Translate this page into:
Hand-held dermatoscope or videodermatoscope: Which one to buy?
Corresponding author: Prof. Chander Grover, Department of Dermatology and STD, University College of Medical Sciences and GTB Hospital, Dilshad Garden, Delhi - 110 095, India. chandergroverkubba@rediffmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Grover C, Jakhar D. Hand-held dermatoscope or videodermatoscope: Which one to buy? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2021;87:739-41.
Dermatoscopy is increasingly being used for diagnosis, prognosis as well as treatment follow-up in the field of dermatology. However, there are still many dermatologists, especially residents, who grapple with the question: ‘Which device should they start working with?’ The lack of formal training in dermatoscopy in teaching departments, as well as the lack of a greater understanding granted by standard textbooks of dermatology has led to further confusion and indecision. Through this article, we wish to highlight important features of different types of devices, so that dermatologists new to this technique can make an informed decision.
Broadly, there are two types of dermatoscopes: hand-held dermatoscopes and videodermatoscopes.1,2 The practice of dermatoscopy started off with the hand held dermatoscopes, which offered a magnification of 10x. Most of the initial work in dermatoscopy was done with these devices. The initial handheld devices used non-polarized light. This would limit the visualization of structures and patterns to the papillary dermis. To overcome this issue, immersion/contact fluids were used to enhance light penetration. With the advent of devices with polarization, the applications and acceptability of dermatoscopes increased tremendously. The algorithms developed for pigmentary disorders, especially melanocytic nevi are based on pattern recognition with polarized light at 10x magnification.
Soon enough, it was realized that just as a 10x magnification offered a new perspective on skin diseases, higher magnification (20-200x) can further enhance diagnostic utility by enhancing/elaborating more features.3,4 This degree of magnification was afforded by videodermatoscopes. Universal serial bus (USB) dermatoscopes, which are marketed as ‘digital microscopes’, fall under this category. Over recent years, there has been an increasing trend of utility for these devices.3-6 Even in this category, there are a range of magnifications, brands and special features available. The higher magnification afforded by these devices helps delineate additional details, especially vascular structures. Table 1 summarizes the major differences between these two types of devices including their features and their utility for various indications. Table 2 summarizes the common brands available in the market.
| Feature | Hand-held dermatoscope | Videodermatoscopes |
|---|---|---|
| Popular dermatoscopes | DermLite, Heine dermatoscopes | Dinolite Edge Series; Dinolite Basic; Firefly DE300 |
| Technical specifications | ||
| Magnification offered | 10x-20x for most devices | 10x-220x for most devices |
| Heine IC1 offers 12x-40x; Heine NC1 offers 6-9x) | Even higher magnifications are available (500-1000x); however, they are not relevant to dermatology | |
| Additional magnification (upto 50x) possible only through the attached smartphone | These dermatoscopes can visualize the same lesion at two different magnifications (lower magnification at 30-50x and higher magnification at 180-200x) | |
| Power source | USB rechargeable batteries for most devices | No charging required. It comes live when connected to the viewing device |
| Viewing mode offered | Image can be viewed by the operator only; cannot simultaneously show to the patient Additional screen mirroring applications may be required for the same | Image is viewed on a computer screen, hence, can be simultaneously viewed by patients/ others |
| Battery life | 0.5-8 h depending on the device used | Not applicable |
| Optical resolution | Very good | Low cost devices have slightly inferior optical resolution; whereas high- end models have a resolution comparable to handheld devices |
| Polarized and nonpolarized modes | Available in most devices. Toggling possible with a switch | Available in most devices. Toggling possible with the turn of a ring |
| Contact/noncontact | Most handheld devices are contact devices i.e., the lens comes in direct contact with the lesion being inspected | |
| Newer devices are coming up with removable contact face-plates. This helps avoid contact with potentially infected lesions as well as blanching of the vascular structures | These are noncontact devices. Only the rim of the spacer comes in contact with the skin surface. The lens is held back at a distance. It is possible to change the spacer; to sterilize it separately; and also, to cover it to prevent cross-infection | |
| Accessories required | ||
| For viewing | None | Requires a computer/laptop screen to view |
| For capturing images | Smartphone/camera with/without a connector (Magneticonnect) | Images can be captured on the viewing device |
| Compatible devices | Smartphones including android phones and iphones; ipads; digital cameras etc | Laptops or computers with a USB port |
| Versatility of the device | ||
| Pigmentary evaluation | +++ | ++ |
| Vascular evaluation | ++ | +++ |
| Trichoscopy | +++ | +++ |
| Onychoscopy | ++ | +++ |
| Nail fold capillaroscopy | +; Blanching of the capillaries is an issue | +++ |
| Entomodermoscopy | ++ | +++ |
| Mucoscopy | + | +++ |
| Oculoscopy | + | +++ |
| Hidroscopy | + | +++ |
USB: Universal serial bus
| Device | Company | Imaging technology |
|---|---|---|
| Hand-held dermatoscopes | ||
| DermLite Cam | 3Gen | Built-in digital camera |
| DermLite DL1 | 3Gen | Mobile device |
| DermLite DL200, DermLite DL3/DL4 | 3Gen | Mobile device or Digital Camera |
| DermLite FOTO System, DermLiteFoto II Pro | 3Gen | DSLR |
| VEOS HD1/HD2 | Canfield | Mobile Device |
| VEOS SLR | Canfield | DSLR |
| NC2 Dermatoscope | Heine | Mobile Device |
| DELTA 20T | Heine | DSLR |
| iC1 | Heine | Mobile Device |
| Illuco IDS-1100 | Dermoscan | Mobile Device or digital camera |
| Video dermatoscopes | ||
| Medicam 1000 | FotoFinder | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| DermoGenious Ultra | Dermoscan | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| MoleMax | Derma Medical Systems | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| Dino-Lite Edge Series, Dino-Lite Premier Series | AnMo Electronics Corporation | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| FireFly DE300, FireFly DE350 | FireFly | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| Hi-Scope | Hirox | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| VideoCap | D.S. Medica | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| Horus | Adamos.r.l | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| Optilia | Optilia instruments | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| VivaCam | Caliber Imaging and Diagnostics | Built-in video dermoscopy |
| C-Cube | Pixience | Built-in video dermoscopy |
For a beginner, especially a post-graduate student, buying an expensive instrument like a dermatoscope is an important investment to make. With limited knowledge and several choices, it is not always easy to make the right decision. This uncertainty prompts many to buy a cheaper dermatoscope in the initial phase of their learning. However, poor resolution and picture quality fail to do justice to dermatoscopy, and may dampen one’s interest. Therefore, it is advisable to research available instruments and invest in the best one possible.
The best dermatoscope to buy is the one which best suits the user’s personal needs in terms of the type of skin lesion to be visualized commonly. This is further based on the type of practice, time available and the ease of carrying accessory equipment for image capture and storage [Figures 1 and 2]. Hand-held dermatoscopes offer low magnification but excellent optical resolution and images, but most devices need to be in contact with the area to be examined, which may limit their use, especially in the current pandemic era. Other advantages of hand-held dermatoscope include ease of use and easy connectivity to the smartphones. For daily practical needs, a hand-held scope might be as good as video one or even better given the practicality of use, while for research purposes, a videodermoscope might be better. Videodermatoscopes are more versatile devices which allow visualization of odd sites like nail, eye and mucosae with ease.6-9 Features like magnification, resolution, ultraviolet light, pigment boost, measurement and calibration add to the versatility of these dermatoscopes. The availability of cross-polarization should always be ensured in the device bought. It is recommended to hold and use the device before investing a major amount, so that individual comfort and ergonomics with the procedure are ensured. Whatever type of dermatoscope one starts off with, there always exists the possibility of switching to another type to discern more features or to capture better images.
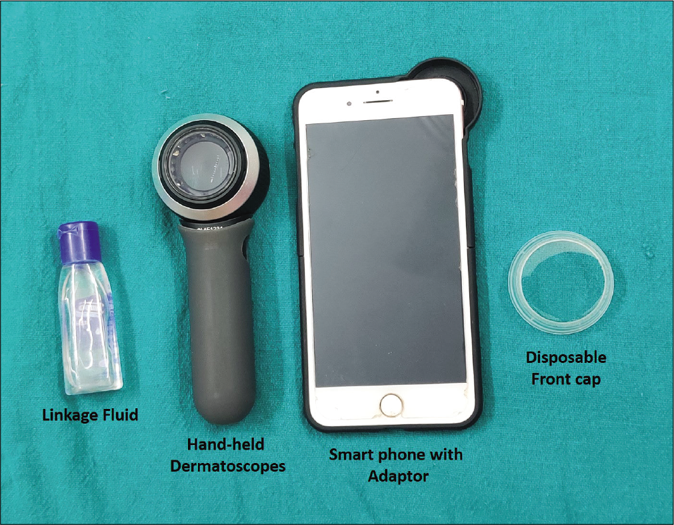
- A hand-held dermatoscope with the accompanying requirements for capturing and storing images

- A universal serial bus dermatoscope with accompanying requirements for capturing and storing images
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Response to “Dermatoscopic features of lichen nitidus”. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:179.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Videodermatoscopy enhances diagnostic capability in some forms of hair loss. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:205-8.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Patient attitude towards videodermatoscopy for the detection of skin cancer: A cross-sectional study. Oncol Res Treat. 2019;42:319-25.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nailfold capillaroscopy with USB dermatoscope: A cross-sectional study in healthy adults. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:33-8.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Innovative modification of the USB dermatoscope for mucoscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:e3-e4.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Universal serial bus dermatoscope as an oculoscopy tool. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:e139-e140.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hidroscopy: In vivo videodermoscopy of the sweat glands. Skin Res Technol. 2019;25:410-1.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]





