Translate this page into:
Comedones in dermatology
Corresponding author: Dr. Vishal Gaurav, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India. mevishalgaurav@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Najeeb A, Gaurav V, Sharma R. Comedones in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:396-407. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_896_2023
The term ‘comedo’ (pl. comedones) is derived from the Latin word comedere which means ‘to eat up’. This term was initially used for parasitic worms that ‘eat up’ the body. Later, the term was used to suggest the worm-like appearance of expressed materials from certain lesions [Figure 1a]. A comedo is a plug of keratin and sebum in a dilated pilosebaceous canal. Classically, comedones are associated with acne and acne-related disorders.1 However, comedones can be seen in many dermatological conditions that are unrelated to acne.
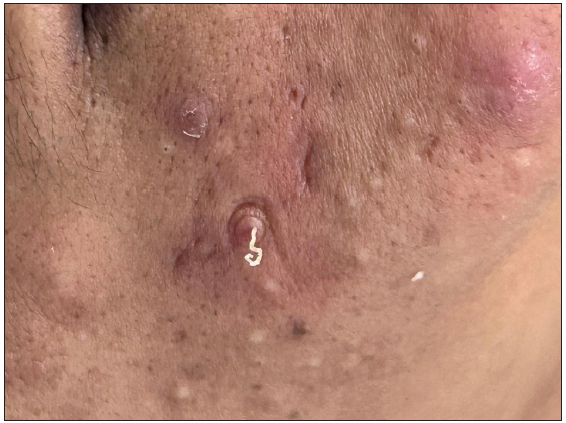
- Worm-like appearance of expressed material from a comedone.
Based on the pathomechanisms of comedo formation, comedones can be primary and secondary:
-
a.
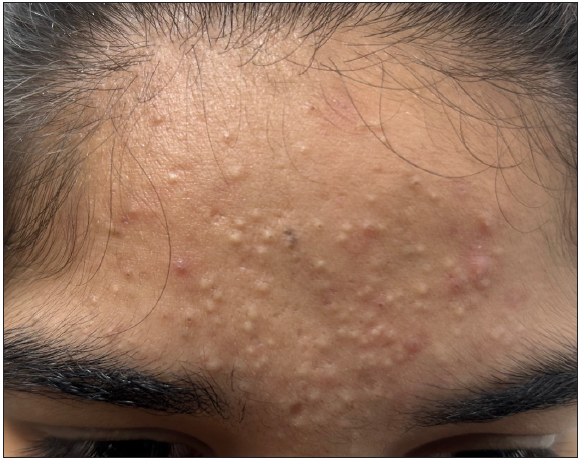
Primary comedones: These are commonly observed in acne vulgaris, where the pilosebaceous ducts become enlarged and filled with keratin due to increased keratinocyte proliferation, corneocyte adhesion, and hyperseborrhea [Figures 1b and 1c]. Histologically, pilosebaceous ducts, even though dilated and keratin-filled, are well preserved.1
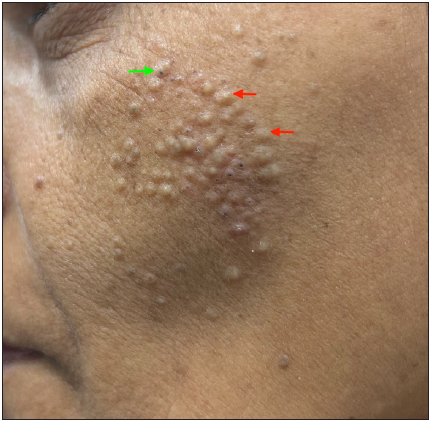 Figure 1b:
Figure 1b:- Primary comedones presenting as multiple closed comedones (red arrows) and a few open comedones (green arrow) over the left cheek of a young woman.
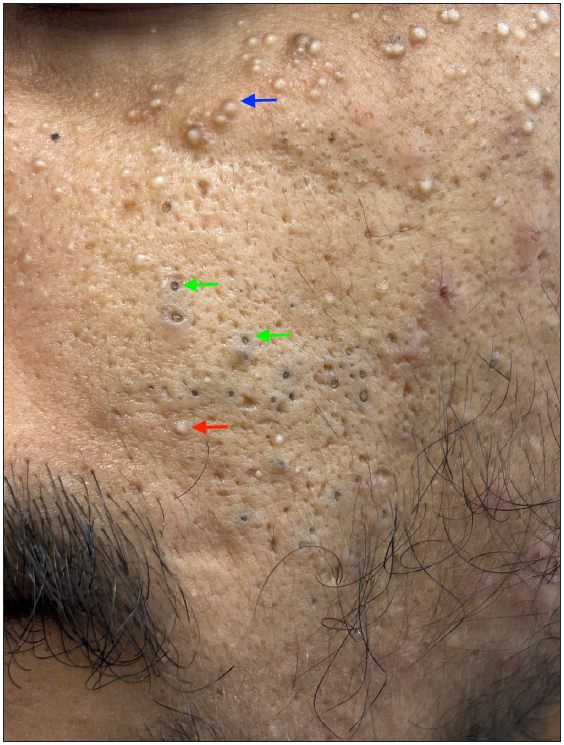 Figure 1c:
Figure 1c:- Multiple open comedones (green arrows), a few closed comedones (red arrow) along with milia (blue arrow) over the left cheek of a young man.
-
b.
Secondary comedones: There are two schools of thought regarding the origin of secondary comedones. The first school of thought considers secondary comedones to be sequelae of a chronic inflammatory process. In contrast to primary comedones, where the comedones become the precursor lesions for future inflammatory lesions like papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts, secondary comedones are remainders of severe inflammation that have resulted in severe scarring, as in the case of acne conglobata and hidradenitis suppurativa [Figure 1d]. In these conditions, there is rupture of hair follicles which results in intense inflammation leading to abscess and cyst formation. In an attempt to control this inflammation, the body tries to encapsulate it, forming a system of interconnected keratin-filled tracts with open comedones on the surface.2 As this encapsulation can be haphazard, these comedones are usually variable-sized and unevenly spaced, in contrast to primary comedones which are folliculocentric and hence more evenly sized and spaced. In secondary comedones, pathological involvement of hair follicles is usually present.
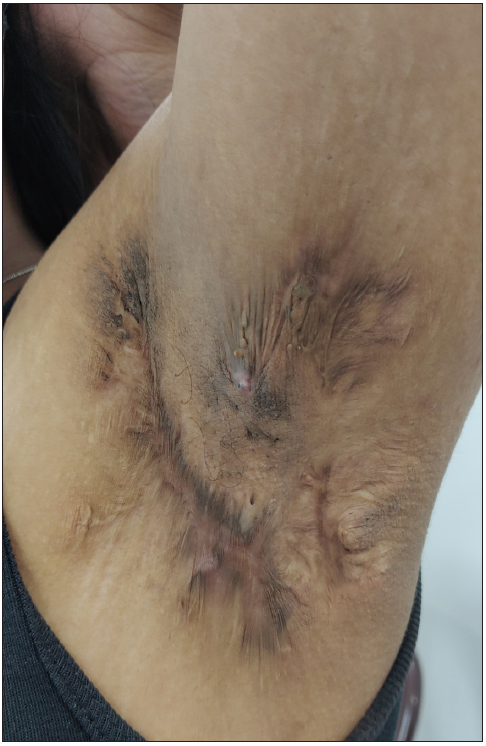 Figure 1d:
Figure 1d:- Secondary comedones of hidradenitis suppurativa on the left axilla in a young woman.
The second school of thought proposes that secondary comedones develop secondary to occlusion of the pilosebaceous duct by external agents like pomade, petroleum oil, pitch, tar, halogenated compounds, or following procedures like waxing, in contrast to primary comedones which occur due to occlusion by endogenous agents.3
For this article, we have grouped the various acne-associated cutaneous disorders into disorders classically presenting with comedones or comedo-like lesions, disorders occasionally associated with comedones or comedo-like lesions, disorders featuring comedones or comedo-like lesions on dermoscopy and disorders showing comedo necrosis on histology.
-
A.
Skin disorders classically presenting with comedones or comedo-like lesions
-
1.
Acne vulgaris
Comedones are the earliest lesions in common acne or acne vulgaris and are formed due to the accumulation of shed keratin and sebum in the pilosebaceous duct, secondary to hyperkeratosis and increased sebum production, respectively. Comedones are considered special primary lesions.1 The different morphological types of comedones seen in acne vulgaris are:
Closed comedones: These are commonly called whiteheads and are present as small (1–5 mm) skin-coloured papules without any visible follicular opening [Figure 1b]. Histology of a closed comedone shows a cyst-like cavity filled with a compact mass of keratinous material and numerous bacteria along with 1–2 trapped hairs without a patent follicular canal. The surrounding sebaceous glands are atrophic [Figure 2a].
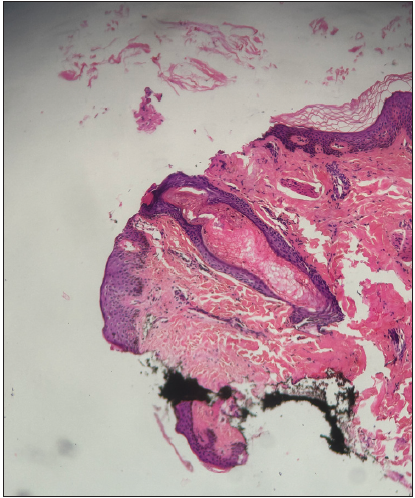 Figure 2a:
Figure 2a:- Histology of a closed comedone showing a dilated follicular canal filled with a compact mass of keratinous material (Haematoxysin and Eosin; 100x).
Open comedones: These are commonly called blackheads and present as monomorphic papules with conspicuous black dots in the centre, corresponding to dilated follicular openings containing keratin and sebum [Figure 1c]. On histology, there is massive follicular dilation which opens to the epidermis.4 The cavity is filled with keratinous and cellular debris and the sebaceous glands are either atrophic or absent [Figure 2b].
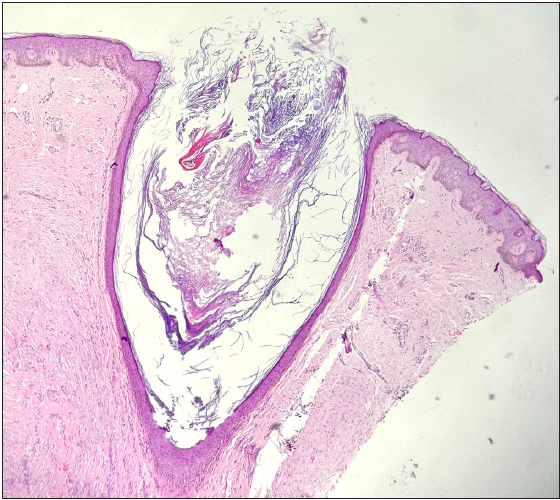 Figure 2b:
Figure 2b:- Histology of an open comedone showing massive follicular dilation that opens to the epidermis. The cavity is filled with keratinous and cellular debris (Haematoxysin and Eosin; 100x).
Other morphological variants of comedones seen in acne are as follows:
-
a.
-
b.
Microcomedones: Hyperkeratosis and increased corneocyte cohesiveness in the upper sebaceous follicle leads to microcomedo formation. These are usually difficult to visualise through the naked eye.1
-
c.
Macrocomedones: Closed comedones >1mm in size are deemed as macrocomedones that respond poorly to both topical and oral retinoids. It may cause a severe flare of disease activity following the initiation of oral retinoids.1
-
d.
-
e.
Secondary comedones: These occur secondary to pomade, petroleum oil, or chemical exposure.3
-
f.
Polyporous comedones: These are also called grouped comedones and have more than one opening on the skin while being interconnected beneath the surface of the skin [Figure 3b]. It is usually seen in severe forms of acne-like acne conglobata, familial dyskeratotic comedones, and other inflammatory disorders like hidradenitis suppurativa [Figure 3c]. They may progress to large nodules, cysts, and abscesses which are often resistant to medical treatment and heal with significant scarring.4,5
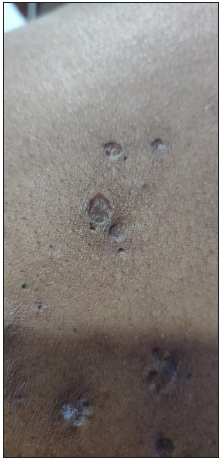 Figure 3b:
Figure 3b:- Polyporous comedones over the back in a 17-year-old boy with familial dyskeratotic comedones.
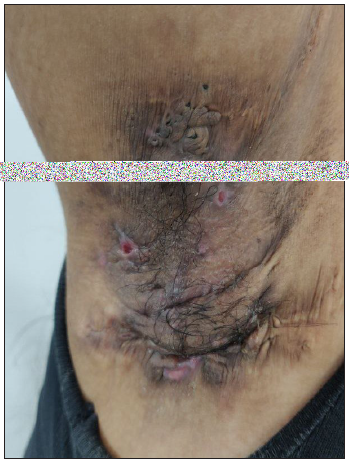 Figure 3c:
Figure 3c:- Polyporous comedones over the right axilla in a young woman with hidradenitis suppurativa.
-
-
2.
Acne venenata
Acne venenata or contact acne occurs due to several products which come in contact with the skin. It is also called acne artificialis.
-
a.
Acne cosmetica: It occurs due to the use of cosmetics containing potentially comedogenic substances like lanolin, petrolatum, lauryl alcohol, and oleic acid. It commonly presents with closed comedones and can exacerbate pre-existing acne.1
-
b.
Pomade acne: It presents as open and closed comedones on the face secondary to the use of ‘pomade’, a greasy substance used for defrizzing curly hair.6
-
c.
Coal tar acne: Oil, tar, and pitch are comedogenic and hence produce acne in workers employed in tarring roads and roofs, especially over the periorbital area, malar area, and sometimes on the extensor aspect of thighs.3
-
d.
Cutting oil/petroleum oil acne: It presents as dirty-looking grey-black open or closed comedones involving the face, forearms, thighs, or other areas where the oil comes in contact with the skin.7
-
e.
Lip balm acne: This occurs secondary to the repeated use of Vaseline to hydrate the lips, resulting in the development of open comedones in a single row, along the cutaneous margin of the upper lip.8
-
f.
Detergent acne: Alkaline soaps and trauma secondary to frequent rough washing of the face can exacerbate pre-existing acne with predominant inflammatory lesions.1
-
-
3.
Hidradenitis suppurativa
It is characterised by the presence of polyporous comedones, nodules, interconnecting abscesses, and sinus tracts which heal with scarring. The pathogenesis seems to be multifactorial. Keratinous occlusion of the hair follicle followed by swelling and rupture of follicles incites severe inflammation to its contents and aberrant immune response to skin commensals in genetically predisposed individuals. Association with nodulocystic acne or acne conglobata is well known. Comedones are the harbinger of the disease.2 Comedones in hidradenitis suppurativa are secondary comedones and they have been qualified by several names:
-
a.
Polyporous comedones: As described above, these are comedones that have multiple keratin-filled openings on the skin surface while being interconnected beneath the skin [Figure 3c].
-
b.
Tombstone comedones: These refer to comedones present in the area of scarring following inflammation. The prefix ‘tombstones’ signifies that these comedones stand as markers of severe inflammation that led to their formation [Figures 1d and 3c].
-
c.
Double-ended pseudocomedones: They are defined as ‘keratin-filled interconnected multipores’.9 They result from keratinization of the residual stump of two adjacent follicles undergoing cicatricial rearrangements without any evidence of hair follicles that have been destroyed by the preceding severe inflammation.
Other disorders classically presenting with comedones or comedo-like lesions are summarised in Table 1.10–47
Table 1: Skin disorders classically presenting with comedones or comedo-like lesionsDisease entity Remarks Nevus comedonicus/comedo naevus Senile comedones/Favre-Racouchot syndrome/solar comedones/nodular actinic elastosis -
Chronic sun damage in the elderly population causes solar elastosis, resulting in loss of connective tissue support to the pilosebaceous ducts which get dilated and distended with impacted corneocytes resulting in open comedones.
-
Common sites: bilateral periorbital, malar, and temporal areas [Figure 5a].1,11
Actinic comedonal plaque Childhood flexural comedones -
Single or multiple double-headed comedones.
-
Common sites: axilla and groin.
-
Hypothesised to be related to early hidradenitis suppurativa or secondary to friction at these sites.12
Dowling–Degos disease (DDD) -
Classical triad: Reticulate hyperpigmentation of flexures, comedo-like follicular keratotic papules over the back, neck, axilla, and pitted perioral scars.
-
The comedo formation occurs due to a defect in the genes involved in keratinocyte differentiation.
-
The follicular variant of DDD presents with punctate folliculocentric pigmented macules, pits, and comedo-like lesions with the absence of characteristic non-follicular flexural hyperpigmentation [Figures 6a and 6b].13
-
Galli-Galli disease, an acantholytic variant of DDD, and reticulate acro-pigmentation of Kitamura can also present with comedo-like lesions.14
Familial dyskeratotic comedones (FDC)/nevoid follicular epidermolytic hyperkeratosis Familial disseminated comedones without dyskeratosis -
Clinical presentation is similar to FDC without dyskeratosis on histology.16
Comedo-like acantholytic dyskeratosis Congenital disseminated comedones -
Congenital variant of FDC.19
Congenital comedones Lichen planus follicularis tumidus -
It is a rare variant of lichen planus which presents in the retro auricular region as tumid violaceous plaque studded with milia-like cysts and comedones.
-
This corresponds to dilated follicular infundibula filled with keratin and surrounded by lichenoid interface dermatitis on histology.22
Dilated pore of Winer Trichostasis spinulosa -
Presents as raised follicular spicules or open comedones over the nose or elsewhere [Figures 9a and 9b].
-
Occurs due to the retention of multiple hair shafts secondary to infundibular keratosis.24
-
On histology, multiple vellus or telogen club hair shafts mixed with keratin can be seen in a dilated hair follicle.
Perianal comedones -
Presents as perianal papules with plugged follicular orifices.
-
May be associated with chronic local pruritus and diarrhoea.
-
Underreported entity due to its asymptomatic nature and occurrence at the covered site.25
-
Small epidermal cysts with complete atrophy of sebaceous glands are seen on histological examination.
Nevus corniculatus -
Rare nevus, presenting as filiform hyperkeratosis with horn-like processes resembling giant comedones and linear hyperkeratotic plaques.
-
On histology, it showed suprabasal and intraepidermal splitting with a dilapidated brick wall appearance.26
Penile acne Radiation-induced comedones Laser therapy–induced comedones Mechanical trauma-induced comedones -
Occurring after repeated mechanical trauma due to tight clothing like bra straps and belts, pressure due to rubbing of the back in truck drivers, and over the neck in violin players.
-
Secondary to follicular hyperkeratosis, microbiome alteration, and aberrant immune response to chronic mechanical injury.33,34
Comedonal Darier’s disease -
Rare variant of Darier’s disease
-
Presenting as multiple open and closed comedo-like lesions over the face, trunk, and scalp.
-
With other overt or subtle signs of classical Darier’s disease
-
On histology, dilated follicular openings with acantholytic dyskeratosis of the follicular epithelium.35
Lupus comedonicus/comedonal discoid lupus erythematosus -
Rare variant of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
-
Presenting as infiltrated plaques with comedones over sun-exposed areas and resolving with acneiform scars.
-
Other classic lesions of discoid lupus erythematosus could be present.
-
Occurs secondary to follicular hyperkeratosis and perifollicular inflammation.
-
On histology, vacuolar interface dermatitis with lymphohistiocytic periadnexal infiltrates are seen.36
Warty Dyskeratoma -
Rare benign tumour of the pilosebaceous unit.
-
Presents over the head and neck region in middle-aged men as slowly growing, umbilicated papule or nodule with central keratotic plugging and rolled out hyperpigmented borders.
-
On histology, a cup-shaped keratin-filled invagination, an acanthotic epidermis with acantholytic dyskeratotic cells, and a suprabasal cleft with villous projections can be seen.37
Pilar Sheath Acanthoma -
It is presented in middle-aged men as a slow-growing papule or nodule with a keratin-plugged central punctum over the upper lips mimicking a dilated pore of Winer.
-
Histopathology shows a cystic cavity filled with keratin and lined by stratified squamous epithelium.38
Keratoacanthoma Porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus (PEODDN) -
Rare nevoid disorder of keratinization involving the intraepidermal eccrine duct.
-
Presenting in children as multiple keratin-studded papules and comedo-like pits over palms and soles.
-
Multiple cornoid lamella-like parakeratotic columns, hyperplastic eccrine ostia, and distal sweat ducts are seen on histology.40,41
Punctate porokeratosis/ punctate palmoplantar porokeratosis -
Multiple keratotic papules with central keratinous plugs, resembling comedones, over palms and soles.42
Punctate palmoplantar keratoderma Epidermoid cyst -
It is also known as infundibular cyst, epidermal cyst, epidermal inclusion cyst, and epidermoid inclusion cyst.
-
A common entity that presents as a non-fluctuant, compressible mass of size varying from centimetres to millimetres with central, dark comedonal opening (punctum) [Figure 13].
-
Histologically, the cyst is lined by an epithelium resembling the epidermis and includes a granular layer and keratin lamellae in the lumen.44
Chloracne -
It presents with comedones, papules, pustules, and cysts, often resolving with scars with a gradual decline in the sebum production leading to xerosis. The cyst content is usually straw-coloured. Seen usually in middle-aged adults who are not acne-prone.1
-
A history of exposure to polyhalogenated organic compounds, also known as chloracnegens, is a must for the diagnosis. Dioxin is the most common and potent chloracnegen known.
-
Histopathologically, they show characteristic epidermal and follicular hyperplasia with involuted sebaceous glands.45
DDD: Dowling-Degos disease, FDC: Familial dyskeratotic comedones, PEODDN: Porokeratotic eccrine ostial dermal duct nevus.
Table 2: Skin disorders occasionally associated with comedones or comedo-like lesionsClinical entity Remarks Pseudoxanthoma elasticum Granuloma annulare Follicular mycosis fungoides Generalised follicular basaloid hamartoma syndrome -
Presents as milia-like cysts and comedo-like lesions at birth or early childhood over the head, upper trunk, and arms.
-
Benign, superficial, folliculocentric, basaloid proliferations are seen on histology.51
Neurofibroma Atrophoderma vermiculatum -
Presents in childhood as follicular keratotic papules and comedo-like lesions over the cheeks, preauricular area, and forehead which slowly progresses over time to honey-comb or reticular atrophy.54
Lichen planopilaris -
Presents as scarring alopecia over the scalp with comedo-like lesions [Figure 15a].55
-
Diffuse involvement of the trunk and extremities in the form of comedo-like lesions has been reported.56
Palmoplantar lichen planus -
Unlike other variants of lichen planus, palmoplantar lichen planus present as hyperpigmented and keratotic papules with a central plug/crater. [Figure 15b].
-
The internal arch of the foot and thenar and hypothenar eminences are common sites of involvement while fingertips are usually not involved.57,58
-
Histopathology showing lichenoid tissue reaction pattern and concomitant presence of classical lesions of lichen planus on the rest of the skin and/or mucosa may help in diagnosis.
Herpes zoster Folliculocystic and collagen hamartomas -
These are uncommon features of the tuberous sclerosis complex.
-
It presents as a plaque studded with comedo-like openings and multiple cysts.
-
Thick collagen deposition along with hair follicles and infundibular cysts are seen on histology.61
Systemic amyloidosis -
Comedo-like lesions and milia have been reported secondary to erosive or bullous forms.
-
Due to the deposition of amyloid in the hair follicles, leading to occlusion.62
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (NLD) -
Rarely, transepithelial elimination of altered collagen through the hair follicles may result in comedo‐like plugs at the periphery of lesions of NLD.63
NLD: Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum
Table 3: Skin disorders featuring comedo-like lesions on dermoscopyDisorder Dermoscopic features Lichen planus hypertrophicus Comedo-like lesions, peripheral striations, yellowish structures, blue-grey globules.64 Seborrheic keratosis Comedo-like lesions, fissures and ridges, network-like structures, milia-like cysts, moth-eaten borders [Figure 16a].65 SK-like melanoma Comedo-like lesions, milia-like cysts, yellowish keratin, scaly hyperkeratotic surface.66 Lichen sclerosus Yellow–white follicular plugs, comedo-like lesions, structureless brownish areas, linear and dotted vessels [Figure 16b].67 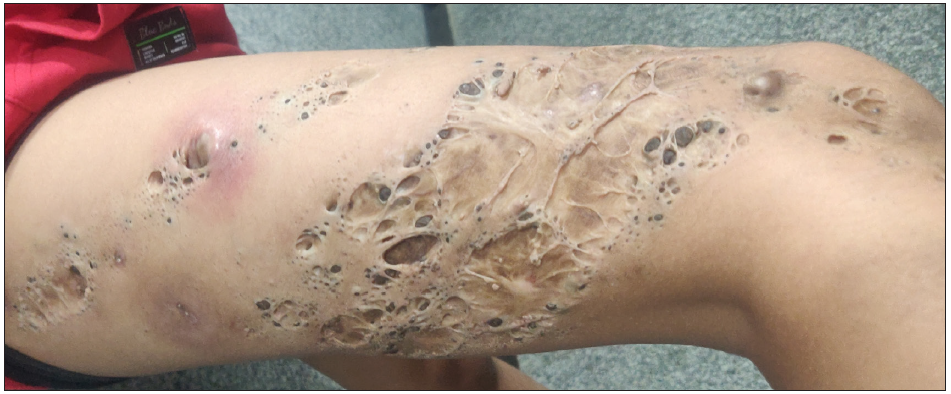 Figure 4:
Figure 4:- Naevus comedonicus over the right thigh in an 18-year-old boy showing giant comedones.
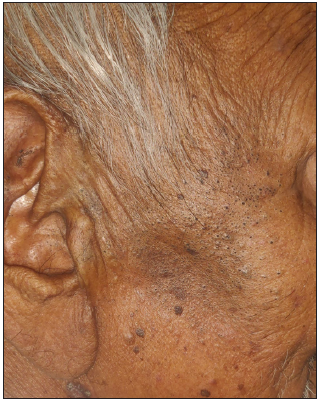 Figure 5a:
Figure 5a:- Senile comedones over the right side of the face in a 72-year-old man.
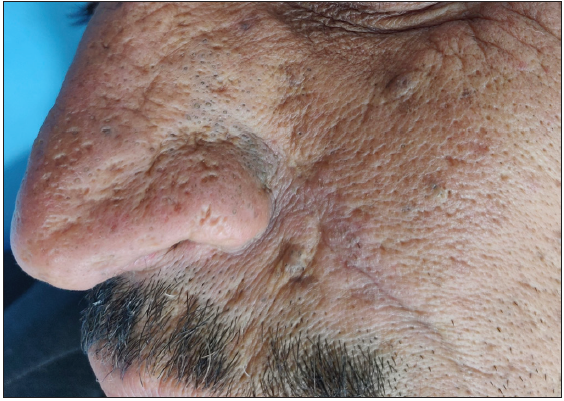 Figure 5b:
Figure 5b:- Actinic comedonal plaques over the nose in a 70-year-old man.
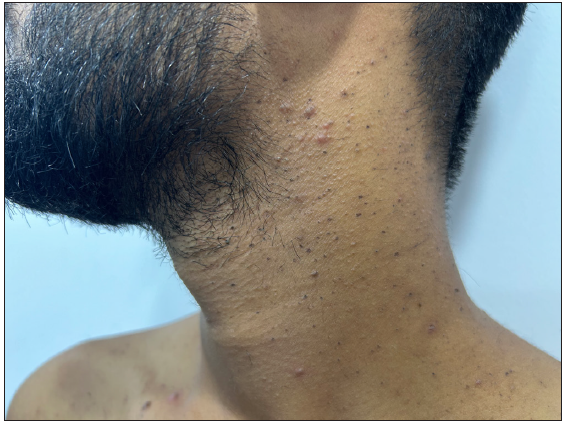 Figure 6a:
Figure 6a:- Dowling-Degos disease presenting as hyperpigmented macules and keratotic papules over the neck.
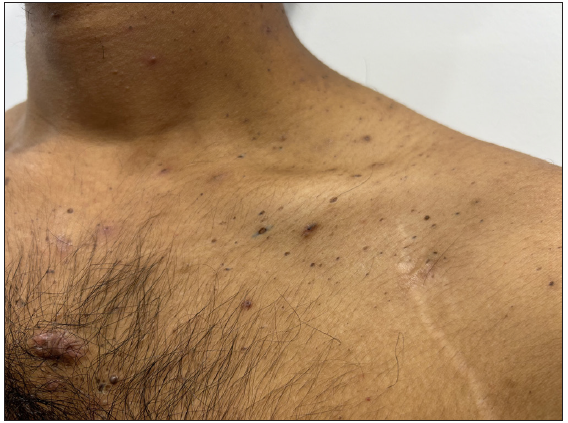 Figure 6b:
Figure 6b:- Dowling-Degos disease presenting as comedo-like lesions over the upper chest.
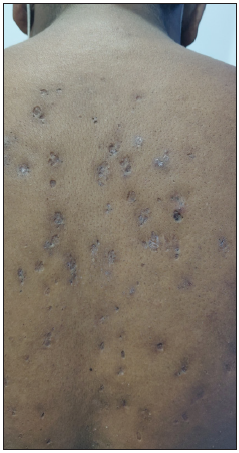 Figure 7:
Figure 7:- Familial dyskeratotic comedones presenting over the back in a 17-year-old boy.
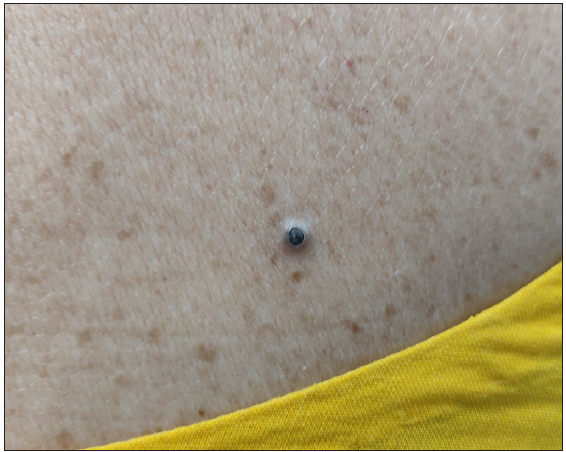 Figure 8:
Figure 8:- Dilated pore of Winer on the upper back in a 38-year-old woman.
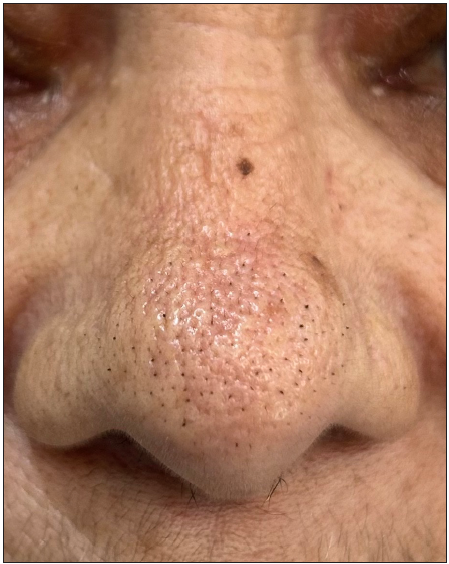 Figure 9a:
Figure 9a:- Trichostasis spinulosa presenting as comedo-like lesions over the nose in a 60-year-old woman.
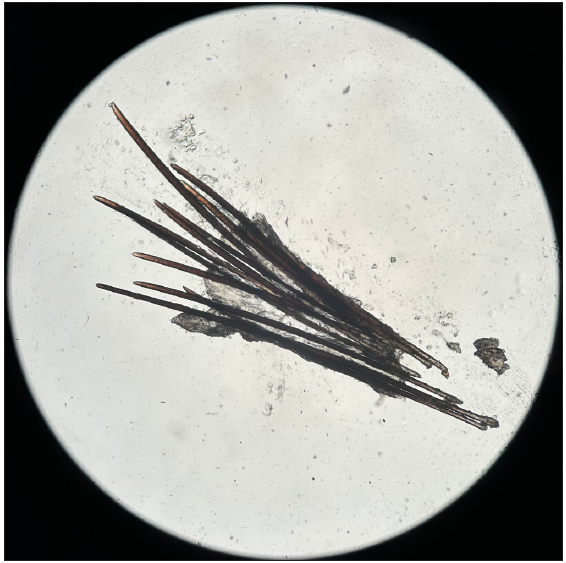 Figure 9b:
Figure 9b:- Microscopy showing multiple telogen club hairs (100x).
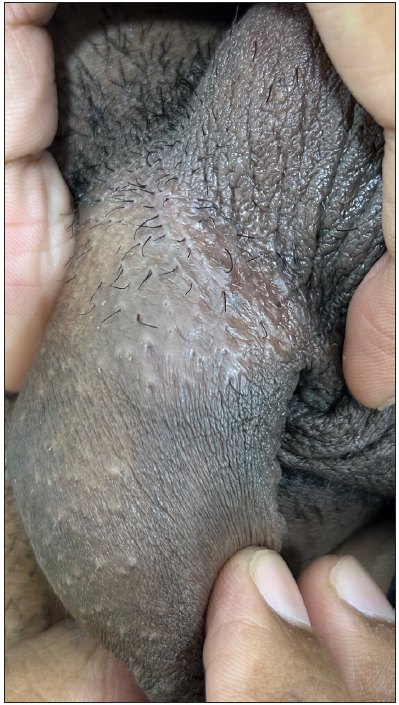 Figure 10:
Figure 10:- Penile acne in a 21-year-old man.
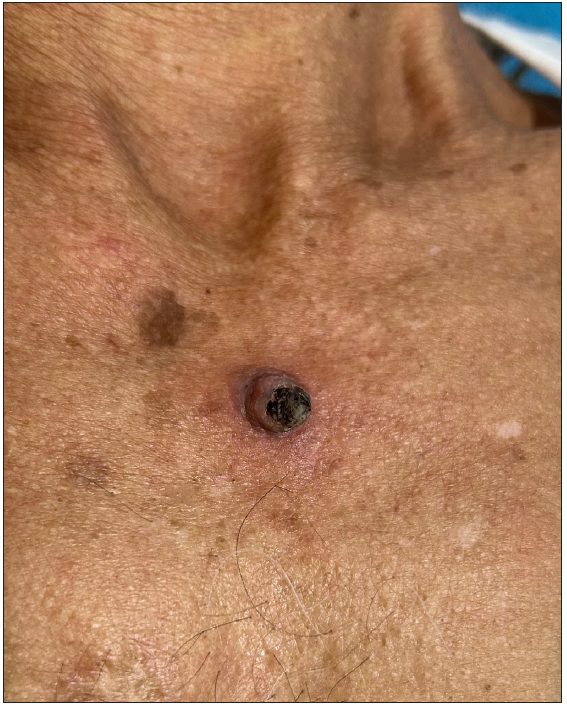 Figure 11:
Figure 11:- Keratoacanthoma over the chest in a 72-year-old man.
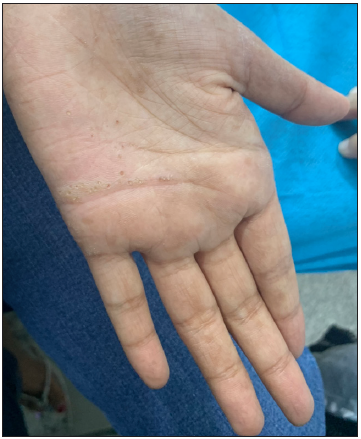 Figure 12:
Figure 12:- Palmoplantar punctate keratoderma in a 28-year-old woman.
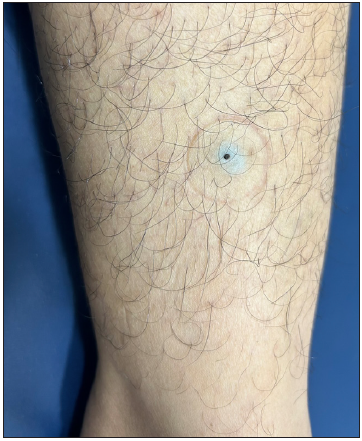 Figure 13:
Figure 13:- Epidermoid cyst with a central comedo-like punctum over the leg in a young woman.
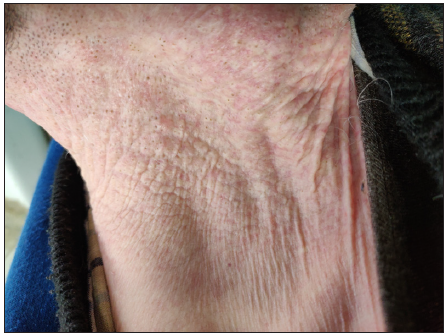 Figure 14:
Figure 14:- Comedones within plaques of pseudoxanthoma elasticum in a 29-year-old man.
 Figure 15a:
Figure 15a:- Lichen planopilaris presenting with comedo-like lesions on the scalp in a 45-year-old woman.
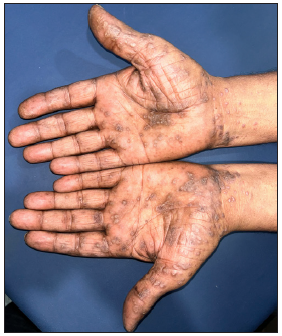 Figure 15b:
Figure 15b:- Palmoplantar lichen planus featuring hyperkeratotic papuloplaques with central keratotic plugs over bilateral palms.
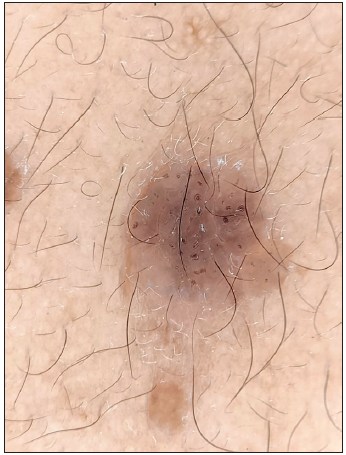 Figure 16a:
Figure 16a:- Polarised dermoscopy showing comedo-like lesions in seborrheic keratosis (Heine Delta 20 Dermatoscope, Heine Optotechnik Gilching, Germany; 10x).
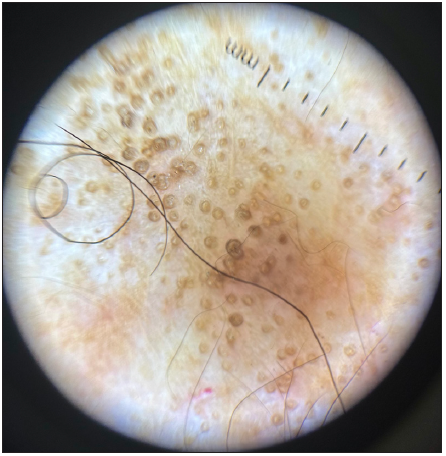 Figure 16b:
Figure 16b:- Polarised dermoscopy showing comedo-like lesions in lichen sclerosus (Heine Delta 20 Dermatoscope, Heine Optotechnik Gilching, Germany; 10x).
-
-
-
Skin disorders occasionally associated with comedones or comedo-like lesions
Many skin disorders may occasionally feature comedones due to loss of structural support to the ostium and infundibulum secondary to connective tissue alteration or follicular hyperkeratosis. These are summarised in Table 2.48–63
-
Comedo-like lesions on dermoscopy
Several disorders can show comedo-like lesions on dermoscopy which are inconspicuous clinically [Table 3].64–67 Comedo-like lesions on clinical examination are almost always replicated on dermoscopy. Hence, they have not been included under this heading to avoid repetition.
-
Comedo necrosis on histology
Comedo necrosis is defined as ‘any central zone necrosis within a duct’ referring to solid intraepithelial growth within the basement membrane with central (zonal) necrosis.68 It is usually seen in adnexal neoplasms.
-
1.
Malignant eccrine poroma
It is considered to be a malignant counterpart of eccrine poroma which presents as an asymptomatic, slow-growing, well-circumscribed papule or nodule with or without ulceration over palms and soles. It arises from the cutaneous intraepidermal ducts of the sweat glands. Histology shows tumour cells containing central necrosis with an inflammatory reaction similar to a comedone, called comedo necrosis, in addition to poorly developed ducts.69
-
2.
Adnexal clear-cell carcinoma
It presents as a rapidly growing, erythematous to flesh-coloured, solitary papule or nodule over the head and neck region in older adults. The histology shows characteristic comedo necrosis with a zonal arrangement, characterised by a central area of degenerating cells and necrosed tissue surrounded by an inner layer of clear cells and an outermost squamous cell layer.70
-
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Acne. In: Griffiths C, Barker J, Bleiker T, Chalmers R, Creamer D, eds. Rook’s textbook of dermatology Vol 90. (9th ed). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley and Sons Ltd; 2016. p. :1-65.
- [Google Scholar]
- Secondary comedones in a case of acne conglobata correlate with double-ended pseudocomedones in hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:969-70.
- [Google Scholar]
- Periorbital comedones and their relationship to pitch tar: A cross-sectional analysis and a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:624-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Indian Acne Alliance (IAA). Acne in India: Guidelines for management - IAA consensus document. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:1-62.
- [Google Scholar]
- Oil acne from mineral oil among workers making prefabricated concrete panels. Contact Dermatitis. 1982;8:141.
- [Google Scholar]
- The ABC of hidradenitis suppurativa: A validated glossary on how to name lesions. Dermatology. 2016;232:137-42.
- [Google Scholar]
- Actinic comedonal plaque-variant of Favre-Racouchot syndrome: Report of two cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:185-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Follicular Dowling Degos disease: A rare variant of an evolving dermatosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:802-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Familial dyskeratotic comedones: A rare entity. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:46-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Familial disseminated comedones without dyskeratosis: Report of an affected family and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2014;228:303-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comedo-like acantholytic dyskeratosis of the face and scalp: A new entity? Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:1047-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Multiple congenital comedones, hearing impairment and intellectual disability: A new syndromic association? Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:807-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic signs in the diagnosis of lichen planus follicularis tumidus. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:576.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic characterization of dilated pore of Winer: Report of two cases. Clinical Dermatology Review. 2019;3:96-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Trichostasis spinulosa: An unusual diagnosis presenting as a double lower eyelid. Int J Trichology. 2016;8:21-3.
- [Google Scholar]
- Perianal comedones: A rare incidental finding. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2017;2017:9019682.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermatoses of the male genitalia. In: Griffiths C, ed. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology Vol 111. (9th ed). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley and Sons Ltd; 2016. p. :1-36.
- [Google Scholar]
- Localised acneiform eruption following X-ray irradiation. Br J Clin Pract. 1981;35:57-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Localized acne as a complication of megavoltage radiotherapy. J Dermatol Treat. 1992;3:137-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Fordyce disease following axillary laser hair removal. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:573-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Mechanical stress and the development of pseudo-comedones and tunnels in hidradenitis suppurativa/Acne inversa. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:396-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comedonal Darier’s disease: Six additional cases and a review of this entity. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020;18:1501-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comedogenic lupus: A rare variant of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus - Case series. An Bras Dermatol. 2023;98:159-67.
- [Google Scholar]
- Warty dyskeratoma - A review of clinicopathological features, nature, morphogenesis, classification and nomenclature. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1978;44:3-11.
- [Google Scholar]
- A clinical and biological review of keratoacanthoma. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:487-98.
- [Google Scholar]
- Porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2013;2013:953840.
- [Google Scholar]
- Porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2011;77:174-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Punctate porokeratosis-pruritic and hyperkeratotic papules on the palms and feet. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020;33:415-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Punctate palmoplantar keratoderma: A case report of type 1 (Buschke-Fischer-Brauer Disease) Case Rep Dermatol. 2019;11:292-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Chloracne and hyperpigmentation caused by exposure to hazardous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16:4864.
- [Google Scholar]
- Familial pseudoxanthoma elasticum associated with multiple comedones. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030.
- [Google Scholar]
- Open comedones overlying granuloma annulare in a photoexposed area. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2006;22:273-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Generalized granuloma annulare with open comedones in photoexposed areas. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:495-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Widespread comedones as the sole clinical manifestation of follicular mycosis fungoides. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:534-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: Clinicopathological features and outcome in a series of 20 cases. JAAD. 2010;62:418-26.
- [Google Scholar]
- Autosomal dominantly inherited generalized basaloid follicular hamartoma syndrome: Report of a new disease in a North Carolina family. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:189-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comedone-like changes overlying neurofibromas. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:271-2.
- [Google Scholar]
- Stimulation of folliculo-sebaceous proliferations by neurofibromas: A report of two cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1998;25:228-32.
- [Google Scholar]
- Lichen planopilaris: A review of evaluation methods. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87:442-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- comedone-like lesions as a manifestation of lichen planopilaris beyond the scalp: A case report with dermoscopic features and literature review. Case Rep Dermatol. 2021;13:106-13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Hyperkeratotic pitted plaques on the palms and soles. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76:52-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Appearance of comedones at the site of healed herpes zoster: Wolf’s isotopic response. Int J Dermatol. 2011;50:633-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comedones appearing after herpes zoster infection: Koebner phenomenon or Wolf’s isotopic response? Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:221-2.
- [Google Scholar]
- Folliculocystic and collagenous hamartoma of tuberous sclerosis complex, not always a single cutaneous lesion. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:1195-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Multiple milia and comedones as a skin manifestation of systemic amyloidosis. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:638-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Role of dermoscopy in the diagnosis of hypertrophic lichen planus and prurigo nodularis. Indian J Dermatol. 2019;64:341-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- A Clinicopathological and Dermoscopic Correlation of Seborrheic Keratosis. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:622-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic clues for diagnosing melanomas that resemble seborrheic keratosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:544-51.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic evaluation of extragenital lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12:e2022125.
- [Google Scholar]
- Variability in diagnostic threshold for comedo necrosis among breast pathologists: implications for patient eligibility for active surveillance trials of ductal carcinoma in situ. Mod Pathol. 2019;32:1257-62.
- [Google Scholar]
- Eccrine Porocarcinoma: A Review of the Literature. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13:1431.
- [Google Scholar]
- Adnexal clear cell carcinoma with comedo necrosis: clinicopathologic analysis of 12 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1655-64.
- [Google Scholar]