Translate this page into:
Bullous pemphigoid successfully treated with omalizumab
2 Department of Pathology, Gazi University Medical Faculty, Ankara, Turkey
Correspondence Address:
M�zeyyen G�n�l
Yıldızevler Mah, 747. Sok, Aykon Park Sitesi, A Block No: 3/3, Çankaya, Ankara 06550
Turkey
| How to cite this article: G�n�l M, Keseroglu HO, Ergin C, �zcan I, Erdem �. Bullous pemphigoid successfully treated with omalizumab. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2016;82:577-579 |
Sir,
Bullous pemphigoid is an acquired, autoimmune, bullous disease.[1],[2],[3],[4] The pathogenic autoantibodies are usually of the IgG subtype, but some patients with bullous pemphigoid have IgE autoantibodies against type XVII collagen, which have been shown to be pathogenic.[1],[3] Ten cases of bullous pemphigoid treated with omalizumab, an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody, have been reported in the last few years.[1],[2],[3],[4],[5] Herein, we present a patient with bullous pemphigoid, who had a very high IgE level and who was treated successfully with omalizumab.
A 70-year-old man, weighing 70 kg, presented with multiple, tense bullae and eroded areas on the trunk and extremities, particularly on the knees, hands and feet [Figure - 1] and several oral erosions. The Nikolsky sign was negative. The skin lesions were itchy and had gradually progressed over the previous 3 months. In addition, he had psychosis and was positive for anti-hepatitis C virus antibody. Investigations revealed a markedly raised IgE level (2500 IU/mL, N: 0–87 IU/mL) and eosinophilia (2.9%, N: 0.03–0.4%). Hepatitis C viral RNA load was 400,000 IU/mL. Histopathological examination showed sub-epidermal separation and accumulation of eosinophils and neutrophils in the bulla cavity [Figure - 2]a. On direct immunofluorescence with fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled anti-C3 and anti-IgG antibodies, there was linear staining of the dermoepidermal zone [Figure - 2]b. Bullous pemphigoid was diagnosed based on the clinical, histopathological and direct immunofluorescence findings. His lesions did not respond to 6 weeks of treatment with topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% and oral tetracycline (4 × 500 mg/day). Hence, these were stopped and oral corticosteroid therapy (1 mg prednisolone/kg/day) was started. Three weeks later, dapsone 100 mg/day was added as new lesions continued to appear. However, dapsone therapy had to be discontinued because of an increase in transaminase levels. His psychosis also deteriorated, most likely because of the systemic steroids. Though disease activity persisted, we were hesitant to step up his immunosuppressive medication because that would require prior treatment of his hepatitis C infection with interferon which was very likely to exacerbate his psychosis. Hence, additional immunosuppressive agents were not considered. Based on the available reports, omalizumab therapy was started at a dose of 300 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks as an alternative treatment. New lesions stopped appearing within 1 week of treatment initiation and eroded areas gradually re-epithelized [Figure - 3]. Several days after the omalizumab injections, thrombocytopenia was detected (80,000/uL, N: 150,000–372,000/uL), but this did not require cessation of the drug and the platelet count gradually improved. When omalizumab became unavailable for 2 months, after the seventh dose, his bullous pemphigoid lesions exacerbated, but the lesions disappeared with re-administration of omalizumab. The platelet count fell minimally after each omalizumab injection. Although the platelet count gradually increased between successive injections, it never reached the normal range. The hepatitis C viral RNA load was stable. Till date, 11 injections of omalizumab 300 mg/injection have been given to the patient. The immunoglobulin E level was found to be decreased to 851 IU/mL just before the 12th dose. His bullous pemphigoid is in remission with oral prednisolone in a dose of 5 mg/day. Stoppage of oral steroids followed by a reduction of omalizumab dosing to 150 mg every 4 weeks is planned, if the patient stays in remission.
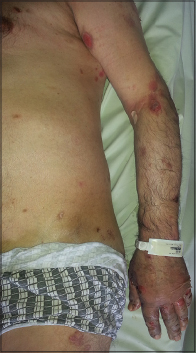 |
| Figure 1: Multiple eroded areas on trunk and hands |
 |
| Figure 2: (a) Subepidermal separation and accumulation of eosinophils and neutrophils in the bulla cavity (H and E, ×100), (b) linear positive staining of the dermoepidermal zone with C3 (direct immunofluorescence, ×100) |
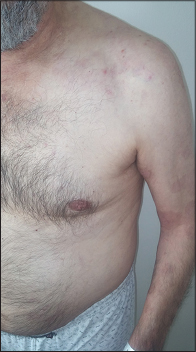 |
| Figure 3: Improved lesions on the trunk |
The antigens targeted by the pathogenic antibodies responsible for bullous pemphigoid are the 230-kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen (BP-230) within basal keratinocytes and the 180-kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen, type XVII collagen (BP-180), within the basement membrane zone.[1],[2] However, in mouse models, it has been shown that IgG antibodies alone do not account for all the features of bullous pemphigoid, as dermal eosinophil infiltration and purely spontaneous blistering could not be induced by IgG antibodies.[1] Moreover, the pathogenicity of IgE autoantibodies in humans has been shown and the first case of bullous pemphigoid treated with omalizumab was reported by Fairley et al. in 2009.[3]
The mechanism of action of omalizumab, a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody against human IgE, is not completely understood in the treatment of bullous pemphigoid. However, it is thought that omalizumab prevents binding of IgE to its receptor and hence inhibits the activation of mast cells that are increased in lesions of bullous pemphigoid. In addition, omalizumab downregulates IgE receptors and circulating eosinophils. Another hypothesis is that omalizumab is able to induce eosinophil apoptosis and the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines.[2]
The standard therapy for severe bullous pemphigoid is systemic steroids plus a potentially steroid-sparing agent such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil and methotrexate. Compared with these agents, omalizumab has a relatively selective effect.[1] Therefore, it may be a favorable alternative therapy for bullous pemphigoid patients, especially those in whom immunosuppressive therapy is contraindicated, as in our patient. The hepatitis C viral RNA load of our patient has stayed stable during 9 months of omalizumab therapy. Improvement of the lesions on omalizumab therapy, exacerbation of the lesions when omalizumab became unavailable for 2 months and the disappearance of the lesions with re-administration are all supporting evidence for the efficacy of omalizumab therapy in bullous pemphigoid. Moreover, our observation shows that 300 mg omalizumab monthly may be an effective therapy for bullous pemphigoid even if the IgE level is very high. This is in contrast to previous reports, in which the omalizumab doses were adjusted according to body weight and baseline IgE levels of the patients.[1],[2],[3] Its onset of action is rapid and our patient improved within 1 week.
Adverse effects of omalizumab treatment include headache, pyrexia, infections, abdominal pain and also thrombocytopenia. Data about omalizumab-induced thrombocytopenia are limited and conflicting.[5] Although our patient had a normal platelet count (168,000/uL) before omalizumab therapy, thrombocytopenia occurred 5 days after injection of the drug. Platelet counts ranged between 110,000 and 130,000/uL during treatment but these values did not require the cessation of omalizumab.
In summary, omalizumab may be an effective and relatively safe therapeutic option for a subset of patients with bullous pemphigoid who do not respond to or have contraindications to standard treatment. Its onset of action is rapid and 300 mg/month may be sufficient to suppress blistering in most patients. Thrombocytopenia is a known side effect and complete blood counts need to be checked regularly during treatment.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
| 1. |
London VA, Kim GH, Fairley JA, Woodley DT. Successful treatment of bullous pemphigoid with omalizumab. Arch Dermatol 2012;148:1241-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Yu KK, Crew AB, Messingham KA, Fairley JA, Woodley DT. Omalizumab therapy for bullous pemphigoid. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014;71:468-74.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Fairley JA, Baum CL, Brandt DS, Messingham KA. Pathogenicity of IgE in autoimmunity: Successful treatment of bullous pemphigoid with omalizumab. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009;123:704-5.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Yalcin AD, Genc GE, Celik B, Gumuslu S. Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody (omalizumab) is effective in treating bullous pemphigoid and its effects on soluble CD200. Clin Lab 2014;60:523-4.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Corren J, Casale TB, Lanier B, Buhl R, Holgate S, Jimenez P. Safety and tolerability of omalizumab. Clin Exp Allergy 2009;39:788-97.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
6,799
PDF downloads
1,669





