Translate this page into:
Risk factors associated with chronic cutaneous graft-versus-host disease: A retrospective study
Corresponding author: Dr. Guan Jiang, Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Quanshan, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China. dr.guanjiang@xzhmu.edu.cn
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Tang H, Guo S, Zhang Y, Xia J, Jiang G. Risk factors associated with chronic cutaneous graft-versus-host disease: A retrospective study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2025;91:108-10. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_842_2023
Dear Editor,
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (CGVHD) can affect many parts of the body, with cutaneous manifestations being the most common.1 The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical features of chronic cutaneous graft-versus-host disease (CCGVHD) following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and the risk factors for its development.
Clinical data were collected from 39 patients who developed CCGVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation at our hospital from January 2018 to October 2022. A control group of 39 patients with CGVHD without cutaneous manifestations who visited the clinic during the same period were also selected. Clinical data such as age, sex, donor–recipient relationship, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) compatibility, history of acute graft-versus-host disease (AGVHD), and time of onset of CCGVHD after transplantation were collected and statistically analysed. In the observation group, there are 19 males and 20 females, aged (32.28±14.93) years. The primary diseases included 16 cases of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), 9 cases of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), 1 case of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), 7 cases of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), 3 cases of aplastic anaemia (AA), 1 case of primary myelofibrosis (PMF), and 2 cases of lymphoma. The donor-recipient relationships were all within the second generation of blood relatives (father, mother, siblings). The donors and recipients were HLA-haploidentical in 28 cases and HLA- identical in 11 cases. There were 21 cases with a history of acute GVHD.
The onset of cutaneous cGVHD was 7.00 (4.00, 10.25) months after transplantation, 17 cases developed within six months after transplantation, 16 cases developed between 0.5 and 1 year, 5 cases developed between 1 and 2 years, and 1 case developed after 2 years. For medication before the onset of cGVHD, 16 cases had stopped all anti-rejection drugs before the onset of disease, 22 cases were applied glucocorticoids, all systematically (dose equivalent to prednisone, 20 mg/d ∼ 120 mg/d), 14 cases were using cyclosporine (50 mg/d ∼ 175 mg/d), 14 cases were using a combination of glucocorticosteroids and cyclosporine; 7 cases were additionally treated with ruxolitinib. Compared with the control group, the observation group had a higher HLA compatibility [(28/39, 71.8%) vs (13/39, 33.3%)] and a lower proportion of patients with no previous AGVHD [(17/39, 43.6%) vs (30/39, 76.9%)]. There were no significant differences between the two groups with regard to age, gender, type of primary disease, and donor–recipient sex ratio. In the observation group, there were 14 cases of lichenoid lesions, nine cases of eczematous lesions, and nine cases of sclerodermatous manifestations [Figures 1a-1d, 2a-2b, and 3a-3b]. None of them showed Raynaud’s phenomenon and the manifestations were predominantly located on the trunk, extremities, head, and neck. Logistic regression analysis indicated that neither previous AGVHD (p = 0.095, OR = 2.337, 95%CI 0.864-6.322) nor HLA compatibility (p = 0.102, OR = 0.453, 95%CI 0.176-1.170) was an independent risk factor for the development of CCGVHD. These results suggest that there is no significant association between HLA compatibility or history of AGVHD and the occurrence of CCGVHD in this study cohort.
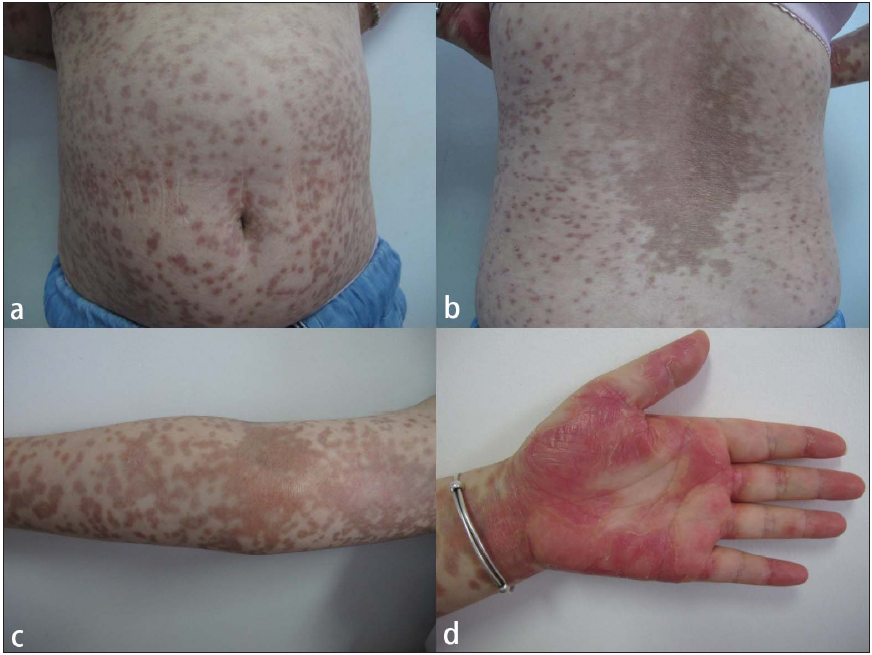
- (a, b) Lichenoid chronic cutaneous GVHD with multiple hyperpigmented scaly patches on the trunk, (c) Multiple hyperpigmented scaly patches on the upper limb, (d) Erythematous scaly plaques on palm.
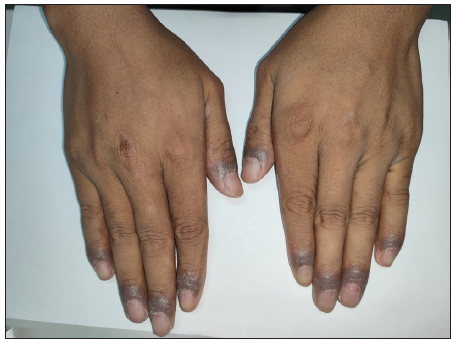
- Lichenoid chronic cutaneous lesions with dark brown patches around the nails of both hands.
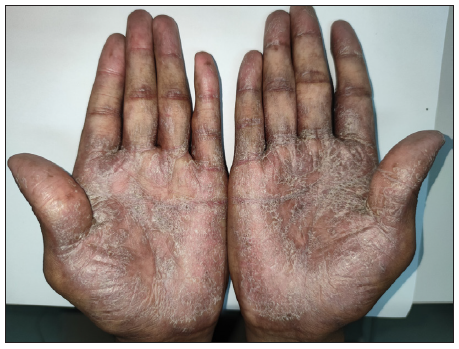
- Lichenoid chronic cutaneous lesions with diffuse hyperpigmented plaques and desquamation on both palms.
- Scleroderma-like chronic cutaneous lesions with multiple sclerotic plaques and pigmentation changes on the trunk.
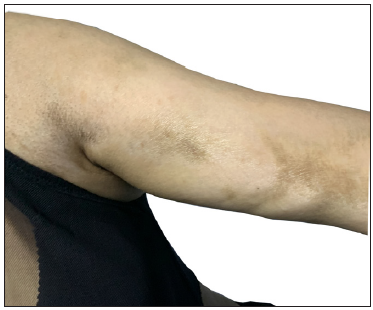
- Scleroderma-like chronic cutaneous lesions with multiple sclerotic plaques and pigmentation changes on the upper limb.
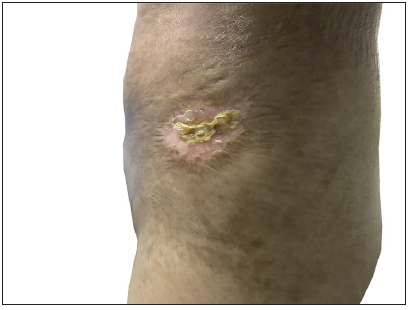
One patient with vasculitic CCGVHD underwent a histopathologic examination of the skin. Microscopic analysis revealed focal and mild hyperplasia of the epidermis, with small blood vessels in the superficial and middle layers of the dermis were infiltrated by a high number of lymphocytes and eosinophils [Figure 4].
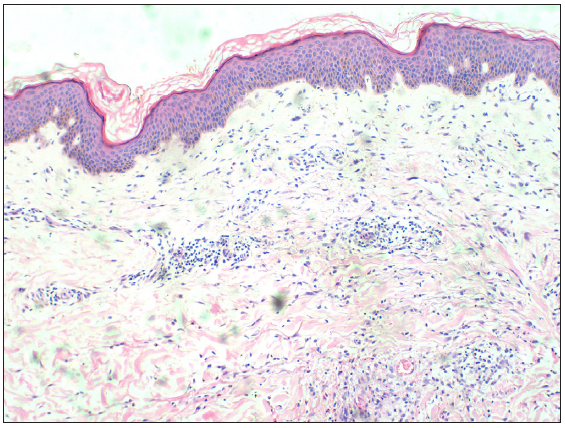
- Focal mild hyperplasia of the epidermis is observed, with a high infiltration of lymphocytes and eosinophils in the small blood vessels of the superficial dermis. (Haematoxylin and eosin, 100x).
In addition to the HLA matching and history of prior AGVHD, which were examined in this study, the literature reports several other risk factors for CGVHD, including donor–recipient age, gender, donor parity, graft source, intensity of conditioning regimen, etc.2-5 Arora et al. found through multivariate Cox regression analysis that AGVHD grade III–IV, peripheral blood stem cell transplantation and HLA mismatch were independent risk factors for CGVHD6. Loren et al. showed that female donors with a history of pregnancy increased the risk of CGVHD in all recipients7. Moreover, older age, intensive conditioning regimens, and the use of total body irradiation were also considered risk factors for CGVHD7.
Our study suggests that factors such as age and gender may not be significantly associated with the occurrence of CCGVHD, which contradicts some literature reports. We further performed a logistic regression analysis of factors such as HLA matching degree and history of prior AGVHD, and the results showed that neither of them was an independent risk factor for the development of CCGVHD. This finding differs from the study by Arora et al6.
The reasons for the above differences may include the following factors: first, this study is a retrospective analysis with a relatively small sample size and insufficient statistical power; second, this study lacks complete information, such as donor parity, and could not conduct a more comprehensive analysis of these factors; third, variations in the definition and diagnostic criteria of CGVHD across different studies may affect the comparability of risk factor analysis results.
This retrospective study examined the clinical features and risk factors of CCGVHD in 39 patients following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Our findings revealed that CCGVHD manifests with diverse clinical presentations, predominantly as lichenoid, eczematous, and sclerodermatous changes, with a median onset time of seven months post-transplantation. Although differences in HLA compatibility and history of AGVHD were observed between patients with and without CCGVHD, these factors did not reach statistical significance as independent risk factors. This study provides valuable insights into the clinical characteristics of CCGVHD, which may aid in early recognition and diagnosis. However, the limited sample size and retrospective nature of this study underscore the need for larger, prospective investigations to further elucidate the risk factors and pathogenesis of CCGVHD, ultimately guiding improved prevention and treatment strategies.
Ethical approval
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Xuzhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, with the ethical approval number XYFY-KL424-01 dated November 17, 2022.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:602-12.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronic GVHD risk score: A center for international blood and marrow transplant research analysis. Blood. 2011;117:6714-20.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Impact of donor and recipient sex and parity on outcomes of HLA-identical sibling allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12:758-69.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comparative analysis of risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease and for chronic graft-versus-host disease according to National Institutes of Health consensus criteria. Blood. 2011;117:3214-49.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Risk factors for acute GVHD and survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;119:296-307.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Chronic GVHD risk score: a Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research analysis. Blood.. 2011;117:6714-20.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Impact of donor and recipient sex and parity on outcomes of HLA-identical sibling allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.. 2006;12:758-69.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





