric "a" value readings (erythema).
The Draize scale SLS scores of Chamber X were compared to those of the other three types of chambers. The score of Chamber X should be equal/greater than the scores of the IQ/Finn/local aluminium chambers so as to prove efficient contact of the chambers.
The saline patch (negative control) was also assessed by the Draize scale.
Method for testing chamber leakage:
- One drop of ink was filled into each of the four types of patch test systems and applied onto a glass slide to visually observe leakage (in vitro).
- One patch of each of the 4 types of patch test systems containing filter paper dipped in a food grade colour dye was applied on the back of 30 volunteers (in vivo).
In vitro testing was done prior to testing in vivo.
Evaluation of leakage
Visual observation and photographic evidence of the food grade color patch and the slides was done to evaluate the chambers′ resistance to leakage.
Method for testing occlusivity
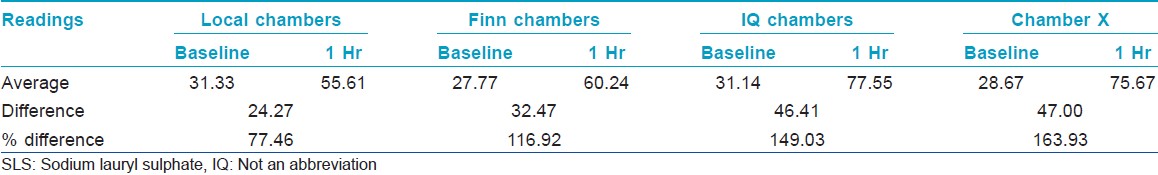
Each of the four different types of patch systems was applied in duplicate for one hour, on the skin of the inner forearm of ten volunteers. Moisturemeter SC readings were taken on the occluded skin before and after application of the chambers to check the moisture build up and hence occlusive property of the chambers.
RESULTS
Statistical analysis was done using Students "t" test or Mann-Whitney U test using SPSS software version 10.0
Tape selection
All the tapes tested showed average irritancy scores below 2 and hence were classified as non-irritant. All the tapes tested also had good adhesivity with average adhesion scores below 1.
Micropore tape was selected as most appropriate for Chamber X as it showed no irritation, good adhesion and was cost effective.
Skin irritancy testing of Chamber X material
There was no significant difference in ′′a′′ scores from baseline (P = 0.5), and the average score at 48 h was 0.31 demonstrating that the empty inverted Chamber X was non-irritant [Table - 1].

Contact, irritancy and leakage test
Evaluation of contact of chambers using Spectrophotometer [Table - 2] and [Table - 3] showed a significant increase in "a" value (erythema) from baseline [Figure - 1] indicating good contact of skin with SLS for all the chambers tested. There is no significant difference in the "a" value between the chambers and the IQ chamber, Chamber X and Finn chamber had similar average "a" value scores.
 |
| Figure 1: Percentage difference between baseline and 48 hour spectrophotometer scores |
All the chambers also showed a significant increase in Draize scores from the baseline [Figure - 2] indicating good contact of skin with SLS. However, there was no significant difference in the Draize score between the chambers.
 |
| Figure 2: Draize score of 30 volunteers at 48 hour against baseline score of ''0'' |
There was no significant change from baseline in Draize scores in chambers filled with filterpaper dipped in 0.9% saline indicating that all the chambers tested including Chamber X were not irritant. There was also no significant difference in the Draize score between the chambers [Table - 4].
Evaluation of leakage
Visual observation of the leakage from the different chambers, as seen in [Figure - 3]a and b, indicated that Chamber X, IQ chamber and Finn chamber showed minimal leakage as compared to local aluminium chambers. Thus, the Chamber X, IQ chamber and Finn chamber are comparable in terms of leakage.
 |
| Figure 3: Photographic Representation of leakage, (a) in vivo; (b) in vitro |
Evaluation of occlusive property of chambers
Chamber X showed the best occlusive property followed by IQ chamber and Finn chamber [Table - 5] and [Figure - 4].
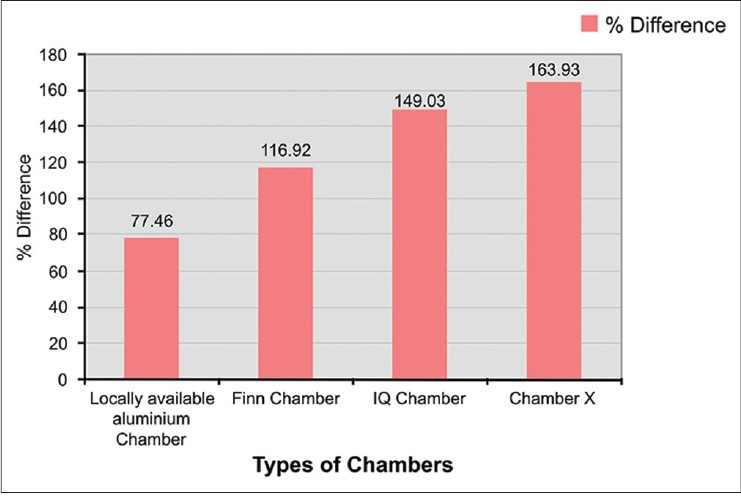 |
| Figure 4: Percentage difference between baseline and 1 h MMSC values |
DISCUSSION
A new patch test system, based on a flexible virgin plastic chamber was tested for its safety, adhesiveness and occlusive properties. It was demonstrated that Chamber X was non-irritant and had good adhesiveness. No significant outward migration of the dye occurred during use as determined by the dye marker. This eliminates problems arising from interaction between samples and adhesive tape. The occlusive properties are related to the chamber design and the selection of plastic from which the chamber was fabricated. The chamber is flexible which allows it to follow the contours of the body and hence maximizes contact between skin and test product. There were also no adverse reactions or discomfort experienced by the volunteers in the experiments detailed.
The results demonstrate that Chamber X is comparable to IQ and Finn chambers in terms of safety, adhesion, leakage and occlusive property. It has been designed to be available at a substantially lower cost.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We hereby acknowledge our colleagues at C.L.A.I.M.S. Pvt. Ltd. Mrs. Meena, Mrs. Preetha Paul and Mr. Mohammmedali Sajun, Ms. Radha Seshadri for their contribution towards this paper.
| 1. |
Quisno RA, Doyle RL; Hill Top Research, Inc. A new occlusive patch test system with a plastic chamber. J Soc Cosmet Chem 1983;34:13-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Bureau of Indian Standards. IS 4011: Methods of test for safety evaluation of cosmetics (1997). 2007; Amendment 2:1-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Wokovich AM, Prodduturi S, Doub WH, Hussain AS, Buhse LF. Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2006;64:1-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
3,675
PDF downloads
2,793





