Translate this page into:
Recalling the recall phenomenon
Correspondence Address:
Sharmila Patil
B -2 ,603, Vikas Complex, M.D. Joshi Road, Thane(W), Maharashtra
India
| How to cite this article: Patil S, Nadkarni N, Shende S. Recalling the recall phenomenon. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2015;81:214-216 |
Sir,
"Radiation recall dermatitis" (RRD) is defined as a "recall" of dermatitis by the skin at the site of previous radiation exposure, in response to administration of certain drugs. It is an acute inflammatory reaction confined to previously irradiated areas and remains a poorly understood phenomenon. [1]
A 62-year-old man presented with an undiagnosed chronic generalized skin disease since 20 years along with inguinal swelling since a month. There was history of whole body narrow band UVB (NB-UVB) received for 2 months in November 2012. A skin biopsy revealed dermal infiltrate with epidermotropism with multiple atypical cells [Figure - 1]. Immunohistochemistry of the lymph node was positive for CD30, CD15 (focal), and leucocyte common antigen (LCA), and oncogene B cell (Pax-5, Oct-2, Bob-1) activity was negative. In situ hybridization of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV RNA) was negative. A final diagnosis of large anaplastic non Hodgkin′s lymphoma was made. Chemotherapy was started with five cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, prednisolone) at an interval of 21 days and gemcitabine, dexamethasone and cisplatin (GDP) salvage therapy.
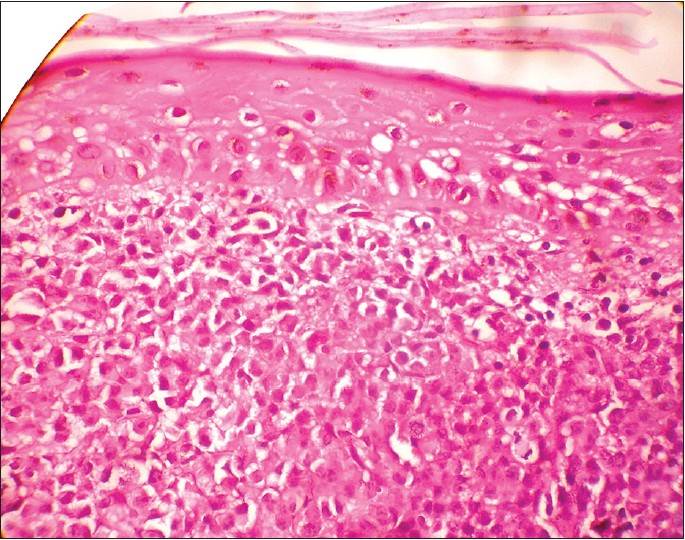 |
| Figure 1: Abnormal T lymphocytes with epidermotropism (H and E, ×40) |
During the second cycle of GDP salvage therapy in March 2013, the patient noticed erythema and moist desquamation, mostly over the skin folds and the trunk. These areas were the same sites where NB-UVB was given earlier. A diagnosis of gemcitabine-induced radiation recall dermatitis Grade 2 was made [Table - 1] and [Figure - 2]. Chemotherapy was stopped and parenteral corticosteroids were given, after which the patient showed significant improvement. However, he developed multiple nodules over his extremities. He was diagnosed to be resistant to chemotherapy and was treated with total skin electron beam therapy (TSET) (6 MeV, 120 cGy) in September 2013. Soon after starting therapy, the patient developed a severe eczematous reaction with painful erosions, necrotic ulcerations and severe edema over the trunk, groin and extremities. This was considered as a re-appearance of radiation recall dermatitis grade 4. He was treated with emollients and non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [Figure - 3]. The patient was advised to continue total skin electron beam therapy with interruptions but he could not tolerate therapy. He developed multiple deep seated necrotic ulcers and eventually succumbed.
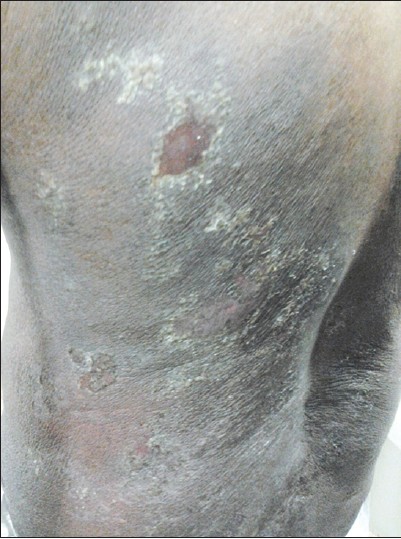 |
| Figure 2: Grade 2 radiation recall dermatitis |
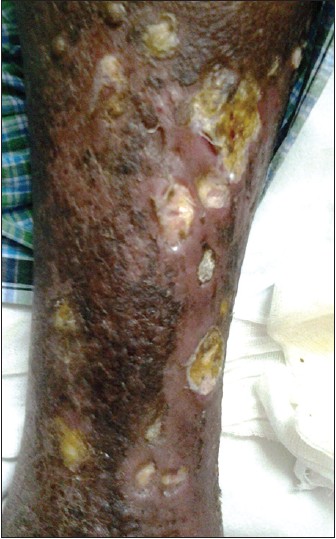 |
| Figure 3: Grade 4 radiation recall dermatitis |

First described in 1959 by D′Angio in connection with actinomycin D, [2],[3] radiation recall is commonly seen with chemotherapeutic drugs, UV radiation, and megavoltage radiation therapy. [3],[4],[5]
Vascular damage, epithelial stem cell inadequacy or sensitivity, and idiosyncratic drug hypersensitivity are the probable pathogenic factors. [2],[3],[5] The time interval between radiotherapy and radiation recall dermatitis ranges from 7 days to 15 years. If the interval is short, the reaction is severe. It is sometimes difficult to differentiate between radiosensitization (in which the use of a drug makes the tumor cells more sensitive to radiation) from radiation recall dermatitis. [2],[3],[5]
In our case, the patient was subjected to narrow band UVB therapy in the initial phase of chemotherapy. This could have been a triggering factor. With the administration of gemcitabine, a reaction was initiated which was rather mild (Grade 2). Although that drug was stopped, total skin electron beam therapy was started, which triggered a very severe radiation recall reaction (Grade 4) that could have been a factor in the patient′s death. Dermatologists must be aware of the existence of this phenomenon in their patients who are receiving non-ionizing radiation therapy and it is also important to be vigilant while giving phototherapy.
| 1. |
Hird AE, Wilson J, Symons S, Sinclair E, Davis M, Chow E. Radiation recall dermatitis: Case report and review of literature. Curr Oncol 2008;15:53-62.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Camidge R, Price A. Characterizing the phenomenon of radiation recall dermatitis. Radiother Oncol 2001;59:237-45.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Caloglu M, Caloglu VY, Alas RC, Saynak M, Karagol H, Uzal C. An ambiguous phenomenon of radiation and drugs: Recall reactions. Onkologie 2007;30:209-14.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Burris HA 3 rd , Hurtig J. Radiation recall with anticancer agents. Oncologist 2010;15:1227-37.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Azria D, Magné N, Zouhair A, Castadot P, Culine S, Ychou M, et al. Radiation recall: A well-recognized but neglected phenomenon. Cancer Treat Rev 2005;31:555-70.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
6,060
PDF downloads
2,557





