Disseminated cutaneous mycobacteria abscessus infection in a patient with chronic renal failure
Corresponding author: Dr. Guiying Zhang, No. 139 Renmin Middle Road, Changsha 410011, Hunan, China. zgylinda@csu.edu.cn
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Luo S, Wang H, Zhang G. Disseminated cutaneous mycobacteria abscessus infection in a patient with chronic renal failure. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2021;87:601.
Sir,
Mycobacterium abscessus, a type of non-tuberculous mycobacteria, is transmitted by inhalation, ingestion, or percutaneous penetration resulted in pulmonary, lymph node, or skin diseases. Disseminated cutaneous infection with M. abscessus is rare and easily misdiagnosed. Here, we described a mid-aged man with chronic renal failure presented with disseminated cutaneous nodules and abscesses.
A 53-year-old Chinese man presented to our hospital with a three-month history of disseminated cutaneous dark red nodules. These nodules were painless with a little itch. He suffered from chronic renal dysfunction and had been on hemodialysis for 9 years. Three months back, he underwent central venous catheterization in the right subclavian vein and then presented with a recurrent low-grade fever so far. He was a farmer without special contact history and family history of this disorder.
Physical examination revealed several reddish nodules, 2–4 cm in diameter, slightly elevated above the skin and scattered on trunk and limbs [Figure 1]. There were tenderness and firm on palpation. Lymph node examination was normal. Laboratory examination showed leukopenia (2.1×109/L) and elevated serum creatinine (735μmol/L). Serological examinations for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) were negative. Skin biopsy from the nodule revealed a large abscess in dermal companied by tissue necrosis, neutrophils, lymphocytes, scattered histiocytes and multinuclear giant cells [Figures 2a and b]. Acid-fast bacilli were identified in acid-fast staining [Figure 2c]. Samples at the biopsy site were collected for culture and pinpoint colonies grew after incubation at 37°C for 72 h on blood agar plate. They grew to white rough colonies and approximately 0.5 mm in diameter after seven-day incubation [Figure 2d]. They also grew well on MacConkey plate and catalase testing was positive. It was identified to be Mycobacterium abscessus using Hsp65 and rpoB gene sequence analysis. A diagnosis of disseminated cutaneous M. abscessus infection was made. Consequently, according to antibiotic susceptibility test results, this patient was under anti-mycobacterial treatment including rifampicin (450 mg/d), moxifloxacin (400 mg/d), clarithromycin (500 mg/d) and nadifloxacin cream (external use at skin ulcers). Blood routine examination, liver and renal function tests were monitored monthly. The lesions started resolving after eight weeks and involuted significantly after six months of treatment. This patient is still at follow-up.
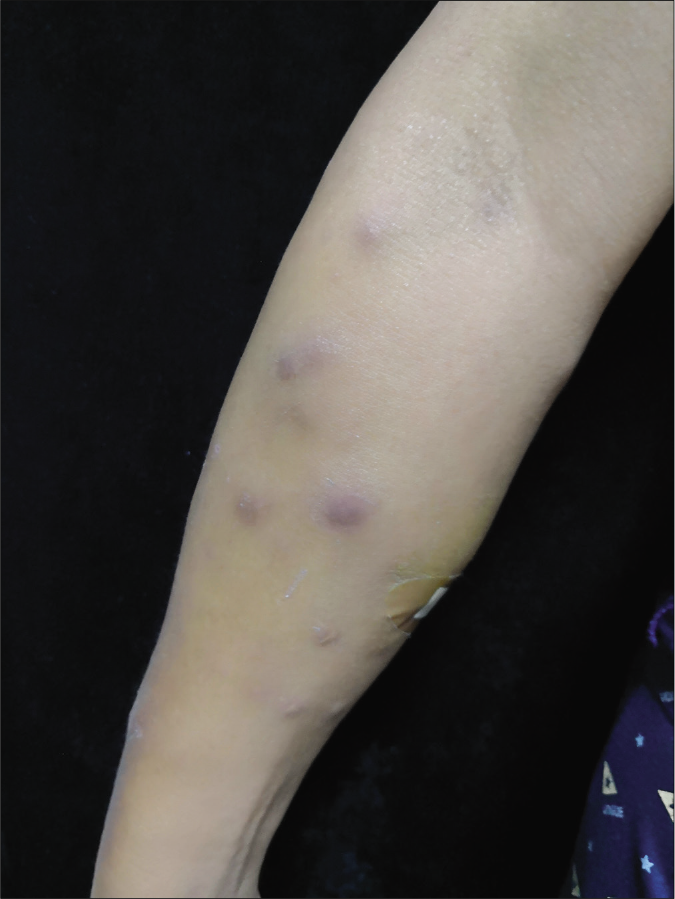
- Multiple dark red nodules on the right arm
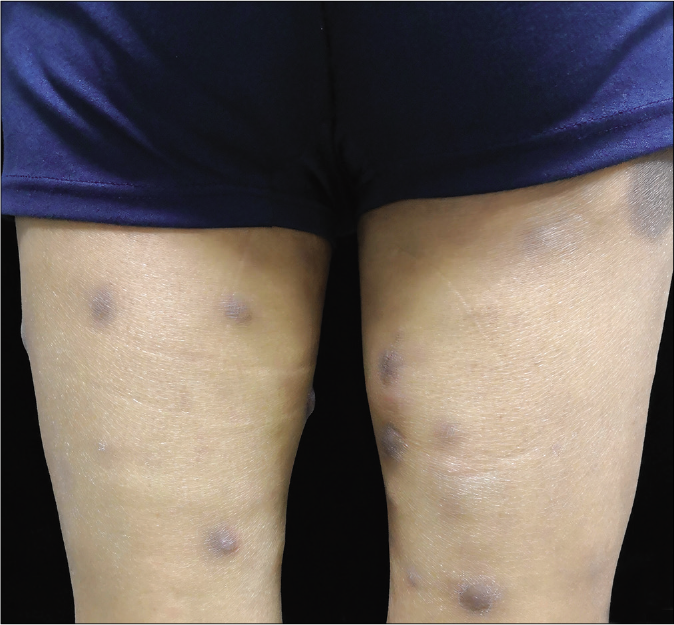
- Multiple dark red nodules on both legs
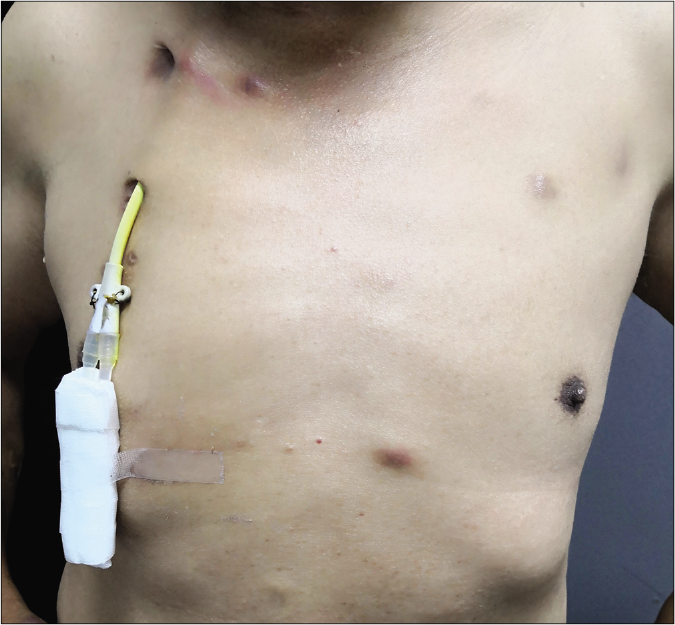
- Multiple dark red nodules on trunk and central venous catheterization can be seen in the right subclavian vein
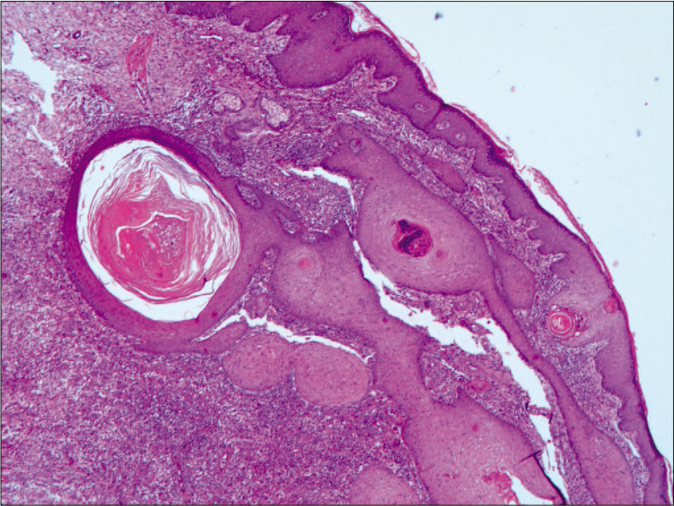
- Histopathological examination in low-power view revealed a large abscess companied by tissue necrosis and inflammatory cells (H and E, ×100)
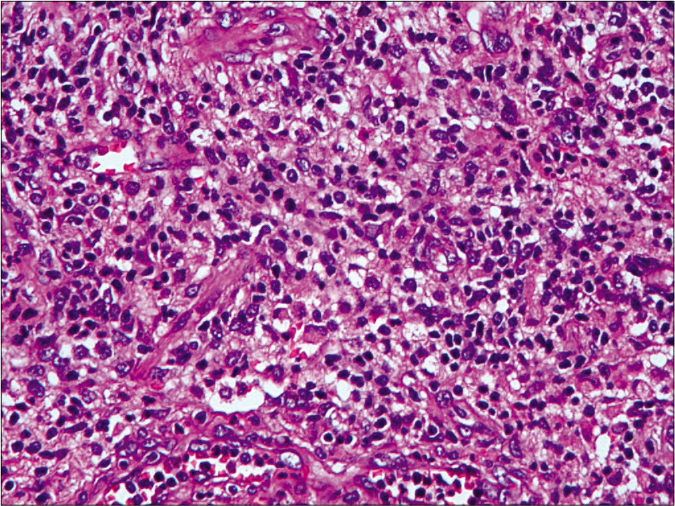
- Histopathological examination in high-power view revealed abundant neutrophils, lymphocytes, scattered histiocytes and multinuclear giant cells in lesion (H and E, ×400)
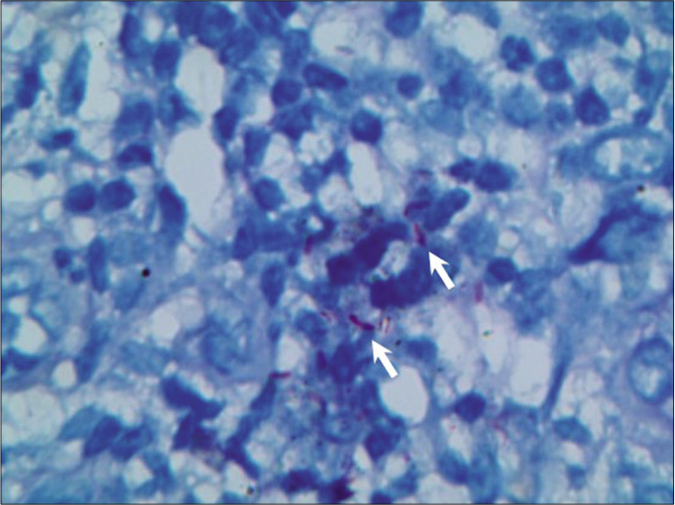
- Several reddish bacilli (arrow) were identified in tissue (acid-fast, ×400)
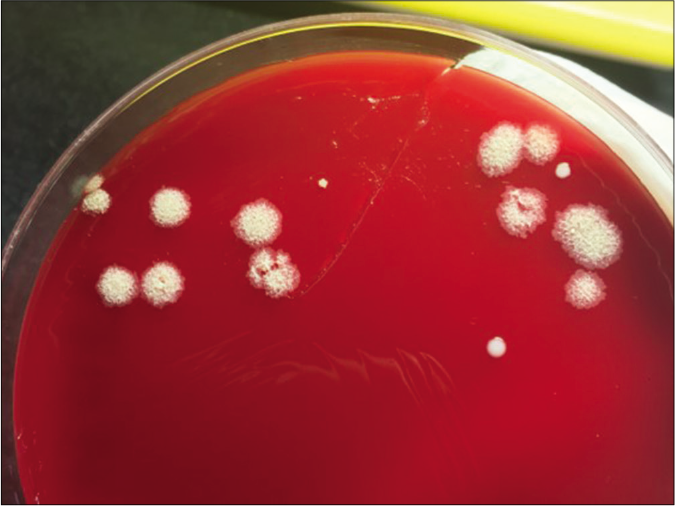
- Tissue culture showed white rough colonies on culture plate after 1 week
M. abscessus was reclassified as a separate species in year, 1992. It which can contaminate inadequately sterilized medical instruments, causing serious postsurgical skin and soft-tissue infections.1 Disseminated cutaneous M. abscessus infection is rare and particularly happens in immunocompromised or postoperative patients, usually presenting as multiple erythematous subcutaneous nodules on distal limbs or in a sporotrichoid pattern.2
M. abscessus infection is often concealed and chronic which is easily misdiagnosed. Clinical differential diagnosis includes cutaneous tuberculosis, bacterial infection and systemic vasculitis. Pathological examination and repeated culture of tissue are significance to make a define diagnosis. Colonies of M. abscessus have two morphology types that rough type has more virulence and is easier to cause persistent infection than smooth type.1 PCR detection of the 16S–23S rRNA gene internal transcribed spacer sequences can be performed to differentiate from other mycobacteria infection. Because M. abscessus appears to be the most resistant species to conventional anti-tuberculous drugs, drug sensitivity tests in vitro are important to select rational treatments.1 Macrolide antibiotics such as clarithromycin or azithromycin are recommended oral drugs for long-term treatment. Excision and debridement may be required for abscesses and ulcers. Review of literatures on M. abscessus infection with cutaneous manifestations is shown in Table 1.3-8
| Gender and age | Duration of symptoms | Clinical presentations | Treatments | Responds to treatments | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, 32 years old | 6 weeks | A tender lump on the face | IV tigecycline and amikacin | Complete resolution of the lesions after 2 months | Grubbs and Bowen, 20193 |
| Male, 75 years old | 2 months | Pruritic diffuse various sized erythematous papuloplaques and pustules on the neck and chest | Clarithromycin, ethambutol | Complete resolution of the lesions after 6 months | Choi et al., 20184 |
| Female, 42 years old | 9 months | A papule-nodular, floating injury with an erythematous surface, a little infiltrative capacity and imprecise limits on the tattoo site | Clarithromycin | Skin lesion improved after 5 months | Sousa et al., 20155 |
| Female, 55 years old | 6 months | A rash with pink-to-red papules and nodules coalescing into plaques in a linear distribution along her incision and involving her autologous skin grafts | Cefoxitin, clarithromycin, moxifloxacin | Skin lesion improved after 6 months | Summers et al., 20186 |
| Female, 61 years old | 2 years | A tender, 2 cm × 2 cm, fluctuant nodule over her left thigh, consistent with the clinical impression of a localized abscess | Amikacin, cefoxitin, clarithromycin | Skin lesion improved after 3 weeks | Shim et al., 20187 |
| Female, 23 years old | 3 months | A 4 cm wide ulcer with small central pustules and raised border on the anterolateral aspect of the right thigh | Clarithromycin, levofloxacin, amikacin | Complete resolution of the lesions after 6 months | Costa-Silva et al., 20188 |
IV: Intravenous
In summary, we reported a rare case of disseminated cutaneous M. abscessus infection presented with multiple nodules and abscesses in a patient with chronic renal failure. Since hemodialysis and central venous catheterization are necessary to these patients, it is important to be aware of immunocompromised state and the risk of disseminated infection caused by rare opportunistic pathogens.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703133) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (No. 2019JJ40448).
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Non-tuberculous mycobacteria and the rise of Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020;18:392-407.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infections from tattooing. Outbreak of mycobacterium chelonae in France. BMJ. 2010;341:c5483.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterium abscessus infection following home dermabrasion. Cutis. 2019;104:79-80.
- [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection after tattooing-Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:741-3.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterium abscessus subspecies massiliense infection after skin graft and cholecystectomy in a burn patient. Int J Infect Dis. 2018;76:29-31.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterium abscessus infection during ustekinumab treatment in crohn's disease: A case report and review of the literature. J Crohns Colitis. 2018;12:1505-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-60.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





