Translate this page into:
Follicular mycosis fungoides: Clinicohistopathologic features and outcomes in a series of 12 Chinese cases
Corresponding author: Dr. Lin Wang, Department of Dermatology, West China School of Medicine/West China Hospital of Sichuan University (WCSM/WCH), Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. lkzwl@126.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Feng X, Xie Y, Li F, Wang L. Follicular mycosis fungoides: Clinicohistopathologic features and outcomes in a series of 12 Chinese cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:68-77. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_1003_2021
Abstract
Background
Follicular mycosis fungoides is a distinct variant of mycosis fungoides with a broad clinical spectrum. Recently, many studies have indicated that follicular mycosis fungoides should be divided into different subtypes with disparate prognoses.
Objective
To define the clinicohistopathologic features and outcomes of follicular mycosis fungoides and to identify risk factors that may be related to the prognosis of Chinese patients with follicular mycosis fungoides.
Materials and methods
We conducted a single-centre retrospective study and reviewed the clinical, histopathologic and immunophenotypic data of 12 patients diagnosed with follicular mycosis fungoides between 2009 and 2020 in the Department of Dermatology of West China Hospital of Sichuan university.
Results
A total of 12 patients (seven males and five females) with a mean age of 30 ± 14 years (age range 16–55 years) were included. Scalp and face were the most common involved sites (100%). Follicular papules, acneiform lesions, plaques, and nodules, were the main clinical presentations. Histopathological findings were consistent with the classic manifestations of follicular mycosis fungoides, including folliculotropism, perifollicular and intrafollicular lymphocytic infiltrates and mucinous degeneration. Interferon α-1b was the most common treatment. Four patients died of follicular mycosis fungoides in three years. Notably, immunohistochemical analysis revealed a decreased number of CD20+ cells in the deceased patients.
Limitations
This is a retrospective evaluation with a small number of cases; further prospective studies are warranted to support our inferences.
Conclusion
Our patients were much younger than in previous studies. The observed difference in this cohort may be explained by race, in addition to the limited number of cases. A decreased number of B cells might be associated with a poor prognosis, and more studies are necessary to discover the role of B cells in follicular mycosis fungoides as well as in mycosis fungoides.
Keywords
Clinicopathology
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
folliculotropic mycosis fungoides
mycosis fungoides
prognosis
Plain Language Summary
Follicular mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) with diverse clinical features and prognosis. This study aimed to define the clinicohistopathologic features and outcomes of FMF and identify prognostic risk factors for Chinese patients. The study analysed 12 patients with FMF, with the head and face being the most commonly involved sites. The most common treatment was Interferon α-1b, and four patients died of FMF in three years. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that decreased numbers of CD20+ cells were associated with poor prognosis. However, due to the small number of cases and retrospective nature of the study, further prospective studies are needed to confirm the findings. Nonetheless, the study sheds light on the clinical heterogeneity and prognosis of FMF, indicating the need for personalized management and prognostic evaluation.
Introduction
Follicular mycosis fungoides has been recognised as a variant of mycosis fungoides by the World Health Organization-European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer since 2005 based on its special clinical and histopathological features.1 Follicular mycosis fungoides is characterised by various types of skin lesions. Besides the characteristic manifestations of classic mycosis fungoides like patches, plaques and tumours, follicular mycosis fungoides patients frequently present with follicular lesions, acneiform eruptions, along with alopecia.2,3 The head, face and neck are generally affected sites in follicular mycosis fungoides, while the trunk and extremities are the commonly involved sites in classic mycosis fungoides.3,4 The histologic hallmark of follicular mycosis fungoides is the presence of neoplastic lymphocytes infiltrating the follicular epithelium and sparing the epidermis (folliculotropism), while the neoplastic lymphocytes in classic mycosis fungoides always infiltrate into the epidermis (epidermotropism).5,6 Follicular mycosis fungoides had once been recognised as a distinct variant of mycosis fungoides with an unfavourable prognosis.4,7 However, recent studies have reported that not all patients with follicular mycosis fungoides present with aggressive clinical behaviour, a subtype of patients have an indolent clinical course with 5-year survival similar to that of patch-stage classic mycosis fungoides.8–10 Also, the tumour-node-metastasis-blood staging system for classic mycosis fungoides cannot estimate the prognosis of follicular mycosis fungoides accurately. Therefore, a follicular mycosis fungoides-specific staging system should be proposed.11,12 The aim of this study was to assess the clinical features, histopathologic characteristics and prognostic aspects of Chinese follicular mycosis fungoides patients. The study also aimed to explore the potential risk factors influencing the prognosis of follicular mycosis fungoides patients. We hope our work may be helpful in devising a better staging system for follicular mycosis fungoides in future.
Materials and methods
Patient recruitment
All patients with follicular mycosis fungoides diagnosed at the Department of Dermatology of West China Hospital of Sichuan University, during the period April 2009–October 2020, were included. The diagnosis of follicular mycosis fungoides was based on clinical and pathological findings according to the criteria of the World Health Organization-European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer classification.1 The criteria emphasise the presence of folliculotropic infiltrates as well as the preferential localisation of skin lesions in the head and neck region. A total of 12 cases with complete clinical records and 14 available histopathologic materials (there were two biopsy specimens each from patients nine and eleven) were included. The haematoxylin and eosin-stained sections were reviewed by at least two pathologists. A diagnosis of follicular mycosis fungoides was made when principally perifollicular or intrafollicular infiltrates of atypical T cells with twisted nuclei were seen. All these patients were followed up until August 2021. At the end of the follow-up, four patients died within three years, and eight survived without progression. A distinction was made between dead patients (D-follicular mycosis fungoides) and alive cases (A-follicular mycosis fungoides). Clinical parameters evaluated included age at diagnosis, sex, lesion distribution and morphology (patch, plaque, tumour, follicular lesions, etc.). Histopathologic parameters included the extent and density of the infiltrate (sparse, moderate, or marked), size of tumour cells (small, medium or large), presence of follicular mucinosis (no or minimal vs prominent) and presence of eosinophils (no or few vs prominent). In this retrospective study, 3-year overall survival and progression-free survival were used as prognostic indicators.
Alcian blue stains were used to demonstrate mucin accumulation. Immunohistochemical staining was performed in every specimen with antibodies against CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD4, CD8, CD20, CD30, CD56, CD68 (PGM-1), PCK, TIA-1, granzyme B and Ki-67.
Result
Clinical findings
Among the twelve patients in the study [Table 1], seven were men, and five were women. The age at the time of diagnosis ranged from 16 to 55 years, and the mean age was 30 ±14 years. The median disease duration before diagnosis was 72 months (6–240 m). All patients had lesions on the head/neck or face region. Patients presented with patches and/or plaques along with various follicular lesions such as follicular papules, Keratosis pilaris-like and acneiform lesions (pustules and comedones). In addition, nodules and tumours could be found in five cases [Figure 1]. All patients in D-follicular mycosis fungoides presented with infiltrated plaques, nodules or tumours. Hair loss was observed in eight subjects, two of them with infiltrated plaques in the eyebrows. Six patients suffered from severe pruritus.
| Gender/age at diagnosis | Clinical presentation | Localisation | Outcome (until last follow-up) | Follow-up (months) | Stage at diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. F/32 | Acne, cyst, nodule | Face | PR | 12 | A-S |
| 2. F/28 | Plaque, acneiform | Face, extremities, trunk | PR | 30 | E-S |
| 3. M/55 | Plaque, follicular papule | Head | CR | 34 | E-S |
| 4. M/25 | Plaque, follicular papule, tumour | Face, head, extremities, trunk | Died of follicular mycosis fungoides | 42 | EX |
| 5. M/42 | Plaque, follicular papule tumour | Face, head, extremities, trunk | Died of follicular mycosis fungoides | 23 | EX |
| 6. M/16 | Plaque, follicular papule | Head | PR | 60 | E-S |
| 7. M/50 | Plaque, follicular papule, tumour | Head, face | PR | 60 | A-S |
| 8. F/21 | Follicular papule, acneiform | Head, neck, lower extremities | PR | 96 | E-S |
| 9. M/49 | Plaque, follicular papule, keratosis pilaris, keratosis pilaris-like | Face, neck, trunk, upper extremities | CR | 108 | E-S |
| 10. F/24 | Plaque, follicular papule, nodule, tumour | Face, head, extremities, trunk | Died of follicular mycosis fungoides | 12 | A-S |
| 11. F/32 | Plaque, follicular papule, nodule | Head, face | Died of follicular mycosis fungoides | 36 | A-S |
| 12. M/28 | Acneiform, follicular papule | Face, head, extremities, trunk | PR | 6 | E-S |
CR: complete response, clearance of almost all skin symptoms >90%, PR: partial response, 50% clearance of skin symptoms, A-S: advanced cutaneous stage, E-S: early cutaneous stage, EX: follicular mycosis fungoides with extracutaneous disease, no patient was lost
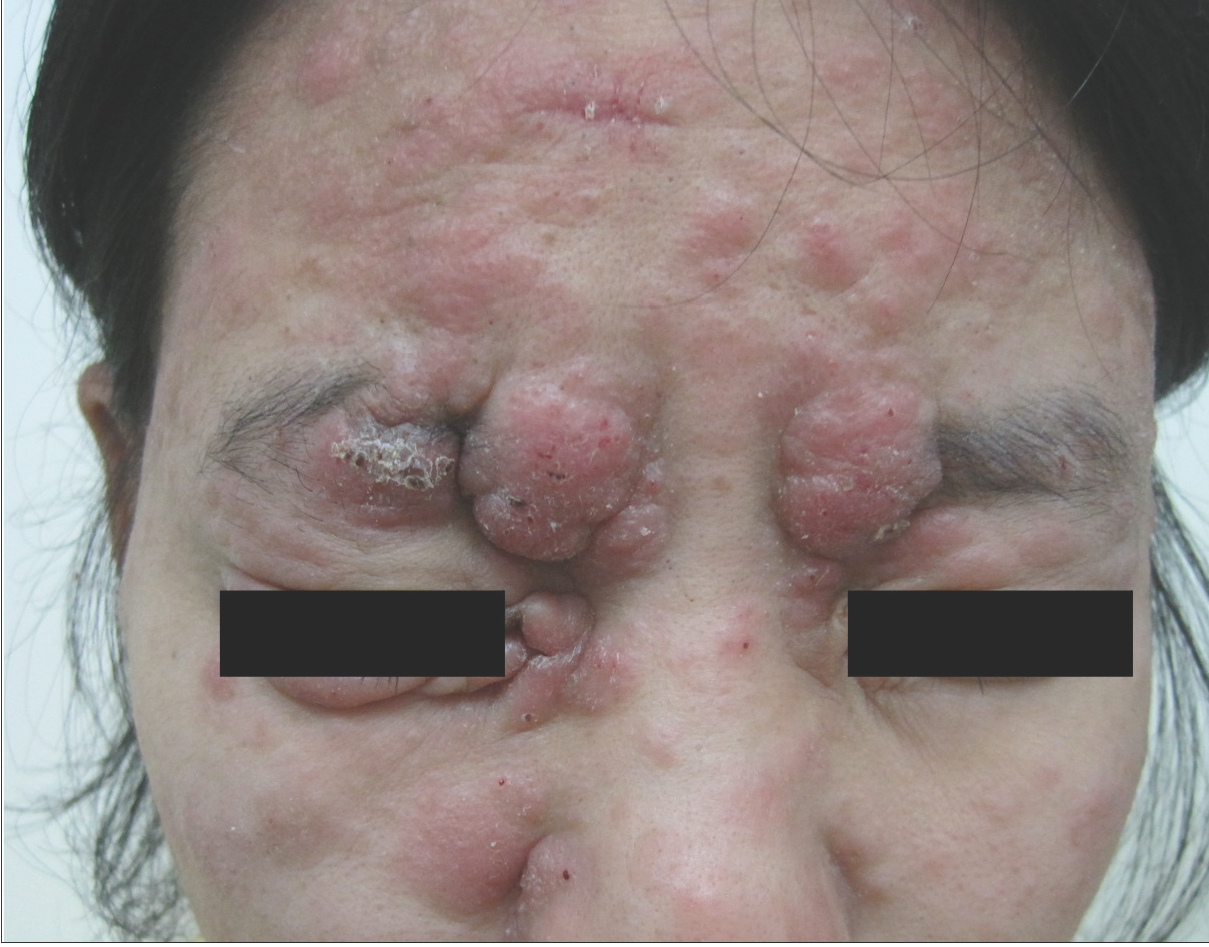
- Multiple nodules and infiltrated plaques on the face.
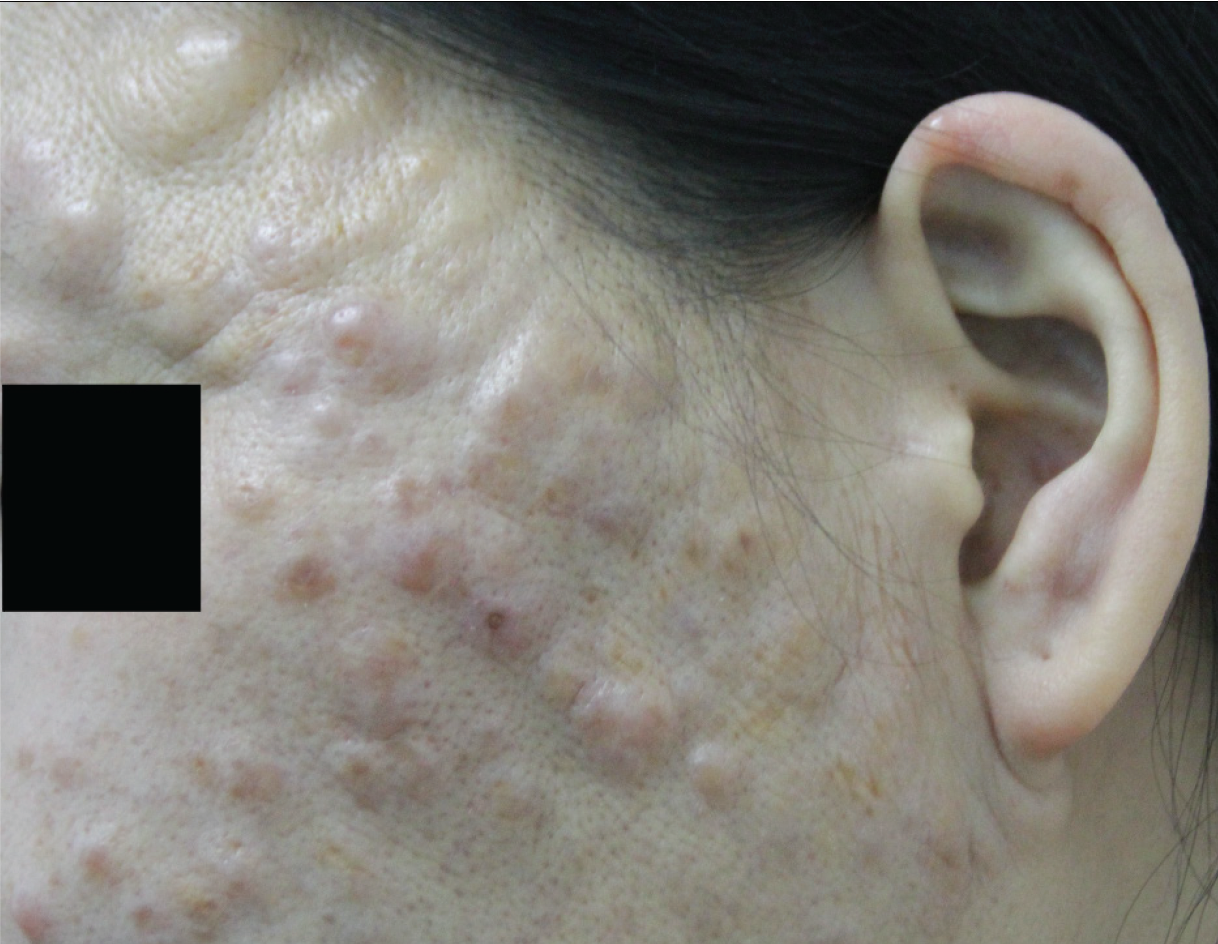
- Pustules and nodulocystic lesions limited to the face.
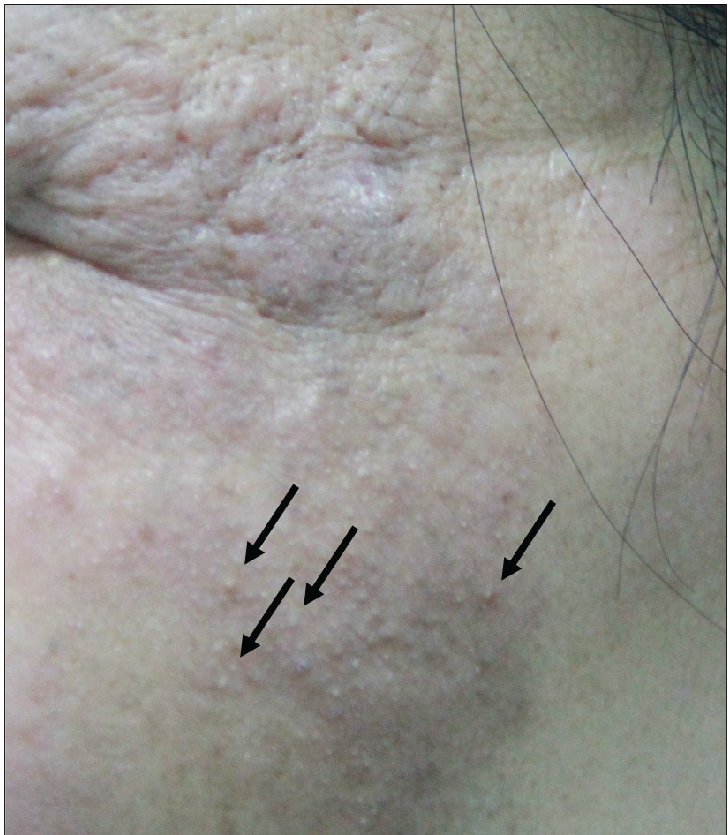
- Erythematous plaques with follicular hyperkeratosis (“comedones”) on the left face (arrows).
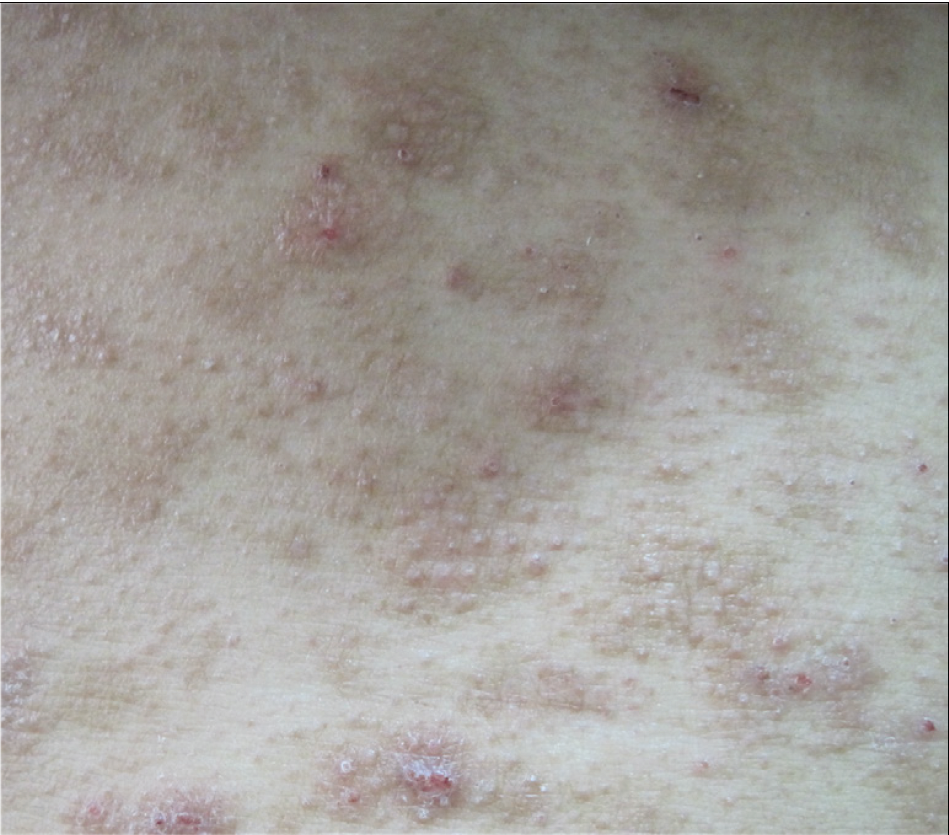
- Follicular papules on chest.
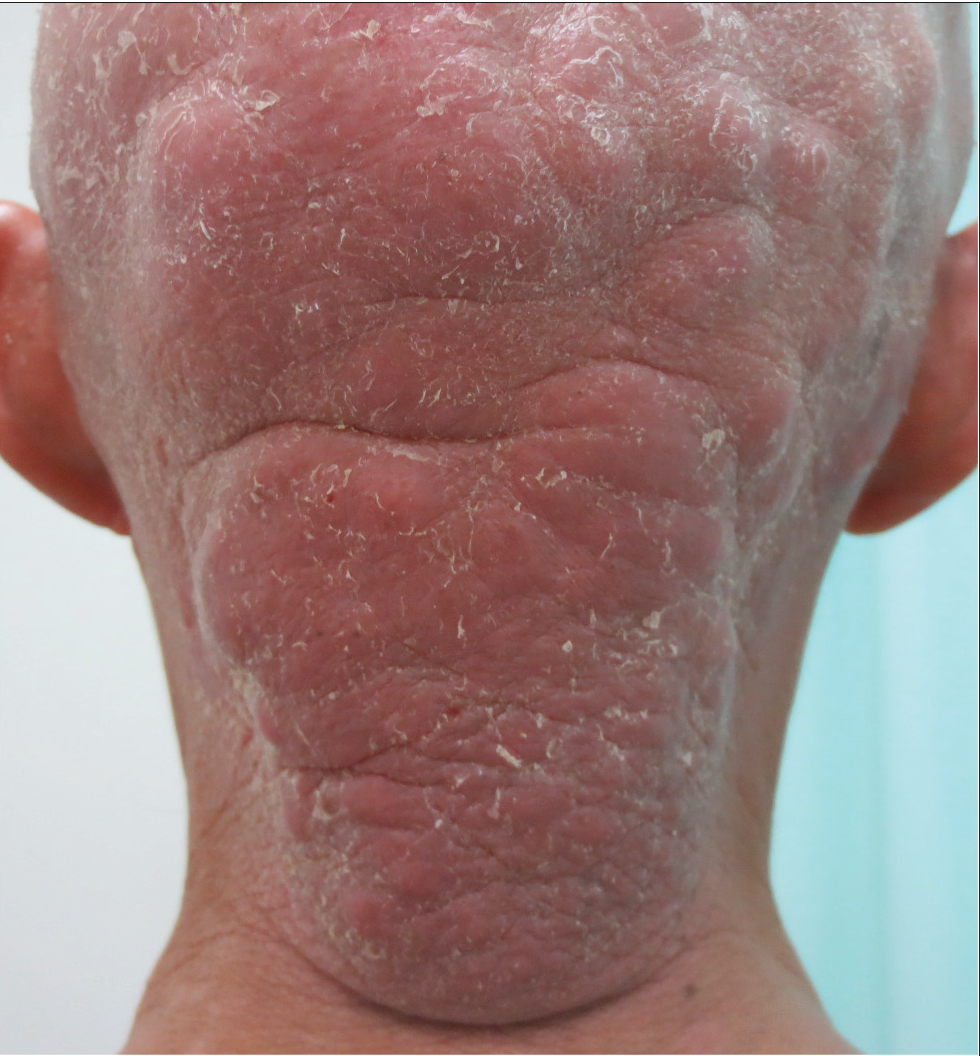
- A huge tumour on the head and neck.
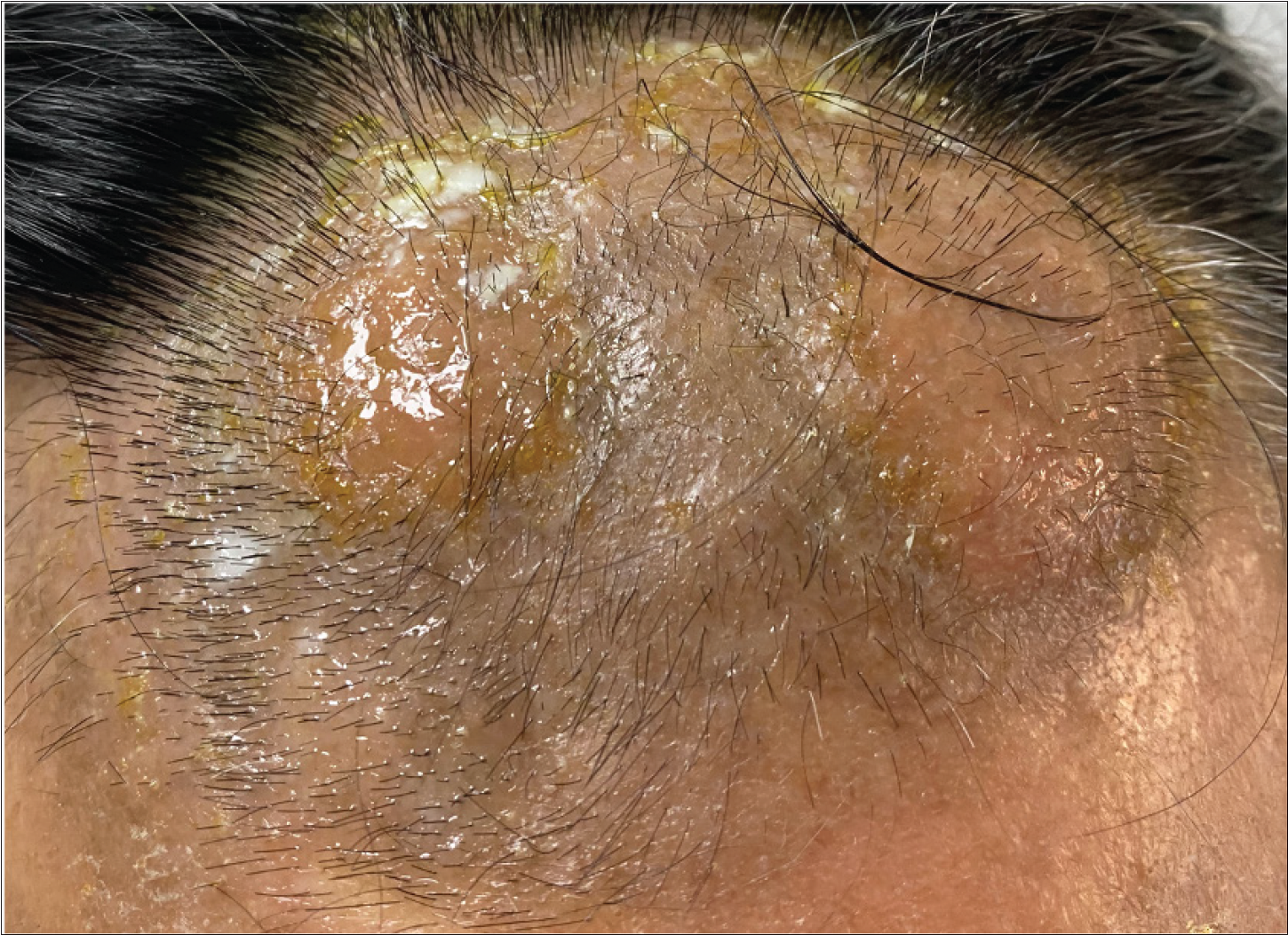
- An infiltrated plaque on the forehead before treatment.
All patients were treated with intramuscular interferon α-1b; topical corticosteroids were the second most frequently used therapy in our patients (10/12), followed by narrow-band ultraviolet B radiation (4/12), local radiotherapy (3/12) or chemotherapy (3/12), as shown in Table 2. The median time of patients’ follow-up was 43 months (6–108 m). At the last follow-up visit, six patients were alive with partial remission, two patients were in complete remission and four patients had died due to follicular mycosis fungoides. Among these, patient four developed peripheral blood and bone marrow involvement, proven by bone marrow biopsy (haematological involvement), and patient five developed nodal disease, which was proven by lymph node biopsy.
| Patients | Treatment | Dose and duration | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | INFα Topical steroids | 500 MU three times weekly × 12 m | None |
| 2 | NB-UVB INFα Topical steroids | 8–10J three times weekly × 12 m 500 MU three times weekly × 20 m | None |
| 3 | INFα | 500 MU three times weekly × 24 m | None |
| 4 | NB-UVB INFα Topical steroids Local radiation Chemical therapy | 8 J three times weekly × 24 m 500 MU daily ×24 m CHOP | Fever, nausea, hypocytosis, alopecia and infection (skin and lung) |
| 5 | NB-UVB INFα Topical steroids Chemical therapy | 8 J three times weekly × 12 m 500 MU daily × 12 m Doxorubicin 30 mg biweekly × 10 m | Nausea, alopecia, hypocytosis and thrombosis |
| 6 | NB-UVB INFα Thymosin | 8 J three times weekly × 10 m 500 MU three times weekly × 60 m 10 mg twice weekly × 12 m | Fever and fatigue |
| 7 | NB-UVB INFα Topical steroids Local radiation | 8 J three times weekly ×12 m 500 MU daily × 12 m | None |
| 8 | INFα | 500 MU three times weekly ×12 m | None |
| 9 | NB-UVB INFα Thymosin Chemotherapy | 8–12 J three times weekly × 6 m 500 MU daily × 12 m 10 mg twice weekly × 8 m Gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2 weekly ×1 m | Nausea and alopecia |
| 10 | INFα Topical steroids Themotherapy | 500 MU daily × 4 m | Alopecia and fatigue |
| 11 | INFα Topical steroids Chemotherapy | 500 MU daily × 6 m Gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2 weekly × 1 m | Nausea, diarrhea hypocytosis and pneumonia |
| 12 | NB-UVB INFα | 8 J three times weekly × 6 m 500 MU daily × 6 m | None |
MU: million units, m: month, NB-UVB: narrow band ultraviolet B radiation, INFα: interferon α-1b, CHOP: cyclophosphamide-hydroxydaunorubicin-oncovin-prednisone
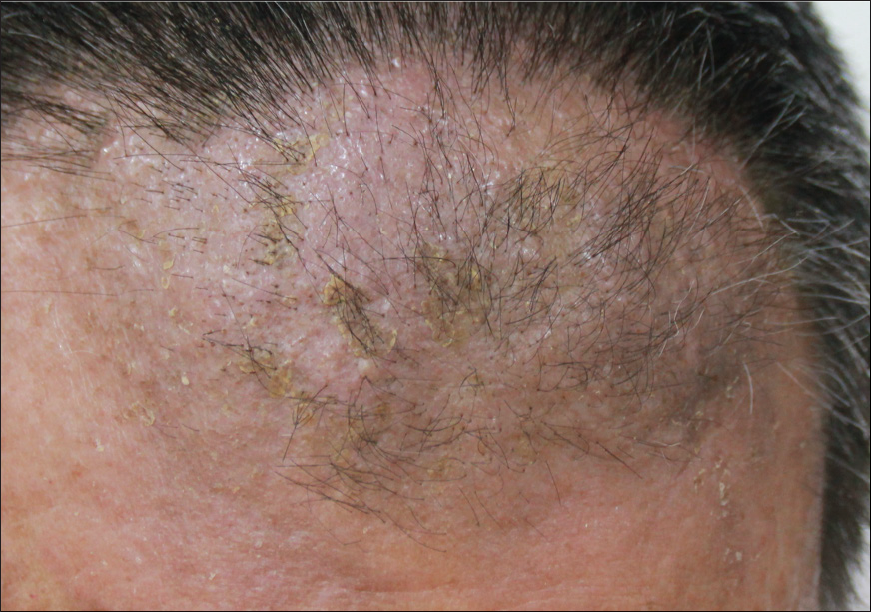
- An infiltrated plaque on the forehead after treatment.
Two patients had a history of hypertension (patients three and seven), for 1 and 6 years, respectively, before the diagnosis of follicular mycosis fungoides was made. Patient nine was diagnosed with hypothyroidism 2 years after the diagnosis of follicular mycosis fungoides.
Histopathological findings
All cases showed perifollicular and/or intrafollicular infiltration with atypical lymphocytes. The main histological characteristics are summarised in Table 2. The suprabulbar region of the follicles was invaded in all samples [Figure 2a], and the external root sheath was heavily involved in all cases excepting patient eight [Figure 2b].
The atypical cells in the majority of cases (8/12, 66.7%) were small to medium-sized [Figure 2c], while the rest (4/12, 33.3%) had predominantly medium to large-sized cells. In three patients of the D- follicular mycosis fungoides group, large cells made up to 10–25% of the lymphoid infiltrate [Figure 2d], showing large cell transformation. We did not find large cell transformation in any patient of the A- follicular mycosis fungoides group. Eosinophils were observed in all cases, and considerable numbers of eosinophils (20–30/high power field) were observed in four cases of the A-follicular mycosis fungoides group.
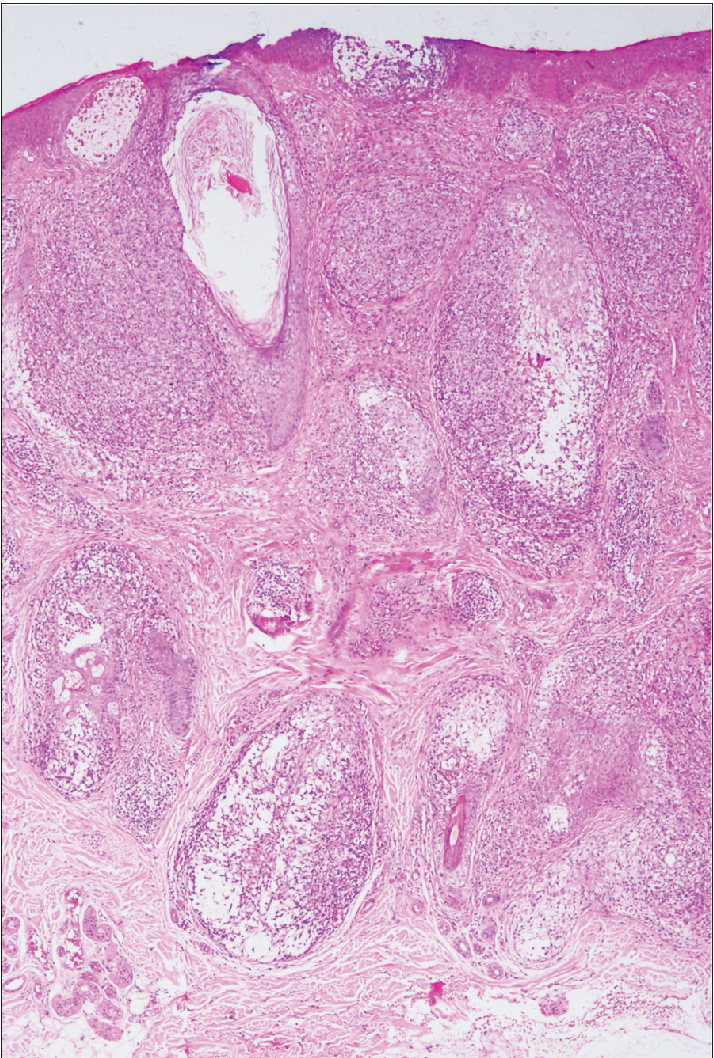
- Dense intrafollicular and perifollicular infiltrates and extensive follicular mucinosis (haematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×40).
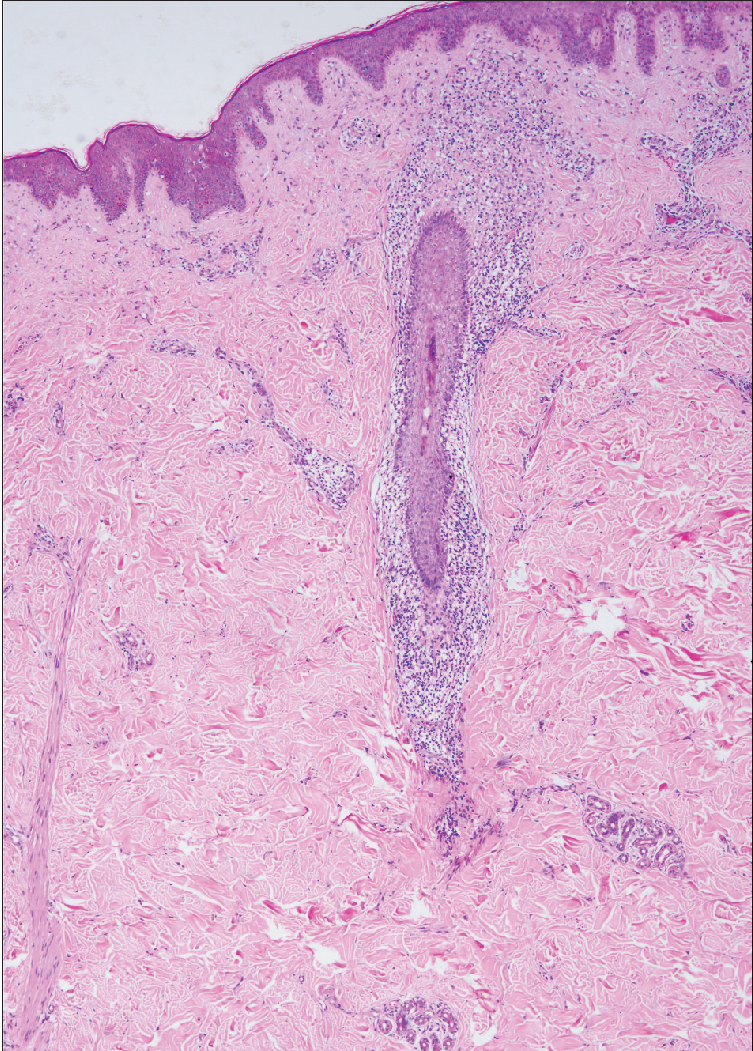
- Sparse perifollicular infiltrates (haematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×40).
| Histological findings | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Perifollicular lymphoid infiltration, and folliculotropism | 12/12 |
| Sparse infiltration | 2/12 |
| Moderate infiltration | 2/12 |
| Marked infiltration | 8/12 |
| No mucinosis | 1/12 |
| Limited follicular mucinosis | 7/12 |
| Prominent mucinous degeneration | 4/12 |
| Mild epidermotropism | 3/12 |
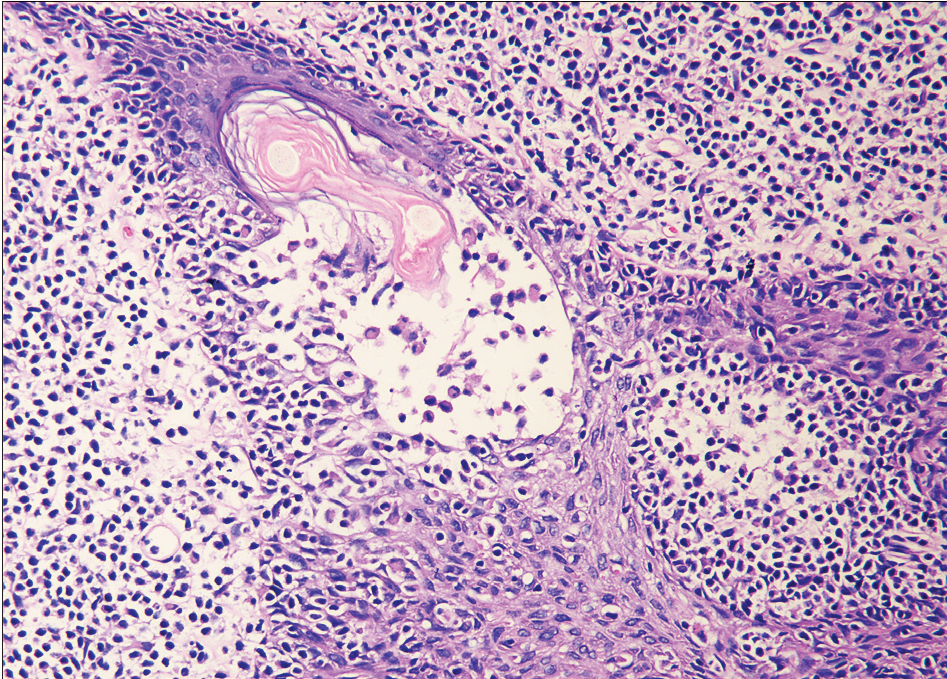
- Infiltration of follicular epithelium by small sized atypical lymphocytes with mucin deposition.
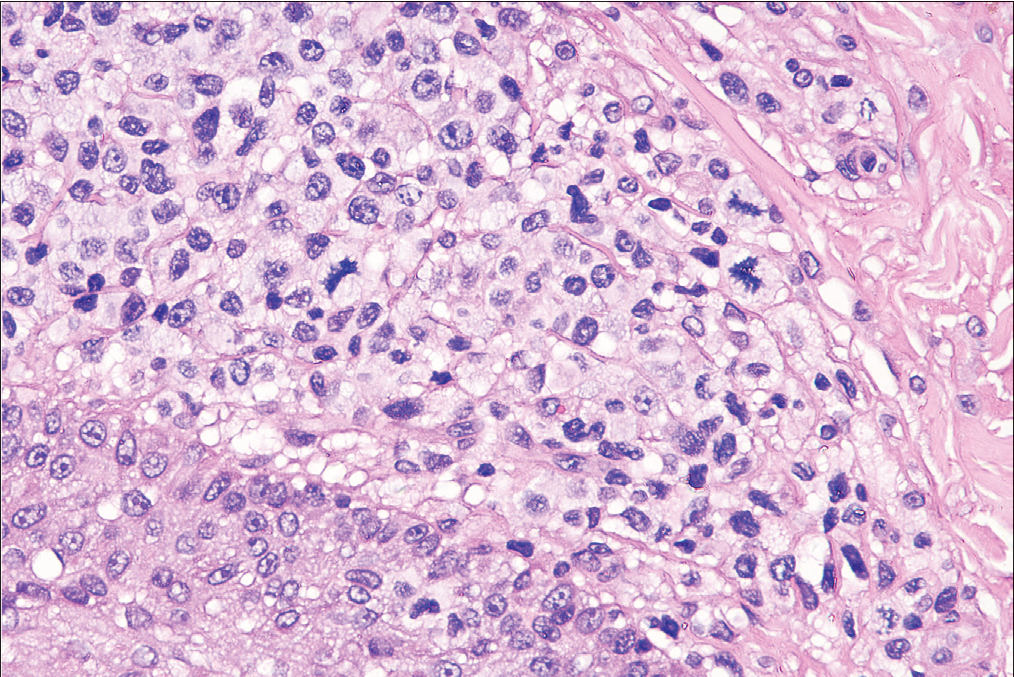
- The blast cells made up more than 25% of the infiltrate (haematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×200).
| Immunohistochemical features (envision ×200) | Frequency |
|---|---|
| CD4+, CD8+ | 10/12 |
| CD4−, CD8+ | 1/12 |
| CD4−, CD8− | 1/12 |
| CD30 > 10% | 2/12 |
| CD20 > 10% | 8/12 |
| CD20 < 1% | 4/12 |
| CD68 > 10% | 6/12 |
| CD56 | 0/12 |
Immunohistochemical and genotypic features [Table 4]
Immunophenotypically, the classic T-cell phenotype CD2+, CD3+ of folliculotropic lymphoid cells with deletion of CD7 was observed in all cases [Table 3]. Expression of CD30 by more than 10% of neoplastic T-cells was observed in 2 patients in the D-follicular mycosis fungoides group, while none in the A-follicular mycosis fungoides group exhibited this. All patients of the D-follicular mycosis fungoides group (100%) had <1% positivity of CD20, while seven patients of the A-follicular mycosis fungoides group (87.5%) had up to 10% positivity Figure 3. There was no significant difference in the Ki-67 proliferative index (ranging from 5 to 50%) between the two groups. Molecular analysis demonstrated the presence of monoclonality of T-cell receptor γ-gene in all cases.
Discussion
We report a Chinese series of 12 patients with follicular mycosis fungoides. Follicular mycosis fungoides mainly occurs in adults, and previous studies have shown that the mean age of onset varies from 46 to 59 years.3 However, our patients were much younger, with a mean age of 30 years. Besides the limited number of cases and selection bias, race and region may explain this difference. On reviewing the literature, previous cohort studies [Table 5] have been from European or North American institutions,8,10,13,14 hence most included patients were either white/caucasians or darker skin types. However, all our patients were Chinese. Previous studies have shown a male preponderance with a male-to-female ratio of 2–5:1. However, there was no obvious gender difference in this cohort with the male-to-female ratio being only 1.4:1. This is probably explained by the limited case numbers. Therefore the relationship between age of onset and race needs to be explored further by larger-scale Asian studies.
| Study | n | Gender | Age (y) | Clinical stage at diagnosis | Treatment | Outcome | Prognostic factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hodak et al. 1999/Israel21 | 9 | M: 6 F: 3 | 55 | Not reported | PUVA: 6 NB-UVB: 1 TSEB: 1 INF: 1 | Not reported: 2 CR: 3 PR: 4 | NM |
| Van Doorn et al. 2002/Netherlands2 | 51 | M: 42 F: 9 | 57 | Only skin lesions: 45 Lymph node involvement: 5 Visceral involvement: 1 | PUVA: 22 TSEBI: 11 Radiotherapy: 7 Other: 11 | CR: 5 PR: 20 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 20 Died of other cause: 6 | NM |
| Gerami et al. 2008/USA4 | 43 | M: 31 F: 12 | 49 | ≤IIA: 32 ≥IIB: 11 | Skin directeda: 12 Irradiation alone: 1 PUVA: 30 Retinoids: 26 INFα: 18 Chemotherapyb: 14 Alemtuzumab: 3 Allo-HSCT: 4 | ≤IIB: 87% at 5 years and 82% at 10 years ≥IIIA: 83% at 5 years and 67% at 10 years | NM |
| Lehman et al. 2010/USA6 | 50 | M: 32 F: 18 | 58.8 | Only skin lesions: 30 Erythroderma: 4 Lymph node involvement: 7 Visceral involvement: 1 Not reported: 8 | PUVA with or without other therapies: 21 radiation therapy: 2 Otherc: 27 | CR: 1 PR: 31 Died of follicular MF: 3 Died of other cause: 12 Lost: 3 | NM |
| Mantaka et al. 2013/Norwegian14 | 15 | M: 10 F: 5 | 65 | Early-stage (IA-IIA): 8 Intermediate-stage (IIB-III): 3 Advanced-stage (IVA-IVB): 2 | PUVA: 6 TSEBI or other radiation: 3 IFNα: 2 Topical steroids: 5 Chemotherapyd: 2 Allo-HSCT: 2 Lost: 4 | PR: 6 PD: 4 Died of unknown cause: 4 Lost: 1 | NM |
| Marschalkó et al. 2014/Hungary22 | 17 | M: 13 F: 4 | 50.7 | Not reported | PUVA: 8 IFNα: 5 TSEBI or other radiation: 9 Retinoid: 9 Topical steroids or bexarotene gel: 5 | PR: 8 CR: 5 PD: 2 Died of unknown cause: 1 Lost: 1 | NM |
| Deonizio et al. 2016/Brazil23 | 33 | M: 20 F: 13 | 46 | Early-stage (≤IIA): 14 Advanced-stage (≥IIB): 19 | NB-UVB and/or PUVA: 22 TSEBI or other radiation: 13 Chemotherapye:12 IFNα: 9 | PR: 22 CR: 6 PD: 7 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 2 | LCT clinical stage |
| Hodak et al. 2016/Israel24 | 49 | M: 35 F: 14 | 44.1 | Early-stage (IA-IB): 34 Advanced-stage (≥IIB): 15 | Not reported | PD: 4 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 5 Alive: 40 | clinical stage |
| Van Santen et al. 2016/Netherlands8 | 203 | M: 147 F: 56 | 59 | Early skin-limited disease: 84 Advanced skin-limited disease: 102 Extracutaneous disease: 17 | Topical steroids: 21 UVB: 12 PUVA: 61 Retinoids: 19 IFN-α: 10 Local radiotherapy 21 TSBEI: 20 Chemotherapy 14 Other73 | PR: 78 CR: 32 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 59 Died of other cause: 34 | clinical stage older than 60 years LCT extensive secondary bac- terial infection |
| Baykal et al. 2017/Turkey25 | 27 | M: 16 F: 11 | 46.2 | Early-stage (≤IIA): 19 Advanced-stage (≥IIB): 8 | PUVA with acitretin or IFN-α, bexarotene: 20 TSEBI: 4 Chemotherapyf: 2 Lost: 1 | PR: 15 CR: 8 PD: 1 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 2 Lost: 1 | clinical stage |
| Wieser et al. 2017/USA10 | 114 | M: 62 F: 52 | 57.1 | Early-stage (≤IIA): 80 Advanced-stage (≥IIB): 34 | Skin directeda: 97 TSEBI or other radiation: 58 Oral Bexarotene: 53 IFN-α: 13 Methotrexate: 15 Other: 20 | PD: 33 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 11 Died of other cause: 15 | stage at diagnosis advanced age65 LCT Leonine facies |
| Kalay et al. 2020/Turkey13 | 53 | M: 43 F: 10 | 56 | Early-stage (≤IIA): 29 (54.7%) Advanced-stage (≥IIB): 24 (45.3%) | Skin directeda: 49 TSEBI or other radiation: 10 Oral Bexarotene:20 IFN-α: 45 Chemotherapyg: 13 Allo-HSCT: 4 | PR: 21 CR: 13 PD: 10 Died of follicular mycosis fungoides: 7 Died of other cause:2 | stage at diagnosis LCT levels of LDH |
M: male, F: female, TSEBI: total skin electron beam irradiation, PUVA: psoralen ultraviolet A, NB-UVB: narrow band-ultraviolet B radiation, PD: progressive disease, allo-HSCT: allogeneic stem cell transplantation, NM: not mentioned, LDH: lactate dehydrogenase, LCT: Large cell transformation, askin-directed therapies included PUVA, NB-UVB: nitrogen mustard, or bexarotene gel in combination with topical steroids, bthis chemotherapy included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine and prednisone), liposomal doxorubicin, gemcitabine, or a combination of these drugs, cincluded topical corticosteroids, nitrogen mustard, narrow-band UV-B phototherapy, extracorporeal photopheresis, topical or oral retinoids, and no therapy, dchemotherapy was given either as a monotherapy (chlorambucil, gemcitabine or high-dose methotrexate) or combination chemotherapy (CHOP: cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone), emultidrug chemotherapy, including CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) and C-MOPP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone), fshort-term methotrexate and CHOP chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine, and prednisone), gdemcitabine hydrochloride and CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride, vincristine sulfate and prednisone)
The head region is commonly reported to be the most favoured site of follicular mycosis fungoides lesions.9 The scalp and face region was the most affected site in our patients too. In our cohort, the most common presentation was follicular papules, followed by erythematous plaques, nodules and acneiform lesions. Thus the clinical features were in agreement with other series.8,10
In 2016, Van Santen et al. suggested dividing patients with follicular mycosis fungoides into three groups with different prognoses—early skin-limited follicular mycosis fungoides characterised by patches, follicular papules and acneiform lesions; advanced skin-limited follicular mycosis fungoides characterised by nodules and tumours; and follicular mycosis fungoides with extracutaneous disease.8 The new classification emphasises the type of lesions rather than the involved areas. Patients with plaques represent a heterogeneous group which should be differentiated by histological features.12 The presence of a dense infiltrate with large lymphocytes confers a prognosis similar to those with advanced disease. On the contrary, the presence of a sparse infiltrate with small lymphocytes indicates a prognosis similar to those with indolent disease. This new staging system has been supported by some other studies.11,13 In our study, all patients in the D-follicular mycosis fungoides group presented with infiltrated plaques, nodules and/or tumours; two of them met the criteria for lymph node involvement [Table 1], hence they qualified as advanced skin-limited follicular mycosis fungoides or follicular mycosis fungoides with extracutaneous disease based on Van Santen’s criteria. Thus, our findings suggest that this new classification is effective in estimating prognosis.
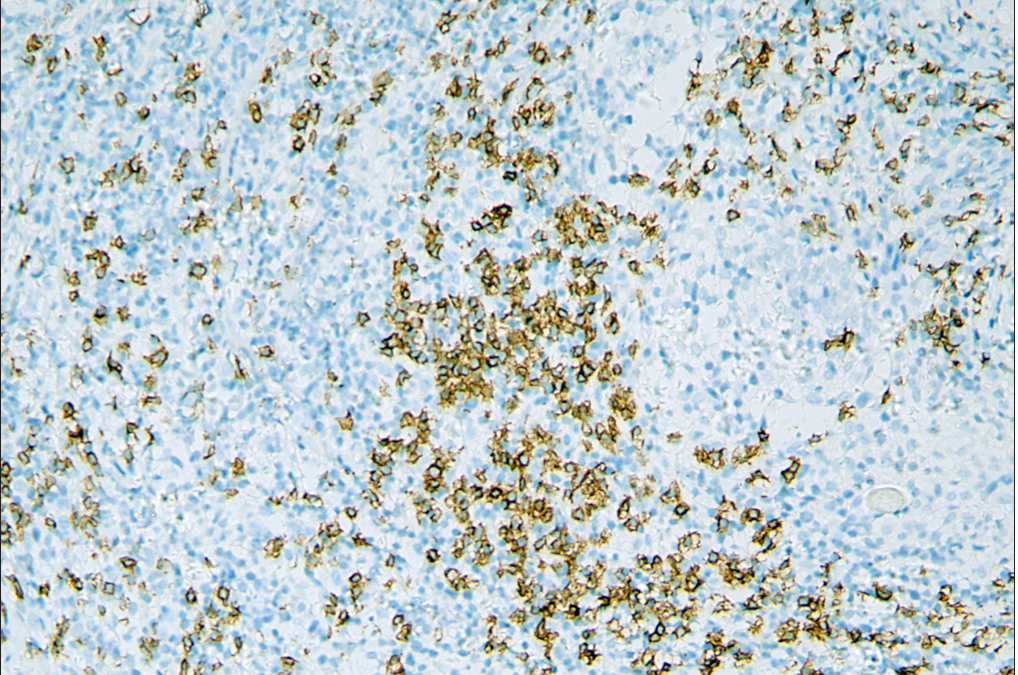
- Increased number of CD20+ B cells in A-follicular mycosis fungoides group.
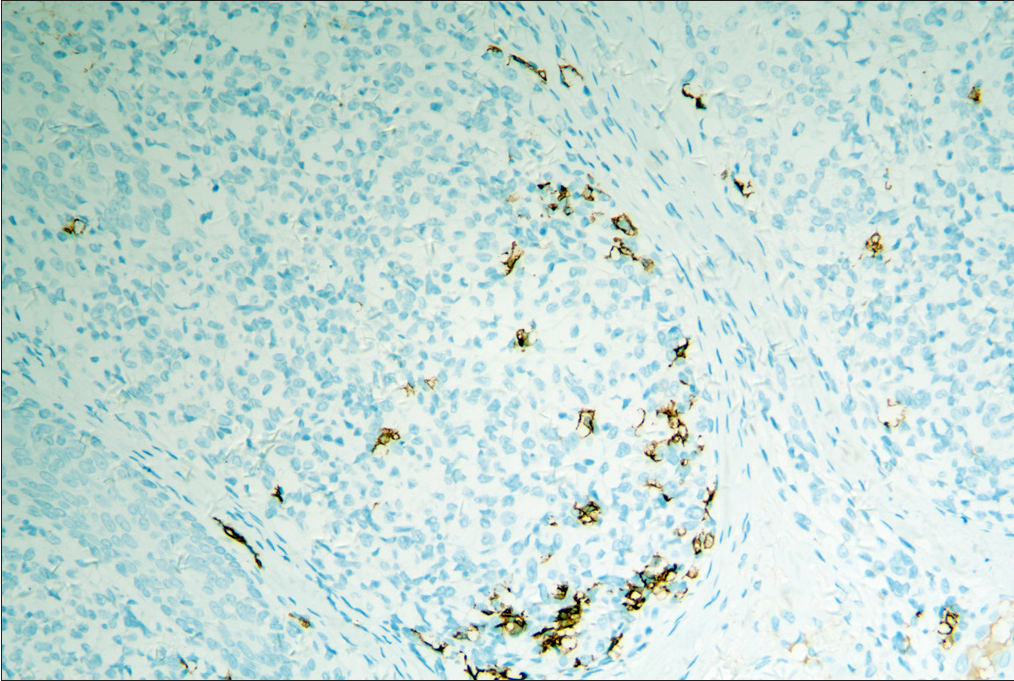
- Decreased number of CD20+ B cells in D-follicular mycosis fungoides group.
In the available literature, more than one study has indicated that risk factors include clinical stage, large cell transformation, and the presence of more than 10% Ki-67 positive cells.10,13,15,16 Large cell transformation is related to the presence of CD30-positive large cells and is associated with a poor prognosis. Although large cell transformation and advanced stage (4/4, 100%) were the prominent features in the D-follicular mycosis fungoides group, the prognostic factors above cannot be confirmed statistically due to the limited number of our cases. Their value in the prognosis of patients with follicular mycosis fungoides still warrants further investigation. Compared with classic mycosis fungoides, eosinophils are more conspicuous within the reactive infiltrate. Whether infiltrating eosinophils is responsible for the poor outcome in patients with follicular mycosis fungoides is unknown.
Furthermore, the role of tumour-associated B cells in the tumour microenvironment is still vague. Atzmony et al. recently reported that the presence of B cells in follicular mycosis fungoides demonstrates a positive correlation with advanced stages.15 Moreover, a previous analysis of 33 cases of mycosis fungoides has already shown that increased B-cell numbers might indicate shortened progression-free survival.17 However, a report of 40 patients of follicular mycosis fungoides showed that the presence of B cells had no effect on prognosis and disease progression.12 Several studies in solid human tumours suggest improved tumour control in the presence of B cells.18,19 Schebye et al. discovered that it might not be beneficial to attenuate B-cell functions in tumour immunotherapy based on glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor family-related protein agonism, and mature B cells are critical to T-cell-mediated tumour immunity.20 In our study, there was a significantly greater number (7/8, 88%) of dermal CD20 positive cells observed in the A-follicular mycosis fungoides group compared with the D-follicular mycosis fungoides group (0/4, 0%). This result suggests that there is a trend towards a good prognosis with the presence of more B cells in follicular mycosis fungoides. However, due to the limited number of cases, larger prospective studies are warranted to discover the impact of tumour-infiltrating B cells in follicular mycosis fungoides, as well as mycosis fungoides.
Limitation
This is a retrospective evaluation of follicular mycosis fungoides in only 12 Chinese patients. The number of cases is small, therefore meaningful statistical analysis was not possible. The average follow-up duration of two patients in the A-follicular mycosis fungoides group was shorter than two years, so the distinction between A-follicular mycosis fungoides and D-follicular mycosis fungoides groups may be less rigorous. Further prospective studies are warranted to assess in more detail the possible risk factors and preferred treatment modalities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as the first Chinese case series of follicular mycosis fungoides, our study analysed the clinical and histologic features of patients with follicular mycosis fungoides as well as evaluated the risk factors for survival. It is remarkable that our patients are younger than those in foreign studies. What’s more, our data suggest that the B cells may play a protective rather than immunosuppressive role in follicular mycosis fungoides. However, more large-scale studies, especially on Asian cases, are required to confirm our conclusion.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-85.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis: A clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:543-57.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: An aggressive variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:738-46.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The spectrum of histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings in folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1430-38.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: Single-center study and systematic rteview. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:607-13.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follicular mycosis fungoides: A clinicohistopathologic study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:563-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical staging and prognostic factors in folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:992-1000.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides is a heterogenous group. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:17-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical characteristics, risk factors and long-term outcome of 114 patients with folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309:453-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Association of a proposed new staging system for folliculotropic mycosis fungoides with prognostic variables in a US cohort. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;157:157-65.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Plaque stage folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: Histopathologic features and prognostic factors in a series of 40 patients. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47:241-50.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: Clinical characteristics, treatments, and long-term outcomes of 53 patients in a tertiary hospital. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13585.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and histopathological features of folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: A Norwegian patient series. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:325-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stage-dependent increase in expression of miR-155 and Ki-67 and number of tumour-associated inflammatory cells in folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00230.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- MicroRNA signatures in diagnosis and prognosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:2024-32.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targeting tumor-infiltrating B cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:e110-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CD20+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes have an atypical CD27- memory phenotype and together with CD8+ T cells promote favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:3281-92.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulatory B cells in anti-tumor immunity. Int Immunol. 2015;27:521-30.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mature B cells are critical to T-cell-mediated tumor immunity induced by an agonist anti-GITR monoclonal antibody. J Immunother. 2010;33:789-97.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follicular cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A clinicopathological study of nine cases. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:315-22.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: Clinicopathological analysis of 17 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;29:964-72.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: Clinical and epidemiological evaluation in a single center in Brazil. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:e256-61.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New insights into folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF): A single-center experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:347-55.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underrecognized clinical features of folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: A large clinical series. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:289-99.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






