Translate this page into:
Classic form of nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis of vulva
2 Department of Pathology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India
Correspondence Address:
Rashmi Kumari
Department of Dermatology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry - 605 006
India
| How to cite this article: Singh N, Kumari R, Thappa DM, Kar R, Kulandaisamy S. Classic form of nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis of vulva. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2014;80:473-475 |
Sir,
Nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis is a rare idiopathic hamartoma of adipocytes. We report a classic form of nevus lipomatosis which occurred on the vulva, an unusual site for this lesion. Nevus lipomatosis involving the genitalia can cause psychological trauma to the child as well as parents and hence requires treatment and counseling.
A 10-year-old girl was brought to us by her anxious parents for a polypoidal growth over the right vulva. It began as an asymptomatic, soft, hypopigmented swelling since birth which was gradually increasing in size for two years. Physical examination revealed a non-tender, well defined, yellow-colored, soft plaque measuring 15 × 9 cm over the right labium majorum, mons pubis, inguinal fold and upper medial thigh. There was a soft pedunculated polyp measuring 1.5 × 1 cm over the right labium majorum [Figure - 1]. The polyp was excised and the surrounding plaque was subjected to a skin biopsy [Figure - 2]. Histopathological examination revealed orthokeratosis, follicular plugging and acanthosis with lobules of mature adipose tissue separated by bundles of collagen in the reticular dermis [Figure - 2]. These findings were consistent with the clinical diagnosis of nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis. The girl was referred to a plastic surgeon for staged excision.
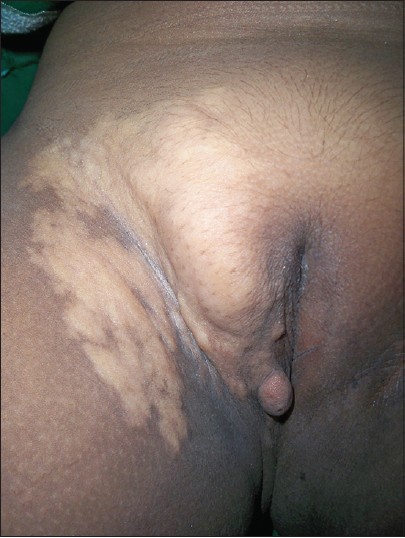 |
| Figure 1: Well-defined yellow colored soft plaque over the right labium majorum and mons pubis extending onto the inguinal fold and upper medial thigh, with a soft pedunculated polyp over the right labium majorum` |
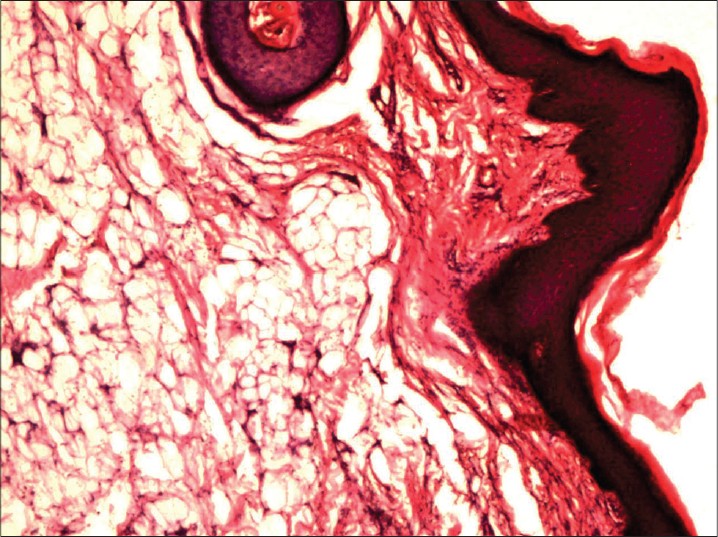 |
| Figure 2: Lobules of mature adipose tissue separated by bundles of collagen in the reticular dermis (H and E, ×40) |
Nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis is a hamartoma of adipocytes, first reported by Hoffmann and Zurhelle [1] in 1921. It is histologically characterized by the presence of mature adipocytes in the dermis that lack any connection with the subcutaneous fat. [2] The pathogenesis of nevus lipomatosis is unknown and several theories including adipose metaplasia, heterotopias of adipocytes, and adipocytes originating from dermal vessel walls have been proposed. [3]
There is no gender predilection and the condition is not heritable. It consists of two clinical subtypes, the classic multiple and the solitary form. [2],[3] The classic form usually appears at birth or within the first two decades of life and presents as multiple, usually unilateral lesions. It may be present in a band-like, linear or zosteriform pattern. It has a predilection for the pelvic girdle area i.e.,buttocks and upper part of posterior thigh but can also occur on the chest, abdomen and face. It presents as multiple dome-shaped papules that are sessile or pedunculated. These usually appear simultaneously and are stable though a few papules may increase in size. The surface of nevus lipomatosis is usually smooth, as was observed in our case. But in rare cases, the surface can be wrinkled, cerebriform or have a peau d′ orange texture. The rare solitary form appears as a plaque or linear lesion in the third to sixth decade of life and has no predilection for any specific site. [3]
Our case is a classic form of nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis of vulva that appears not to have been previously reported though there are reports of the solitary form of nevus lipomatosis involving the labium majorum [4] and clitoris. [5] The differential diagnosis includes lipoblastoma and congenital lipoma. [4] Lipoblastoma, a rare benign mesenchymal tumor of infancy arising from fetal adipose tissue shows lobules of immature adipocytes in a myxoid matrix. Congenital lipoma shows mature adipocytes in subcutaneous tissue unlike nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis, where mature adipocytes are seen in the dermis without having any connection to the subcutaneous fat. [4]
Nevus lipomatosis cutaneous superficialis usually does not require any treatment but surgical excision or intralesional phosphatidylcholine can be tried if it involves the genitalia and causes psychological trauma to the patient. [6] Intralesional sodium deoxycholate (24 mg/ml) followed by intralesional phosphatidylcholine (50 mg/ml) has been reported to cause clinical and histological resolution but post-injection erythema, postinflammatory pigmentation and scarring have been observed. [7] The detergent action of sodium deoxycholate causes fat cell destruction and the released fatty acids are emulsified by phosphatidylcholine. [8],[9] The optimal concentration and the injection depth of these drugs is not yet established.
| 1. |
Hoffmann E, Zurhelle, E. Über einen Naevus lipomatodes cutaneous superficialis der linken Glutaalgegend. Arch Dermatol Syphilol 1921;130:327-33.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Jones EW, Marks R, Pongsehirun D. Naevus superficialis lipomatosus: A clinicopathological report of twenty cases. Br J Dermatol 1975;93:121-33.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Dotz W, Prioleau PG. Nevus lipomatosus cutaneous superficialis. A light and electron microscopic study. Arch Dermatol 1984;120:376-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Nakashima K, Yoshida Y, Yamamoto O. Nevus lipomatosus cutaneous superficialis of the vulva. Eur J Dermatol 2010;20:859-60.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Hattori R, Kubo T, Yano K, Tanemura A, Yamaguchi Y, Itami S, et al. Nevus lipomatosus cutaneous superficialis of the clitoris. Dermatol Surg 2003;29:1071-2.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 6. |
de Paula Mesquita T, de Almeida HL Jr, de Paula Mesquita MC. Histologic resolution of naevus lipomatosus superficialis with intralesional phosphatidylcholine. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009;23:714-5.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 7. |
Kim HS, Park YM, Kim HO, Lee JY. Intralesional phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate: A possible treatment option for nevus lipomatosus superficialis. Pediatr Dermatol 2012;29:119-21.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 8. |
Rotunda AM, Suzuki H, Moy RL, Kolodney MS. Detergent effects of sodium deoxycholate are a major feature of an injectable phosphatidylcholine formulation used for localized fat dissolution. Dermatol Surg 2004;30:1001-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 9. |
Salti G, Ghersetich I, Tantussi F, Bovani B, Lotti T. Phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate in the treatment of localized fat: A double-blind, randomized study. Dermatol Surg 2008;34:60-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
2,967
PDF downloads
1,778





