Translate this page into:
Chronic subcutaneous nodules, plaques and ulcers of the hand
2 Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Celal Bayar University, Manisa, Turkey
3 Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Celal Bayar University, Manisa, Turkey
4 Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Ege University, İzmir, Turkey
Correspondence Address:
Aylin Türel Ermertcan
Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine, Celal Bayar University, 45010 Manisa
Turkey
| How to cite this article: Ermertcan AT, Özkütük N, Temiz P, Çavuşoğlu C, Sürücüoğlu S. Chronic subcutaneous nodules, plaques and ulcers of the hand. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2017;83:133-135 |
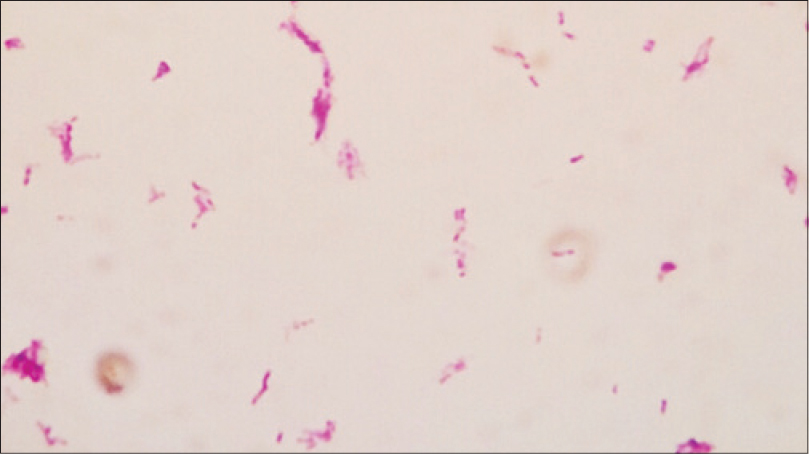
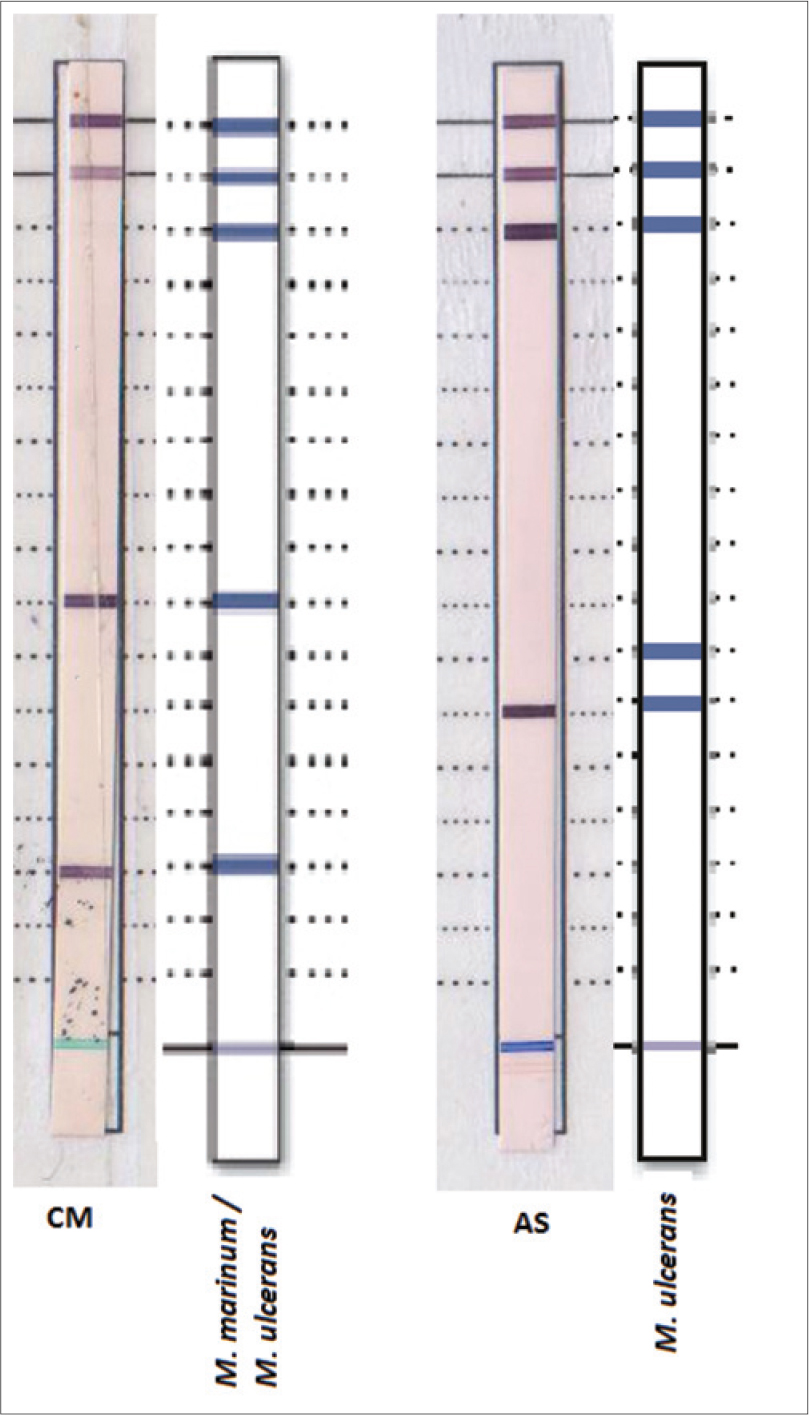
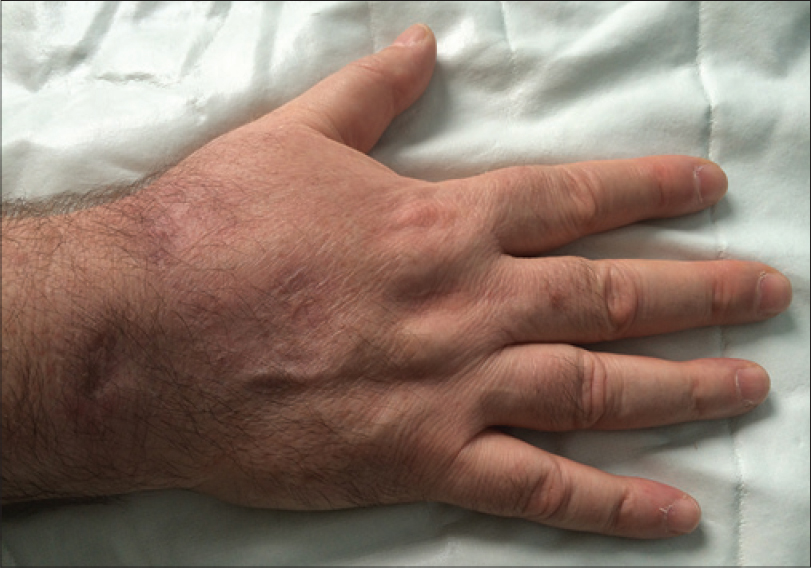
A 54-year-old man presented with multiple draining sinuses on the right hand for 2 years. Dermatological examination revealed erythematous nodules and pustules leading to draining abscesses localized on the dorsal aspect of the right hand [Figure - 1]. The infection had not responded to several courses of antibiotics. There was no history of trauma or foreign body. A punch biopsy was performed for histopathological, bacteriological, mycobacterial, parasitological and mycological examinations. Routine bacterial, fungal and parasitological cultures were negative. Histopathological examination revealed granulomas along with an infiltrate of lymphocytes. Areas of caseous necrosis surrounded by histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells were observed [Figure - 2].
 |
| Figure 1: Erythematous nodules and pustules leading to draining abscesses localized on the dorsal aspect of the right hand |
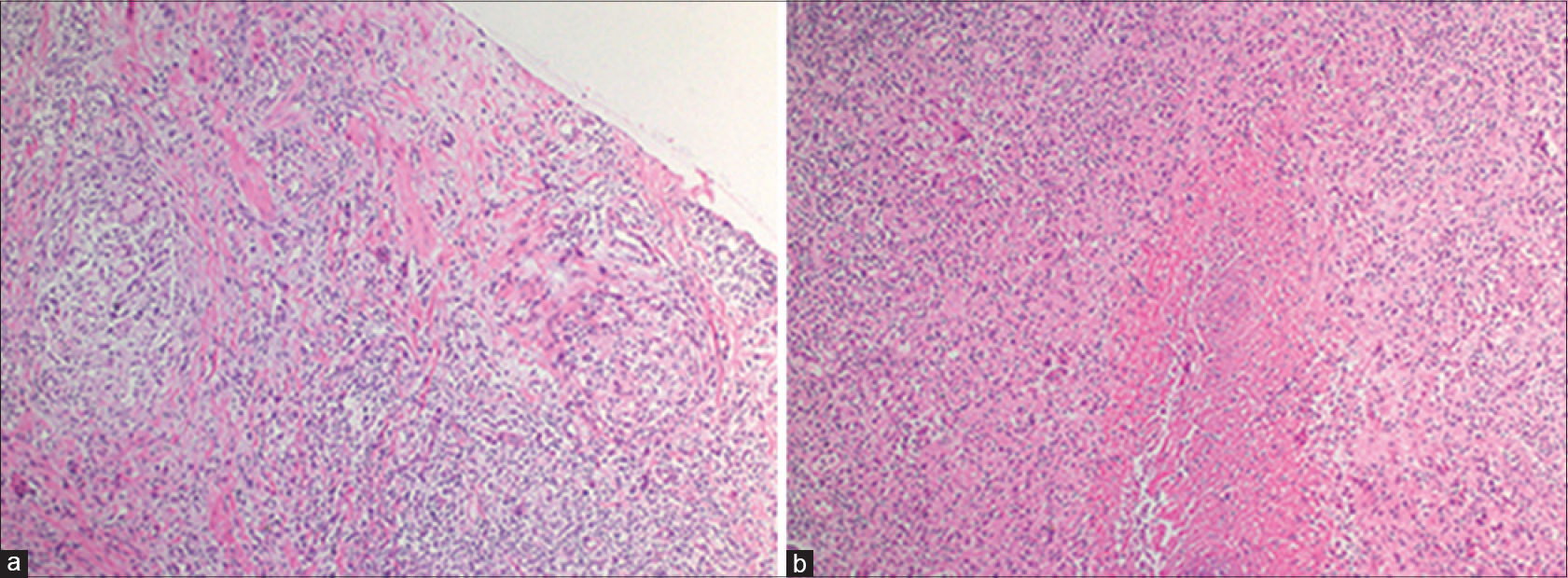 |
| Figure 2: (a) Granulomas with lymphocytic infiltrates in the soft tissue (H and E, ×100). (b) Caseous necrosis areas surrounded by histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells (H and E, ×100) |
What Is Your Diagnosis?
| 1. |
Dolenc-Voljc M, Zolnir-Dovc M. Delayed diagnosis of Mycobacterium marinum infection: A case report and review of the literature. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2010;19:35-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Lee WJ, Kang SM, Sung H, Won CH, Chang SE, Lee MW, et al. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections of the skin: A retrospective study of 29 cases. J Dermatol 2010;37:965-72.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Balagué N, Uçkay I, Vostrel P, Hinrikson H, Van Aaken I, Beaulieu JY. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections of the hand. Chir Main 2015;34:18-23.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Veraldi S, Cuka E, Nazzaro G. Treatment of sporotrichoid fish tank granuloma with pulsed clarithromycin. Dermatology 2014;229:83-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Sette CS, Wachholz PA, Masuda PY, da Costa Figueira RB, de Oliveira Mattar FR, Ura DG. Mycobacterium marinum infection: A case report. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis 2015;21:7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 6. |
Kump PK, Högenauer C, Wenzl HH, Petritsch W. A case of opportunistic skin infection with Mycobacterium marinum during adalimumab treatment in a patient with Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:e15-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 7. |
Guyot A, Begon E, Abramowitz L, Landry J, Marinho E, Descamps V, et al. Acase of acute and necrotizing cutaneous Mycobacterium marinum infection in a patient treated with infliximab for Crohn's disease. Ann Dermatol Venereol 2009;136:806-10.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
3,379
PDF downloads
3,670