Translate this page into:
Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology: A scientometric analysis
Corresponding author: Dr. Virendra S Ligade, Department of Pharmacy Management, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India. virendra.sl@manipal.edu
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Ligade VS. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology: A scientometric analysis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:788-91.
Abstract
Background
A study related to an overview of the editorial workflow, editorial decision-making and timelines of the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology (IJDVL) had been published earlier. However, a study on publication pattern, citations, contributing organizations, most cited publications etc. of IJDVL has not been performed till now.
Objectives
This study aims to identify and analyse the impact of IJDVL on various scientometric indicators viz. year-wise publication growth, impact factor trend, most contributing organizations, global outreach, most cited papers, and cited and citing journals, over the years 2007 to 2019.
Methods
Data for this study were retrieved from the Web of Science-core collection database of Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics, 2021) on 12th May 2021. The search was performed by using the advanced search feature of the database. Using the “InCites”, a search for journal citation reports of IJDVL was performed.
Results
The highest number of cumulative citations have been received by publications published in the year 2019 with 2,122 citations which is 91.53% in citable items. In the year 2009 journal, the impact factor was 0.976, which jumped to 2.712 (Journal Citation Reports™ 2018). IJDVL received its highest impact factor (3.030) in the year 2019. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi is the most prolific organization contributing to IJDVL with 51 publications. Among foreign countries, China is leading with reference to most contributions by any foreign country with 51 publications in IJDVL. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology having an impact factor 8.277 has been cited 145 times in this journal.
Limitations
Only one database was used for the study.
Conclusion
The high proportion of frequently cited articles in recent years, together with its currently high journal impact factor and quartile two-factor, give sustenance to the view that IJDVL publishes high-standard articles relevant to dermatology research and clinical practice.
Keywords
Scientometric analysis
dermatology
journal
bibliometric studies
Plain Language Summary
Recent trends in the field of dermatology are published in various dermatology journals. Researchers try to publish their research work in reputed journals to get maximum visibility for their research work around the world. Quality of journals are measured by many parameters. The present study was performed to measure the growth and performance of Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology (IJDVL). IJDVL is one of the reputed journals published from India in the field of dermatology. In this study, Web of Science-core collection database was used to extract the data. According to the current study results, analysis showed that IJDVL had a greater number of publications over the years, which is likely to be due to growth of the journal and also due to its being one of the oldest and reputed journals in dermatology field. The number of credentials increased for the journal over the study period. IJDVL also has a global reach, as a total of 32 countries have contributed in publications. Reputed international journals in the field of dermatology have cited articles from IJDVL, which displays its reach among International authors. The results of this study can be used to measure the current state of dermatology research and will be useful to dermatologists, researchers, teachers and postgraduate students in evaluating the published research and status of the journal.
Introduction
Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology (IJDVL) is an open-access peer-reviewed journal dedicated to publishing high-quality articles in the field of dermatology. The journal, which was established in 1940, is owned by the Indian Association of Dermatologists, Venereologists & Leprologists and published by Scientific Scholar. IJDVL includes only authenticated material that is of scientific value to the clinicians or postgraduates in the specialty of dermatology in India, in particular.1 For researchers, the selection of a quality journal for publishing research findings in their field of expertise is a tedious task. There are various dermatology journals mushrooming every day; thus, evaluation of journals becomes important to get information about, and suggest stakeholders, in a particular research area. Journals are broadly evaluated by quantitative metrics and subjective methods. There are various methods proposed to evaluate journals depending upon several parameters, thus making it a complex task to evaluate unbiased evaluation of journals.2 A systematic trend analysis aids in predicting the prospects of a journal. Single journal studies are essential because they reveal important journal features, such as the themes published, geographical distribution and citation patterns to potential journal contributors.3 Some of the widely used methods to evaluate journals are through bibliometric or scientometric analysis, of which the latter has been employed in this study.
Bibliometric studies are crucial because they reveal essential journal features, published topics, distributions, citations and authors.4 Recent methods used to analyse scientific articles include Altmetrics,5 Cybermetrics6 and Webometrics,7 which were developed as web-based and online information began to evolve.8
Earlier, a study related to an overview of the editorial workflow and a detailed picture of various characteristics of submissions, editorial decision-making and timelines had been published in the IJDVL.9,10 We were unable to find any report on publication pattern, citations, growth of impact factor, contributing organizations, contributing countries and most cited publications etc. of the IJDVL. A scientometric analysis of the IJDVL is of special interest because of the journal’s consistent high impact factor (2.712 for 2019), a level which is unprecedented among dermatology journals and publications in India. This study aims to identify and analyse the impact of the IJDVL on various scientometric indicators, viz., year-wise publication growth, impact factor trend, most contributing organisations, global outreach, most cited papers and cited and citing journals, over the years.
Methods
Data search and strategy
Data for this study were retrieved from the Web of Science-core collection database of Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics, 2021) on 12th May 2021. The search was performed by using the advanced search feature of the database. With the help of the “InCites” feature, a search for journal citation reports for the IJDVL was performed. A detailed journal profile was available, consisting of general information about the journal, journal impact factor, citation distribution, impact factor calculation, journal source data, various metric trends and a detailed analysis of the journal profile for the years 2007-2019. Indexing and abstracting information was retrieved from the journal’s webpage.
Data analysis
To perform the descriptive scientometric analysis, we used Journal Citation Reports as the built-in functions. For trend analysis, we extracted data with reference records (all article information available, including a number of articles, citations per year, impact factor percentile, journal quartile status, contributing institutions and countries, most cited publication, citing journal and cited journal data). The information was collected and downloaded in CSV format from the InCites Journal Citation reports database into Excel (Microsoft, USA).
Results
The metric trend of year wise total cites, citable articles, journal rank, quartile and journal impact factor percentile
The highest number of cumulative citations have been received by the journal in the year 2019 with 2,122 citations which is 91.53% in citable items, followed by years 2018 and 2017 with citations of more than two thousand, (2017 and 2018 with 74.51% and 77.36% of articles in citable items). Overall citation behaviour indicates that it is increasing exponentially with total citations from (670) in the year 2009 to (2122) in the year 2019. From the year 2009, the journal was in quartile (Q4) with a Journal Impact Factor™ percentile of 17.708, and from the year 2012 journal was in the (Q3) quartile. IJDVL entered quartile (Q2) from the year 2016, as the Journal Impact Factor™ percentile increased over the period. This was a remarkable achievement by IJDVL among dermatology journals in India [Table1].
| Year | Total cites | Citable items | % articles in citable Items | Rank | Quartile | Journal impact factor percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2,122 | 59 | 91.53 | 26/68 | Q2 | 62.500 |
| 2018 | 2,007 | 53 | 77.36 | 18/66 | Q2 | 73.485 |
| 2017 | 2,018 | 51 | 74.51 | 23/64 | Q2 | 64.844 |
| 2016 | 1,775 | 50 | 82.00 | 28/63 | Q2 | 56.349 |
| 2015 | 1,305 | 46 | 86.96 | 34/61 | Q3 | 45.082 |
| 2014 | 1,252 | 51 | 94.12 | 34/63 | Q3 | 46.825 |
| 2013 | 1,189 | 78 | 76.92 | 38/61 | Q3 | 38.525 |
| 2012 | 1,060 | 90 | 87.78 | 38/59 | Q3 | 36.441 |
| 2011 | 867 | 73 | 87.67 | 45/58 | Q4 | 23.276 |
| 2010 | 844 | 92 | 89.13 | 43/55 | Q4 | 22.727 |
| 2009 | 670 | 96 | 89.58 | 40/48 | Q4 | 17.708 |
Impact factor trend of IJDVL
Journal Citation Reports™ provides transparent, publisher-neutral data and statistics on evolving scholarly publishing landscape. It helps to quickly understand a journal’s role within and influence upon the global research community by exploring a rich array of citation metrics, including the Journal Impact Factor™.
In the year 2009 journal impact factor was 0.976, which jumped to 2.712 (Journal Citation Reports™ 2018). IJDVL received its highest impact factor (3.030) in the year 2018; this is a remarkable achievement by the journal. Its five-year impact factor has shown an increasing trend, with figures above 2 from the year 2017 [Figure 1]. Other dermatology journals published in India and neighbouring countries do not have such high impact factors. In the year 2019, journals in the region having an impact factor were the Indian Journal of Dermatology (1.523) and Annals of Dermatology (Impact Factor 1.412). The total citations of Indian Journal of Dermatology were 1,209 in 2016, 1,507 in 2017, 1,475 in 2018, 1,716 in 2019 and 2,425 in 2020). Annals of Dermatology is a journal published in South Korea in the Asia region. The total citations for this journal were 1,113 in 2016), 1,358 in 2017, 1,527 in 2018, 1,722 in 2019 and 2,158 in 2020.
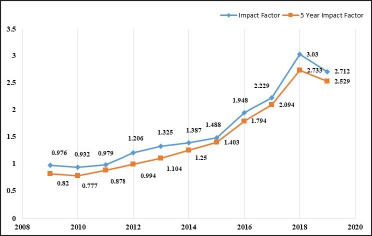
- Impact factor trend of Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology
Contributions by organisations/institutions and countries of origin
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi is the most prolific organization contributing to IJDVL with 51 publications followed by the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh (29 publications). Of the top 10 organizations, two are from foreign countries, viz., Sichuan University, China and King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia with 12 and 11 publications respectively. USA, Egypt, Brazil, Thailand, Tunisia, Mexico and Chile contributed more than five publications to the journal.
Contributions by country/region
Country-wise analysis reflects which country contributed the maximum to the journal. India has a maximum count of 370 publications. Among foreign countries, China is leading with reference to most contributions by any country with 51 publications, followed by Spain with 31 publications. Other countries namely Turkey, South Korea, Saudi Arabia, Italy, Iran, Singapore and Taiwan also contributed significantly to the journal.
Most cited publications (2017-2018)
Table 2 highlights the most cited articles in IJDVL. Out of ten most highly cited articles, nine have been published in the year 2017 and one article was published in 2018. This reveals that articles published in the year 2017 were the most impactful. The most cited work was entitled “Effects of air pollution on the skin: A review” by Puri et al. published in 2017 with 21 citations. Another publication entitled “A prospective study of the epidemiological and clinical patterns of recurrent dermatophytosis at a tertiary care hospital in India” by Pathania et al. received eight citations. There were total of 104 citable items in the year 2018 and 2017.
| Authors | Item title | Volume | Issue | Publication year | Document type | Number of citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Puri, Poonam. et al. | Effects of air pollution on the skin: A review | 83 | 4 | 2017 | Review | 21 |
| Pathania, Sucheta. et al. | A prospective study of the epidemiological and clinical patterns of recurrent dermatophytosis at a tertiary care hospital in India | 84 | 6 | 2018 | Article | 8 |
| Shanshanwal, Sujit J. et al. | Superiority of dutasteride over finasteride in hair regrowth and reversal of miniaturisation in men with androgenetic alopecia: A randomised controlled open-label, evaluator-blinded study | 83 | 1 | 2017 | Article | 7 |
| Pai, Varadraj Vasant et al. | Topical peptides as cosmeceuticals | 83 | 1 | 2017 | Review | 6 |
| Mahajan, Soniya et al. | Clinico-mycological study of dermatophytic infections and their sensitivity to antifungal drugs in a tertiary care centre | 83 | 4 | 2017 | Article | 5 |
| Singh, Sanjay et al. | End of the road for terbinafine? Results of a pragmatic prospective cohort study of 500 patients | 84 | 5 | 2018 | Article | 5 |
| Grover, Chander et al. | Onychoscopy: A practical guide | 83 | 5 | 2017 | Review | 4 |
| Hwang, Sewon et al. | Clinical characteristics of acquired ungual fibrokeratoma | 83 | 3 | 2017 | Article | 4 |
| Bhat, Yasmeen Jabeen et al. | Update on etiopathogenesis and treatment of acne | 83 | 3 | 2017 | Review | 4 |
| Nagar, Rahul | Autophagy: A brief overview in perspective of dermatology | 83 | 3 | 2017 | Review | 4 |
| Bhatt, Kalpana Deepak et al. | Utility of high-frequency ultrasonography in the diagnosis of benign and malignant skin tumours | 83 | 2 | 2017 | Review | 4 |
Citing journal data (2019)/ Cited journal data (2019)
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology having an impact factor of 8.277 has been cited 145 times in this journal, followed by the British Journal of Dermatology with impact factor of 7 having been cited 106 times. Other internationally reputed journals with more than two impact factor have also been cited in IJDVL.
Among the high impact journals in which published articles of IJDVL have been cited are the Indian Journal of Dermatology (1.523), Dermatology Therapy (2.327), International Journal of Dermatology (2.067), Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (8.277) and the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (5.248).
Discussion
The present study employed a scientometric method for evaluating the performance of journals over the period. A bibliometric index can aid researchers search for valued scientific information and support clinicians to execute daily practice.11-13 In the current study, the descriptive scientometric analysis showed that IJDVL had an increasing number of publications over the years, which is likely to be due to its growth. The number of citations increased for journal articles within the specified period, which led to the surge in journal impact factor. However, the maximum impact achieved by a dermatological journal is within the expected range based on the accessible number of journals in dermatology.14 IJDVL has a global reach, as a total of 32 countries have contributed to publications. Reputed international journals in the field of dermatology have cited articles from IJDVL, which displays its reach among foreign authors. Moreover, the journal received research papers from both Indian and international authors in similar numbers. The journal’s acceptance rate during the study period was 19%, which compares favourably with most other dermatology journals. The acceptance rate for submissions from Indian authors was higher than from foreign authors, probably indicating the quality of articles the journal attracts from Indian authors.9 As evidenced by this study, IJDVL has made considerable progress over the past 11 years. The growth of IJDVL and its significant contributions to the field of dermatology in India is remarkable. The results of this study can be used to assess the current state of dermatology research and can be identified to guide future research. Moreover, it will also be useful to dermatologists, researchers, teachers and postgraduate students in evaluating the research quality and the status of the journal.
Only the Web of Science database was used for this study; if other databases had been used, the results of this study might have been slightly different. This is one of the limitations of the study.
Conclusion
From the scientometric analysis, it can be concluded that IJDVL is one of the most significant journals in the field of dermatology research in India. Research papers published after the year 2016 have received numerous citations. The high proportion of frequently cited articles in recent years, together with its currently high journal impact factor and quartile status factor, lend sustenance to the view that IJDVL publishes high-standard articles relevant to dermatology research and clinical practice.
Declaration of patient consent
Patients’ consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology. 2021. https://ijdvl.com/aboutus Last accessed 10 May 2021
- Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research: A scientometric analysis. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2020;54:264-70.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- A bibliometric analysis of the Journal of Advanced Nursing, 1976-2015. J Adv Nurs. 2017;73:2407-419.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibliometric analysis of six nursing journals from the Web of Science, 2012-2017. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75:543-54.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybermetrics-meaning, definition, scope and constituents. Ann Lib Inf Stud. 2004;51:116-20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Informetric analyses on the world wide web: Methodological approaches to ‘webometrics’. J Doc. 1997;53:404-26.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Informetrics at the beginning of the 21st century—A review. J Informetr. 2008;2:1-52.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Analysis of submissions, editorial and peer-review process, and outcome of manuscripts submitted to the Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology over a 6-month period. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:519-25.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The manuscript review process: What do editors do? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:599-602.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citation analysis: a comparison of Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. Proc Am Soc Inf Sci Tech. 2006;43:1-15.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- A bibliometric analysis of Periodontology 2000. Periodontol 2000. 2020;82:286-97.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Impact factors of dermatological journals for 1991 - 2000. BMC Dermatol. 2001;1:7.
- [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






