Translate this page into:
An overview of mycetoma and its diagnostic dilemma: Time to move on to advanced techniques
Corresponding author: Dr. Uneza Husain, Department of Microbiology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India. uneza47@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Husain U, Verma P, Suvirya S, Priyadarshi K, Gupta P. An overview of mycetoma and its diagnostic dilemma: Time to move on to advanced techniques. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2023;89:12-7.
Abstract
The neglected tropical disease mycetoma can become extremely devastating, and can be caused both by fungi and bacteria; these are popularly known as eumycetoma and actinomycetoma respectively. The classical triad of the disease is subcutaneous swelling, multiple discharging sinuses and the presence of macroscopic granules. The present study aims to highlight the existing diagnostic modalities and the need to incorporate newer and more advanced laboratory techniques like pan fungal/pan bacterial 16S rRNA gene polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing, Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), rolling circle amplification (RCA), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA). It is important for the medical team to be aware of the various diagnostic options (both existing and future), so that diagnosis of such a debilitating disease is never missed, both by clinicians and microbiologists/pathologists. The newer diagnostic methods discussed in this article will help in rapid, accurate diagnosis thus facilitating early treatment initiation, and decreasing the overall morbidity of the disease. In the Indian context, newer technologies need to be made available more widely. Making clinicians aware and promoting research and development in mycetoma diagnostics is the need of the hour.
Keywords
Mycetoma
laboratory diagnosis
MALDI-TOF
PCR
rolling circle amplification
loop-mediated isothermal amplification
recombinase polymerase amplification
Introduction
Mycetoma is a disfiguring, granulomatous neglected tropical disease said to be caused by either bacteria (actinomycetoma) or fungi (eumycetoma). In 1842, John Gill gave the first description of mycetoma in India at Madurai.1,2 Maximum cases have been reported from the ‘mycetoma belt’ which includes equatorial regions of Africa, Latin America and Asia including India. In India maximum cases have been reported from Rajasthan and South India.3 Prevalence of actinomycetoma is more in the southern part of India, southeast Rajasthan, along with Chandigarh, while eumycetoma is found to be more predominant in North India and desert regions of central Rajasthan.3 Sawatkar et al. reported seven cases of actinomycetoma and four eumycetoma cases out of a total of 11 cases in a year (2015-2016) from Nagpur, Maharashtra supporting the evidence that actinomycetoma is more common than eumycetoma in this region.4 Padhi et al. identified Actinomadura madurae and Madurella mycetomatis to be the most common agents of mycetoma in their case series.5 Bakshi et al. also reported Madurella mycetomatis as the most frequent etiological agent of eumycetoma.6 In contrast to the above studies, Dubey et al. (2019) reported Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus nidulans, Fusarium solani, Sarocladium kiliense, Curvularia lunata as the predominant agents of eumycetoma in New Delhi, India.3 People of all age groups can be affected, the most common being young adults between 20 and 40 years.7-11 This is the most active age group involved in various outdoor activities and hence the disease should not be neglected in any case. The male: female ratio was found to vary between 3:1 and 5:1 in different studies.9,11,12 The disease tends to occur in poor communities in remote areas. Lack of education and awareness of the disease, along with its painless nature, adds to the burden, as amputation is the only solution in such cases if left untreated.
Etiopathogenesis
Infection occurs in humans by the entry of organisms from the soil into subcutaneous tissue through repeated trauma, penetrating injury or breach of the skin by thorn prick. The foot is considered to be the most common site, others being hands, shoulder, abdomen, buttocks and scalp. While eumycetoma is slowly progressive and well encapsulated, actinomycetoma is characterised by a more rapid course, inflammation and destruction. The incubation period varies from 3 months to 9 years.13 The classical triad of the disease is subcutaneous swelling, multiple discharging sinuses and the presence of macroscopic granules within discharging sinuses. The various causative organisms and the corresponding appearance of grains have been described in Table 1.12,14-17 Once the organism enters the skin, it resides in micro abscesses formed by polymorphonuclear cells. The disease is characterised by the presence of large filamentous aggregates of causative organisms which are the centre of its inflammatory activity. The disease may take the most devastating form by the involvement of muscle and bone, causing osteosclerotic/osteolytic lesions if no treatment is initiated at an appropriate time.
| Eumycetes | Actinomycetes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism | Colour of grains | Organism | Colour of grains | Organism | Colour of grains |
| Trematosphaeria (Madurella) grisea | Black | Cylindrocarpon cyanescens | White | Streptomyces somaliensis | Yellow/ brown |
| Madurella mycetomatis | Black | Cylindrocarpon destructans | White | Actinomadura madurae | White/yellow/pink |
| Aspergillus nidulans | White | Leptosphaeria senegalensis | Black | Actinomadura pelletieri | Red |
| Exophiala jeanselmei | Black | Leptosphaeria thompkinsii | Black | Actinomyces israelii | White/ yellow |
| Pseudallescheria boydii | White | Polycytella hominis | White | Nocardia asteroides | White |
| Fusarium oxysporum | White | Pseudochaetosphaeronema larense | Black | Nocardia brasiliensis | White |
| Fusarium solani | White | Pyrenochaeta mackinnonii | Black | Nocardia caviae | White/ yellow |
| Fusarium moniliforme | White | Pyrenochaeta romeroi | Black | Nocardia farcinica | White/ yellow |
| Phialophora verrucosa | Black | Neotestudina rosatii | White | Nocardia transvalensis | White |
| Aspergillus flavus | Green | Plenodomus avramii | Black | Nocardia dassonvillei | Cream |
| Curvularia geniculata | Black | Acremonium falciforme | White | ||
| Curvularia lunata | Black | Acremonium kiliense | White | ||
| Corynespora cassiicola | Black | Acremonium recifei | White | ||
Laboratory Diagnosis
Gross examination, microscopy and culture
The specimen is collected by pressing the sinus from suspected lesions to collect grains which are then subjected to gross examination, microscopy and culture. The gross examination includes an assessment of the colour, size, shape and texture of grains. For example, black grains are suggestive of eumycetoma, and red grains are seen in Actinomadura pelletieri. Grains of Nocardia asteroides and Nocardia brasiliensis are smaller in size while large-sized grains are observed in Madurella spp. and Actinomadura madurae. Grains harbouring Streptomyces somaliensis and Madurella mycetomatis can be hard in consistency though grains of other pathogens are mostly soft in consistency.18,19
The various techniques of microscopic examination include Gram stain, modified Ziehl Neelsen (Z-N), or haematoxylin and eosin (H and E) stain for actinomycetoma and potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount, histopathological stains like H and E, Gomori’s methenamine silver (GMS) or periodic acid Schiff (PAS) stains for eumycetoma. In 2009, Alam et al. reported five cases of mycetoma from India presenting with ulcers/purulent discharge admixed with black granules. Haematoxylin and eosin stained sections and Gram stain showed thin filamentous bacteria (actinomycetoma) and thick club-shaped structures (eumycetoma).18
Culture is required to identify the organism properly, as morphological features of grains can be similar in many of the agents causing mycetoma. The various culture media required are Sabouraud Dextrose Agar with and without antibiotics, 5% sheep blood agar, brain heart infusion agar, Lowenstein Jensen media in multiple sets. Each set of culture media is incubated at both 25°C and 37°C and observed for growth which occurs usually after 7-10 days,20 though delayed growth may be observed especially in case of fungal pathogens, hence culture media needs to be incubated for 4-6 weeks before reporting it as negative.19 Padhi et al. detected 13 cases of mycetoma by histopathological examination but in only 8 /13 cases growth was seen on culture (though in 1/5 of remaining cases, culture was not done).5 A flowchart of routine diagnostic workup is demonstrated in Figure 1 which can be done in resource-poor settings with no access to molecular facilities.2
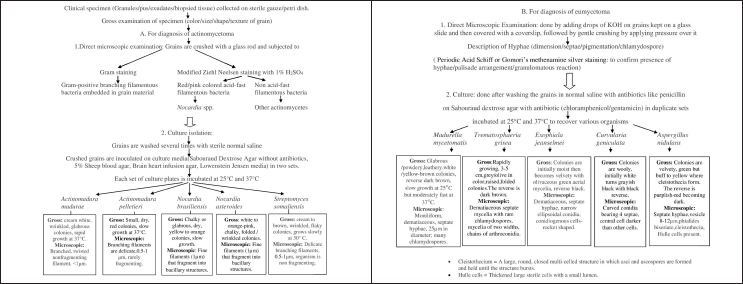
- Diagnostic algorithm for mycetoma2
Cytodiagnosis
Cell block technique can provide us with the combined advantages of routine histopathology and fine needle aspiration (FNA) direct smears. Aspirated material from suspected lesions can be used to prepare a fixed cell block. This technique is described as safe, rapid, and effective by Yousif et al. in a study done on 240 patients.21 The authors reported sensitivities of 85.7% and 87.5% for actinomycetoma and eumycetoma, respectively utilising this technique and there was no difference statistically in the findings obtained by the histopathological sections and cell block. The cell blocks have the added advantage of being stored for the prolonged duration for future studies and hence provide a ray of hope for researchers working on mycetoma.
Mycetoma Research Centre of the University of Khartoum, Sudan conducted a study using FNA from lesions for the identification of grains and tissue reaction. Surgical biopsies and histopathological examinations were performed if FNA was found to be negative in a suspicious case. In the study, 3177 (47%) patients underwent FNA for cytological examination and the findings were compatible with Madurella mycetomatis in 2379 (75%) cases, Actinomadura madurae in 316 (10%) cases, Streptomyces somaliensis in 277 cases (7%), Actinomadura pelletieri was uncommon and was detected in 39 (1%) cases.22
Radiology
Extension of the lesions in bone and other tissues can be determined by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-rays, and tomography.23 In MRI, ‘dot in circle’ is a radiologically relevant sign of mycetoma.24 This sign is described as hypointense foci within the hyperintense spherical lesions that comprise granulomatous tissue surrounding fungal elements/bacterial colonies. Limited availability of MRI and lack of expertise are hindrances in diagnosis, especially in rural areas where the disease is prevalent. In the context of ultrasonographic findings, thick-walled cavities with hyper-reflexive echoes representing grains may be seen in eumycetoma while in actinomycetoma fine, closely aggregated hyperechoic foci are seen at the bottom of rounded lesions.19
Serology
Serological tests are of limited value in the diagnosis of mycetoma as most of the tests utilise cell extracts instead of exoantigens and cross-reaction can occur with other diseases. The various serological methods that have been used are the complement fixation test, immunodiffusion, counter-immunoelectrophoresis, western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.2
Molecular diagnosis
Though molecular techniques are heading towards advancement in routine diagnosis of mycetoma, these are costly methods and still lack standardisation in many laboratories. These methods can also be used for epidemiological studies and generating accurate therapeutic options thus minimising the use of combination drugs. In 2017, Bitan et al. reported four new cases from Israel and also documented 17 other case reports between 1942 and 2015 from the same place. They included pan-fungal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) according to the protocol described in http://sites.biology.duke.edu/fungi/mycolab/primers.htm and pan bacterial PCR (16S rRNA gene PCR and sequencing) in diagnosis apart from conventional methods.25 Out of four, two culture-negative cases were successfully detected by PCR.
Rolling circle amplification (RCA) that uses species-specific padlock probes, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) proved to be highly useful techniques for the diagnosis of mycetoma in studies done by Ahmed et al. 26,27 The basic methodology of RCA involves the detection of specific sequences of nucleic acid and enzymatic amplification of circularised oligonucleotide probes under isothermal conditions.28 It is a highly specific, simple, rapid, single-day protocol and is of low cost. Sixty-two isolates were identified by Ahmed et al. utilising the RCA technique and the results were 100% specific with zero cross reactivity.27 The major limitations of RCA are the culture of the pathogen and the requirement of PCR amplification.26,27
LAMP technique relies on the utilisation of four primers that identify six regions in the target DNA, followed by amplification via auto-cycling and strand displacement with a specialised DNA polymerase.29-31 RPA is another rapid detection isothermal technique which can be utilised in places where mycetoma is endemic. The risk of contamination was reported to be lower than LAMP by Ahmed et al. Both RPA and LAMP techniques (sensitivity and specificity=100%) were found to be equal in performance to PCR in detecting Madurella mycetomatis directly from clinical samples.26
MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight mass spectrometry)
MALDI-TOF MS is a high throughput proteomic technique that requires co-crystallisation of an analyte with a matrix that absorbs laser striking it and converts the analyte molecules into the gas phase. The ions thus formed, travel, and reach the detector at a speed inversely proportional to their mass/charge (m/z) ratio. A signal is created indicating m/z ratio (x -axis) and ion intensity (y -axis), according to the time taken to hit the detector by each of the ion particles.32 By incorporating this method, rapid and accurate identification of etiological agents of eumycetoma is possible thus eliminating the need to wait for culture reports. Fraser et al. tested 57 organisms corresponding to 10 different species from confirmed cases of subcutaneous pedal masses and eumycetoma, identified previously by PCR amplification and sequencing of Internal Transcribed Spacer 1 (ITS 1). They demonstrated accurate identification of all of the test organisms with the help of this technique, obtaining log scores more than 1.8, 1.9 and 2.0, in 100%, 90.4% and 67.3% of isolates respectively.33 Recently, dermatophytic mycetoma of scalp was reported by Diongue et al. which is a rare condition. The causative organism was identified as Microsporum audouinii (atypical strain) by MALDI-TOF MS with a Biotyper score of 2.022. They further confirmed the organism by nucleotide sequence analysis of the ITS region of the rRNA gene.34
MALDI-TOF MS is less labour-intensive, more cost-effective, and gives faster results in approximately 1 day, as compared to partial (500-bp) 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Buckwalter et al. were able to detect Nocardia species (90%) and other aerobic actinomycetes (51%) by MALDI-TOF with the help of a custom enhanced library, and some additional processing steps.35
While utilising MALDI-TOF technique in the identification of genus Nocardia, spectra adequate for identification cannot be obtained using only processes for general bacteria because their cell wall contains aliphatic acid such as mycolic acid, hence Segawa et al. proposed another method, Nocardia extraction method in Department of Clinical Laboratory at Chiba University Hospital (NECLC). In this method, the ethanol-formic acid extraction technique is utilised, silica beads are added as a part of the high-temperature extraction method, and extraction of formic acid is done within 10 minutes.36
The various advantages and disadvantages of different techniques used in the diagnosis of mycetoma are summarised in Table 2.2,7,13,18,21,26,27,35-38 Recently, an interesting survey was done by Hay et al. based on responses given by 23 clinicians and mycologists on the diagnostic techniques of fungal neglected tropical diseases. Percentage positive response of participants regarding the optimal diagnostic method in well-equipped settings versus diagnostic methods of use in peripheral clinics and laboratories for mycetoma (in terms of percentage) is depicted in Table 3.39 In the Indian context, newer technologies are not available everywhere and much needs to be done in this field. Making clinicians aware and promoting research and development in mycetoma diagnostics is important in the current situation.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Microscopy | Simple, inexpensive, rapid, differentiate between actinomycetoma and eumycetoma. | Low sensitivity and specificity |
| Histology | Suppurative granuloma. Neutrophilic infiltrate, palisading histiocytes, eosinophil, lymphocytes, macrophages, fibrosis, multinucleated giant cell (occasional). Eumycetoma = hyphae, thick club-shaped structures, embedded in cement like matrix Actinomycetoma = multilobated colonies, pale central eosinophilia, basophilic outer border with ill-defined branching filaments |
Need expertise |
| Cell block technique | Cost-effective, rapid, general/spinal anaesthesia not required, cell blocks can be preserved for a long period | Pain in patients with a low pain threshold |
| Culture | Identification of causative organisms. | Results may be delayed (Time-consuming) |
| Serology | Detection of circulating antibodies may help in guiding management. | Chances of cross-reactivity, of limited value |
| Radiodiagnosis | Differentiate between actinomycetoma and eumycetoma Characteristic features like ‘dot in circle’ sign can be seen. The extent of the disease can be assessed. |
Limited availability of MRI in peripheral areas. Need expertise. |
| Molecular | Can identify the specific organism up to species level. |
Lack of standardisation in many places |
| PCR and sequencing | High sensitivity and specificity. Clinical samples can be directly used. |
Costly compared to other newer molecular techniques. DNA extraction required. |
| RCA | Highly specific, rapid single-day protocol. | Culture and DNA extraction required, sensitivity is low. |
| RPA and LAMP | Culture not required. Thermal cycler not required. It can be used for point of care testing, turnaround time = 3 hrs. High sensitivity and specificity. |
DNA extraction required. |
| Mass spectrometry(MALDI-TOF MS) | Accurate, less labour-intensive, faster results possible, economical (though the initial cost of a mass spectrometer is high, the cost of identifying one species is low compared to molecular methods). | May require some additional processing steps for agents of mycetoma compared to routine identification, the enhanced database needed. |
Abbreviations: MRI = Magnetic resonance imaging, PCR = Polymerase chain reaction, RCA = Rolling circle amplification, RPA = Recombinase polymerase amplification, LAMP = Loop-mediated isothermal amplification, MALDI-TOF MS = Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
| Diagnostic method | Positive response (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Well-equipped settings | Resource limited settings | |
| Clinical features | 92% | 96% |
| Direct microscopy | 88% | 88% |
| Histopathology | 88% | 43% |
| Culture | 96% | 33% |
| Serology | 8% | __ |
| Molecular diagnosis | 71% | 13% |
| Other | Imaging, dermoscopy | Imaging |
Conclusion
Despite diagnostic techniques having evolved from microscopy to molecular, there are still complexities concerning the diagnosis and treatment of the devastating disease mycetoma. Though eumycetoma and actinomycetoma have subtle differences in clinical presentations, their treatment protocols are completely different. Early and accurate diagnosis is extremely beneficial in optimising treatment, hence teamwork between clinicians, microbiologists and pathologists is the need of the hour.
Key points of the review include limitations of the newer techniques
Microscopy is relevant and irreplaceable for a basic workup to differentiate Actinomycetoma from Eumycetoma.
Teamwork between clinicians, microbiologists and pathologists have to be strengthened as it plays a vital role in the diagnosis of mycetoma.
Molecular methods can make the diagnosis easy, timely and definite. Hence it will help the clinicians to avoid prescribing combination drugs, thus helping to fight emerging resistance.
Newer diagnostic methods like MALDI-TOF, can accurately diagnose various pathogens causing mycetoma but are still sidelined and not being incorporated at places with good access to laboratory facilities.
The newer techniques are mainly limited by the cost, especially in resource-poor regions where mycetoma is more common.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
List of Abbreviations
PCR: Polymerase chain reaction
MALDI-TOF MS: Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
RCA: Rolling circle amplification
LAMP: Loop-mediated isothermal amplification
RPA: Recombinase polymerase amplification
Z-N: Ziehl-Neelsen
H and E: Haematoxylin and eosin
KOH: Potassium hydroxide
GMS: Gomori’s methenamine silver
PAS: Periodic acid-Schiff
FNA: Fine needle aspiration
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging
m/z: Mass-to-charge ratio
ITS 1: Internal Transcribed Spacer 1
NECLC: Nocardia extraction method in Department of Clinical Laboratory at Chiba University Hospital
References
- Mycetoma In: Textbook of Medical Mycology (4th ed.). New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers; 2017. p. :203-19. In
- [Google Scholar]
- Epidemiological profile and spectrum of neglected tropical disease eumycetoma from Delhi, North India. Epidemiol Infect. 2019;147:e294.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma: A common yet unrecognized health burden in central India. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:256-61.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma in south India: Retrospective analysis of 13 cases and description of two cases caused by unusual pathogens: Neoscytalidium dimidiatum and Aspergillus flavus. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:1289-96.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incidence and changing pattern of mycetoma in western Rajasthan. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2008;51:154-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma: A clinical dilemma in resource limited settings. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018;17:35.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma: A unique neglected tropical disease. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:100-12.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma: Experience of 482 cases in a single center in Mexico. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3102.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Management of mycetomas in France. Med Mal Infect. 2013;43:286-94.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetomas: An epidemiological, etiological, clinical, laboratory and therapeutic review. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:8-18.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma caused by Madurella mycetomatis: A neglected infectious burden. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004;4:566-74.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Deep fungal infections In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, eds. Fitzpatrick’s dermatology in general medicine (5th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill; 1999. p. :2372-7. In ed. Vol. 2. New nation of medical treatments
- [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology. Vol Vol. 1. New York: Mosby; 2003. p. :1187-8. In ed.
- [Google Scholar]
- Histological diagnosis of madura foot (mycetoma): A must for definitive treatment. J Glob Infect Dis. 2009;1:64-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma: Reviewing a neglected disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:123-29.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A new technique for the diagnosis of mycetoma using fixed blocks of aspirated material. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2010;104:6-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma in the Sudan: An update from the Mycetoma Research Centre, University of Khartoum, Sudan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003679.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eumycetoma due to Madurella mycetomatis from two cases of black grain mycetoma in Morocco. Journal de mycologie médicale. 2011;21:281-4.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- “Dot in Circle” sign in actinomycotic mycetoma on MRI and ultrasound− A case series. MAMC Journal of Medical Sciences. 2019;5:145.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mycetoma (Madura Foot) in Israel: Recent cases and a systematic review of the literature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;96:1355-61.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Application of isothermal amplification techniques for identification of Madurella mycetomatis, the prevalent agent of human mycetoma. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53:3280-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapid identification of black grain eumycetoma causative agents using rolling circle amplification. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3368.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- DNA replication: The rolling circle model. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:473-84.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J Appl Microbiol. 2018;124:626-43.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:E63.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Applications of loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2011;163:845-50.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mass spectrometry-based proteomic profiling of lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6:159-70.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapid and robust identification of the agents of black-grain mycetoma by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 2017;55:2521-28.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermatophytic mycetoma of the scalp due to an atypical strain of Microsporum audouinii identified by MALDI-TOF MS and ITS sequencing. J Mycol Med. 2019;29:185-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of Mycobacterium species, Nocardia species, and other aerobic Actinomycetes. J Clin Microbiol. 2016;54:376-84.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Identification of Nocardia species using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Proteomics. ;12:6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An approach to histology-based diagnosis and treatment of Madura foot. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2012;6:684-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight (maldi-tof) mass spectrometry for detection of antibiotic resistance mechanisms: From research to routine diagnosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:103-14.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The diagnosis of fungal neglected tropical diseases (fungal NTDs) and the role of investigation and laboratory tests: An expert consensus report. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2019;4:122.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






