Translate this page into:
Evaluation of serum neuropeptide levels in patients with chronic urticaria
2 Department of Biochemistry, S�leyman Demirel University, Isparta, Turkey
Correspondence Address:
Pinar Yuksel Basak
Department of Dermatology, Suleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Medicine, Isparta
Turkey
| How to cite this article: Basak PY, Erturan I, Yuksel O, Kazanoglu OO, Vural H. Evaluation of serum neuropeptide levels in patients with chronic urticaria. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2014;80:483 |
Sir,
Stress is known to influence the course of a number of skin diseases possibly via neuropeptides, which possess vasoactive properties. Neuropeptides are implicated in non-immunologic mast cell activation and histamine liberation contributing to lesion induction in chronic urticaria. Substance P (SP), stem cell factor (SCF), and nerve growth factor (NGF) were found to be the foremost neuropeptides triggering mast cell activation, as well as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), and neuropeptide Y (NPY). [1]
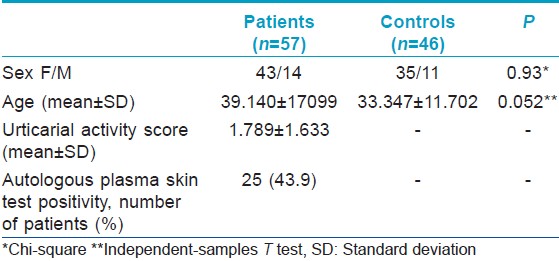
The aim of this study was to compare the levels of selected neuropeptides in serum samples of 57 chronic urticaria patients with 46 age and sex-matched healthy controls. Descriptive features of the study group are presented in [Table - 1]. In all patients, autologous plasma skin test was performed and severity of urticaria was determined by urticarial activity score (UAS). Levels of neuropeptides in patients and controls is depicted in [Table - 2]. The only neuropeptides showing significant elevation in urticaria patients compared to controls were stem cell factor and substance P.
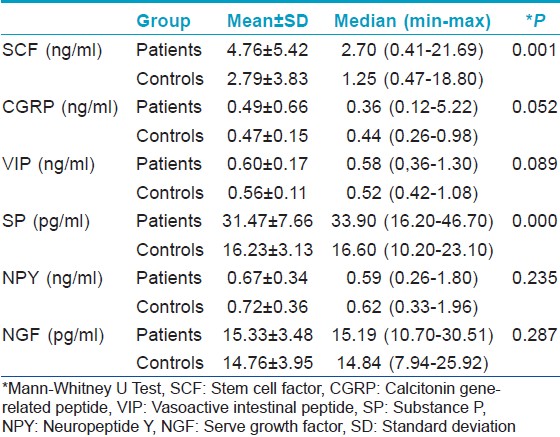
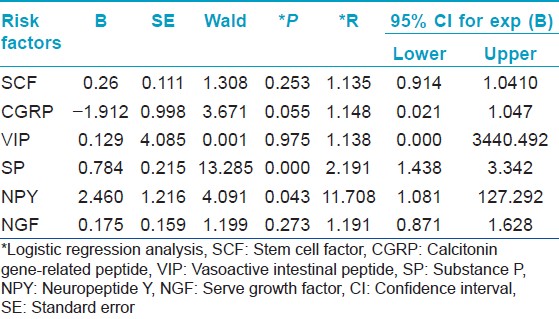
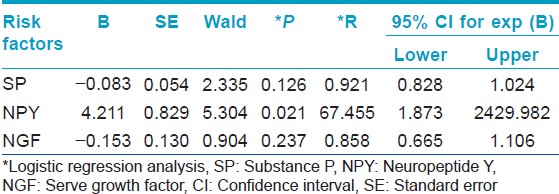
In a previous study, no statistically significant difference in serum stem cell factor levels was found in urticaria patients with positive autologous serum skin test compared to controls. [2] In contrast, our study demonstrated significant elevation of this peptide in chronic urticaria patients compared to controls while there was no significant difference in levels between APST-positive and negative patients. Although substance P has mostly been assessed in chronic skin diseases, there is a single recent study performed in chronic urticaria in which no significant difference was found in substance P levels between patients and controls. However, in a few patients higher serum substance P concentrations were suggested as a trigger of urticarial symptoms. [3] In our study, stem cell factor and substance P were determined as the most important neuropeptides in the development of urticaria [Table - 3]. Absence of a significant difference in neuropeptide Y levels from controls could be explained by the selective uptake of this peptide by lesional skin. In addition, on logistic regression analysis, neuropeptide Y was found as the selected peptide predictive of APST positivity [Table - 4]. Though recent evidence has identified the significance of neuropeptide Y in pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, [4] its role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune chronic urticaria may be considered a novel observation of the present study. These results require further investigation for validation.
Bonini et al. have previously reported elevated serum nerve growth factor levels in 14 patients with chronic urticaria. [5] In contrast, our study found elevated nerve growth factor levels only in APST-negative patients. Release of neuropeptides in skin microenvironment could be insufficient to cause increase in blood concentration or rapid inactivation of this peptide might account for our results. When the role of mast cells in the pathogenesis of chronic urticaria was considered, this finding in patients might be attributed to the limited effects of nerve growth factor on mast cell activation, while it is comparable to stem cell factor regarding its effects on mast cell differentiation. [1]
Calcitonin gene-related peptide might possess initial effects in tissue rather than peripheral blood. Being a weak histamine releaser, [1] it seems to have limited effects on mast cells compared to substance P, as confirmed by our results. In addition, the explanation for similar vasoactive intestinal peptide levels in patients and controls could be the raised metabolism and increased sensitivity of microvasculature to this peptide in chronic urticaria patients.
Previous studies have not demonstrated that any serum markers correlated with disease severity in chronic urticaria. This study too did not find any correlation of levels of neuropeptides with disease activity (urticarial activity score). However, since the mean UAS in our patients was classified as mild, it is suggested that UAS correlation needs to be re-evaluated in patient groups with moderate and severe disease activity also.
In conclusion, this study demonstrated the participation of serum stem cell factor, substance P, and neuropeptide Y among the selected neuropeptides in the pathogenesis of chronic urticaria. Moreover, a novel finding of this investigation was revealing of neuropeptide Y as the most important peptide predictive of APST positivity. The role of neuropeptides in this complex system of interactions seems to be an important component of chronic urticaria pathogenesis and is, therefore, worth exploring in further clinical studies.
| 1. |
Yosipovitch G, Papoiu A DP. Cutaneous Neurophysiology. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, editors. Dermatology. 3 rd ed. New York: Elsevier; 2012. p. 99-109.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Asero R, Tedeschi A, Lorini M, Gerosa M, Meroni P, Riboldi P. Circulating stem cell factor in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2003;91:79-81.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Tedeschi A, Lorini M, Asero R. No evidence of increased serum substance P levels in chronic urticaria patients with and without demonstrable circulating vasoactive factors. Clin Exp Dermatol 2005;30:171-5.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Dimitrijevic M, Stanojevic S, Kustrimovic N, Leposavic G. End-point effector stress mediators in neuroimmune interactions: Their role in immune system homeostasis and autoimmune pathology. Immunol Res 2012;52:64-80.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Bonini S, Lambiase A, Bonini S, Angelucci F, Magrini L, Manni L, et al. Circulating nerve growth factor levels are increased in humans with allergic diseases and asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996;93:10955-60.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
2,450
PDF downloads
2,288





