Translate this page into:
Adult xanthogranuloma of the vulva: A rare occurrence
Corresponding author: Dr. Yi Chen, Department of Dermatology, Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing, China. yichenderma@163.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Wang Q, Feng L, Zhong J, Chen Y. Adult xanthogranuloma of the vulva: A rare occurrence. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_1899_2024
Dear Editor,
Xanthogranuloma (XG) is a benign proliferation of the non-Langerhans histiocytic cells mostly affecting children. Adult XG (AXG) usually occurs in the third to fourth decade of life.1, predominantly involving the head, neck, and trunk. XG of the testicles and penis is rare,2 and XG of the vulva is extremely rare.3,4 Herein, we report a case of solitary XG involving the vulva of an adult woman.
A 41-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic solitary papule on the root of her clitoris for 1 month. She denied any history of trauma or high-risk sexual intercourse prior to lesional onset. Physical examination revealed a red, dome-shaped, papule on the vulva sized 5mm, with smooth surface [Figure 1]. No regional lymphadenopathy or systemic abnormalities were detected. Treponema pallidum haemagglutination assay (TPHA) was negative. Routine blood biochemistry including lipid profile was unremarkable, and a chest CT scan also revealed no abnormalities.
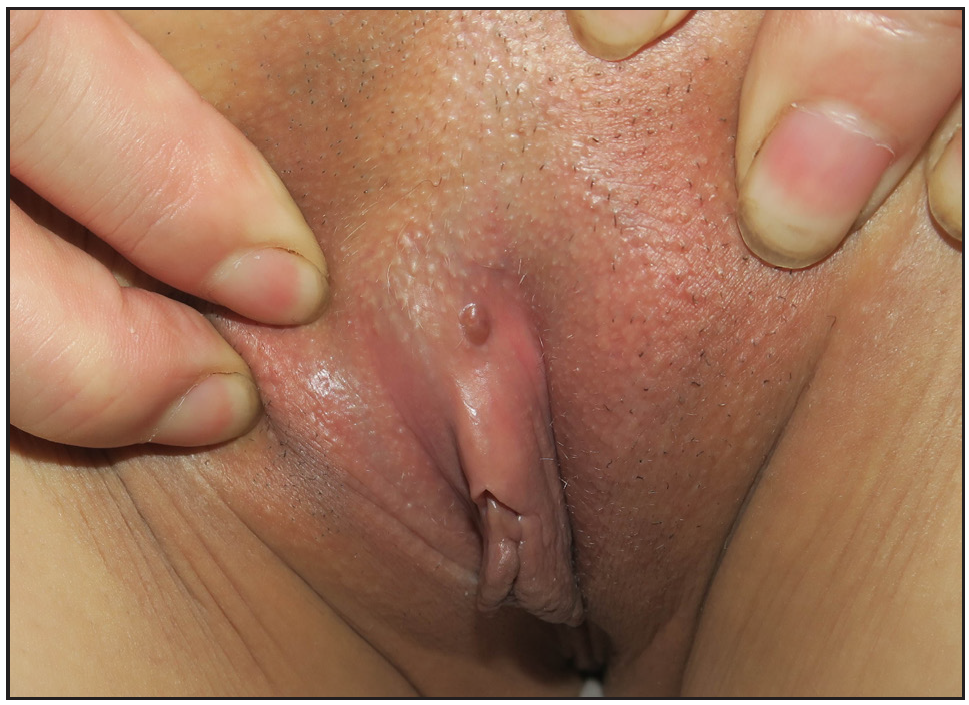
- A red, dome-shaped, 5-mm-diameter, papule with smooth surface on the vulva.
Additionally, the peripheral blood smear was unremarkable. The excision biopsy showed a nodular, well-circumscribed dermal infiltration of histiocytes, lymphocytes, foamy macrophages, eosinophils, and multiple Touton giant cells [Figure 2a and 2b]. Neither cell atypia nor mitosis was observed. Immunohistological tests were positive for CD68 [Figure 3a], but negative for S100 and CD1a [Figure 3b and 3c]. Based on the clinico-pathologic correlation, and immunohistochemical staining, we made a diagnosis of AXG. After excision biopsy, 6-months follow-up period was uneventful.
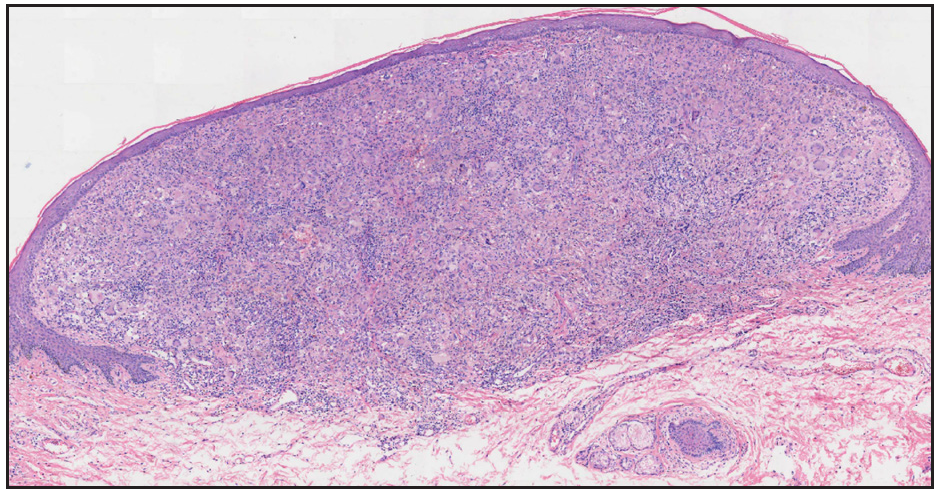
- Excision biopsy of the lesion showed a nodular, well-circumscribed dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Haematoxylin-eosin, 40x).
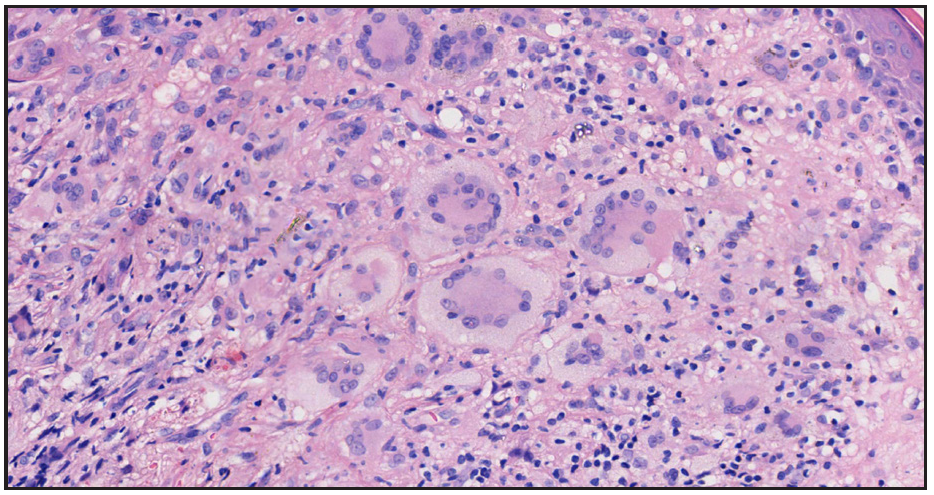
- High power view showed that the inflammatory cells are composed of lymphocytes, foamy histiocytes, as well as multiple Touton giant cells (Haematoxylin-eosin, 200x).
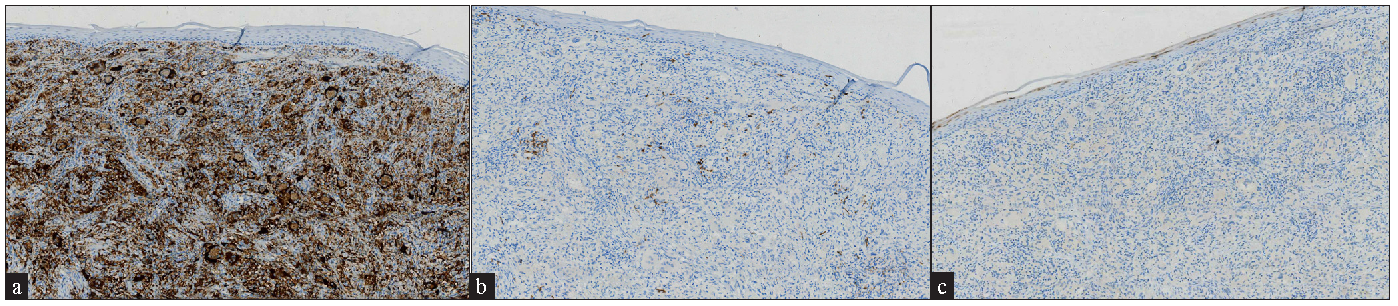
- Immunohistochemical staining positive for a) CD68 (100x) and b) negative for S100 (100x) and c) CD1a (100x).
XG is a fibrohistiocytic lesion that usually appears as yellow-red, round, or dome-shaped papules. Pathologically, XG is characterised by dermal infiltration of histiocytes and Touton giant cells. Possible differentials include other vulvar cystic or papular diseases, such as epidermoid cyst, molluscum contagiosum, condyloma acuminatum, and Spitz naevus. Epidermoid cysts often histologically appear as white or skin-coloured papules or nodules and cystic structures that are composed of stratified squamous epithelium. Molluscum contagiosum is characterised by molluscum bodies. Condyloma acuminatum commonly appears as verrucous or mamillated papules with rough surfaces with pathognomonic koilocytosis. Spitz naevus can also show papular red changes clinically, while pathologically, it shows tumorous changes that are composed of epithelioid or spindle cells.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice, and relapse is uncommon. Some reports have revealed that XG may be associated with other diseases like neurofibromatosis, acute leukaemia, urticaria pigmentosa, Rosai-Dorfman disease, and renal amyloidosis.3 Thus, careful systemic examination is necessary in such patients.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Multiple generalized xanthogranuloma in adult: Case report and treatment. Indian J Dermatol. 2011;56:197-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Adult xanthogranuloma on penis: A case report. Int J Dermatology. 2022;61
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Isolated juvenile xanthogranuloma of clitoral connective tissue. Klin Padiatr. 2005;217:238-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adult xanthogranuloma of the vulva: Case report and review. Pathology. 2002;34:86-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





