Translate this page into:
Mucosal syphilide
Corresponding author: Dr. Neirita Hazarika, Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy, AIIMS, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India. neirita.derma@aiimsrishikesh.edu.in
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Hazarika N, Maisnam S, Azad S. Mucosal syphilide. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:537. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_391_2023
A man in his twenties presented with painful, whitish, raised lesions inside his mouth and on lips for 7 months. Personal history was positive for unprotected, men-who-have-sex-with-men (MSM) behaviour. Examination revealed whitish to erythematous, hypertrophic tumid plaques on soft palate and lips [Figures 1 and 2]. Histopathology revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with dense dermal plasma cell infiltration. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was positive for CD-38 and CD-138, and no restriction pattern on Kappa and Lambda. IHC suggested reactive mature plasma cells. Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test (1:64 dilution), and Treponema pallidum haemaggulitination (TPHA) test were positive. Retrovirus serology was negative. These investigations confirmed the diagnosis of secondary syphilis and the patient was treated with single intramuscular injection of benzathine penicillin 2.4 million international unit (IU).
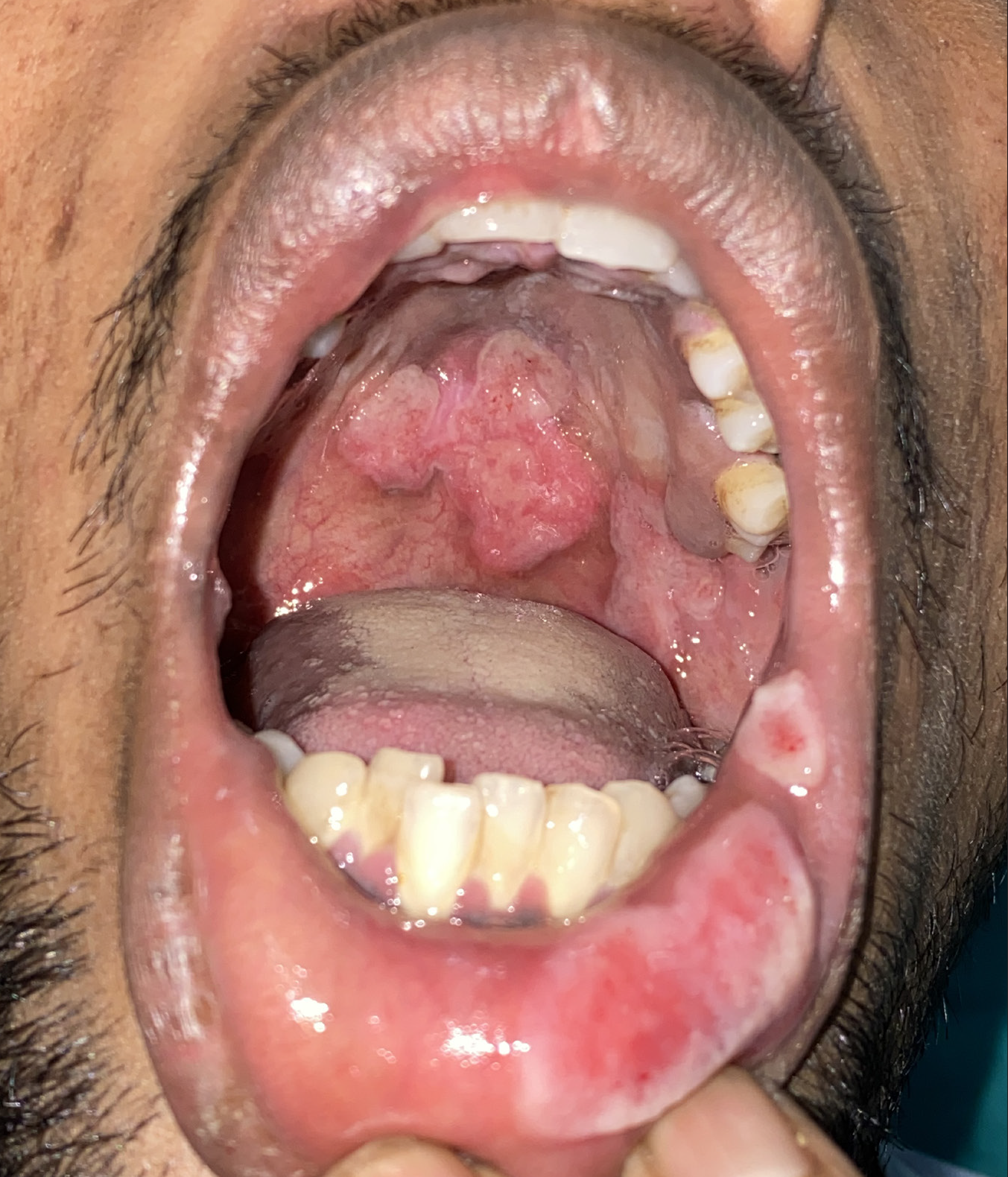
- Erythematous tumid plaques on the soft palate and lips.
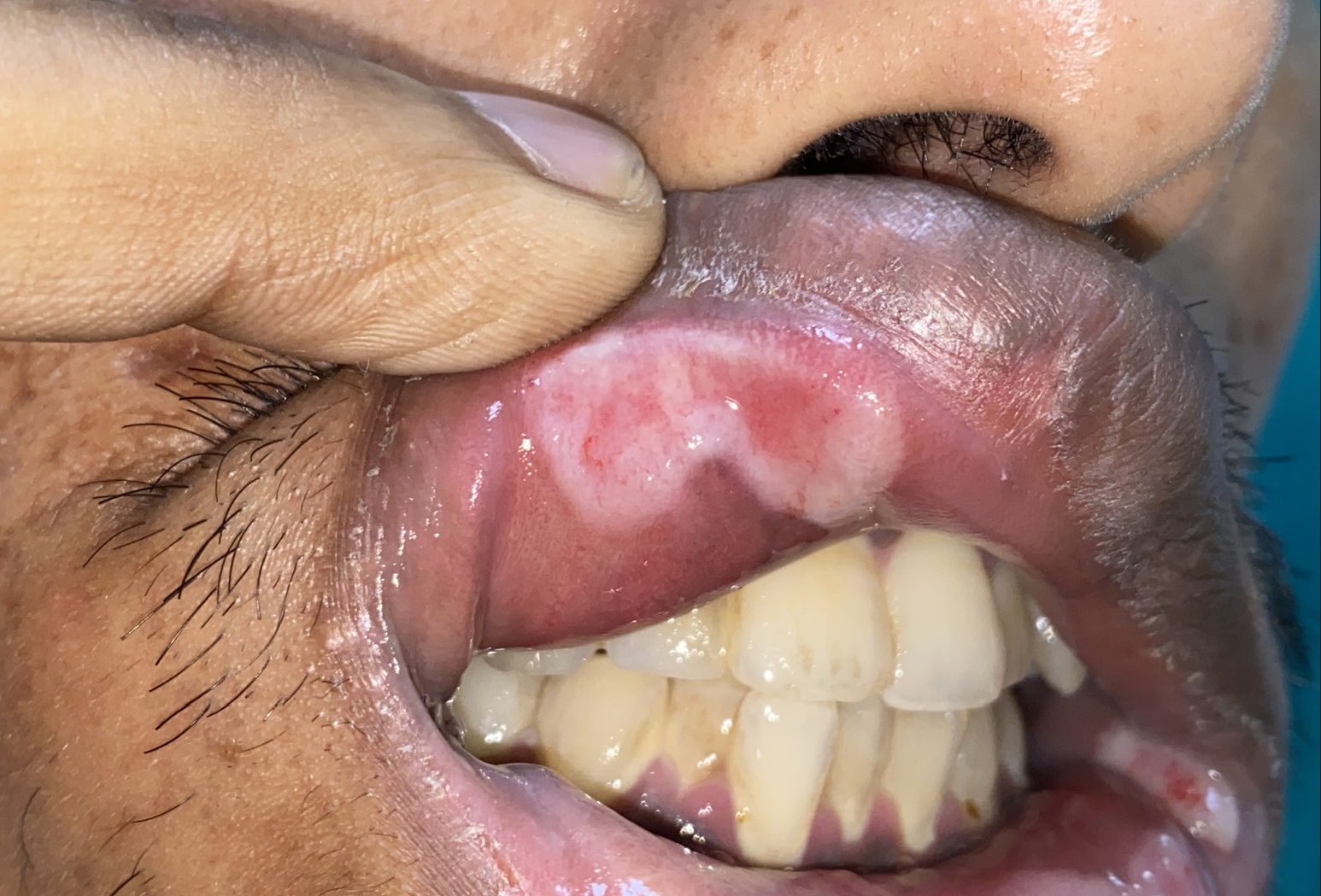
- Erythematous to whitish tumid plaque seen on the upper labial mucosa and split papule seen on the left angle of mouth.
Declaration of patient consent
The patient’s consent not required as the patient identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.





