Translate this page into:
Invasive extramammary Paget’s disease presenting as scrotal nodules
Corresponding author: Dr. Xiang-xi Wang, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China. sherrywangx@sina.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Liang T, Wang X-X. Invasive extramammary Paget’s disease presenting as scrotal nodules. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_1563_2024
A 63-year-old man presented with multiple, asymptomatic, erythematous coalescing nodules over his scrotum and penis [Figure 1]. Skin biopsy from a nodule revealed atypical epithelioid cells with foamy and eosinophilic cytoplasm infiltrating the epidermis, dermis and lymphovascular structures, and stained positive for cytokeratin (CK)7 and negative for P40 [Supplementary Figures], consistent with Paget cells.
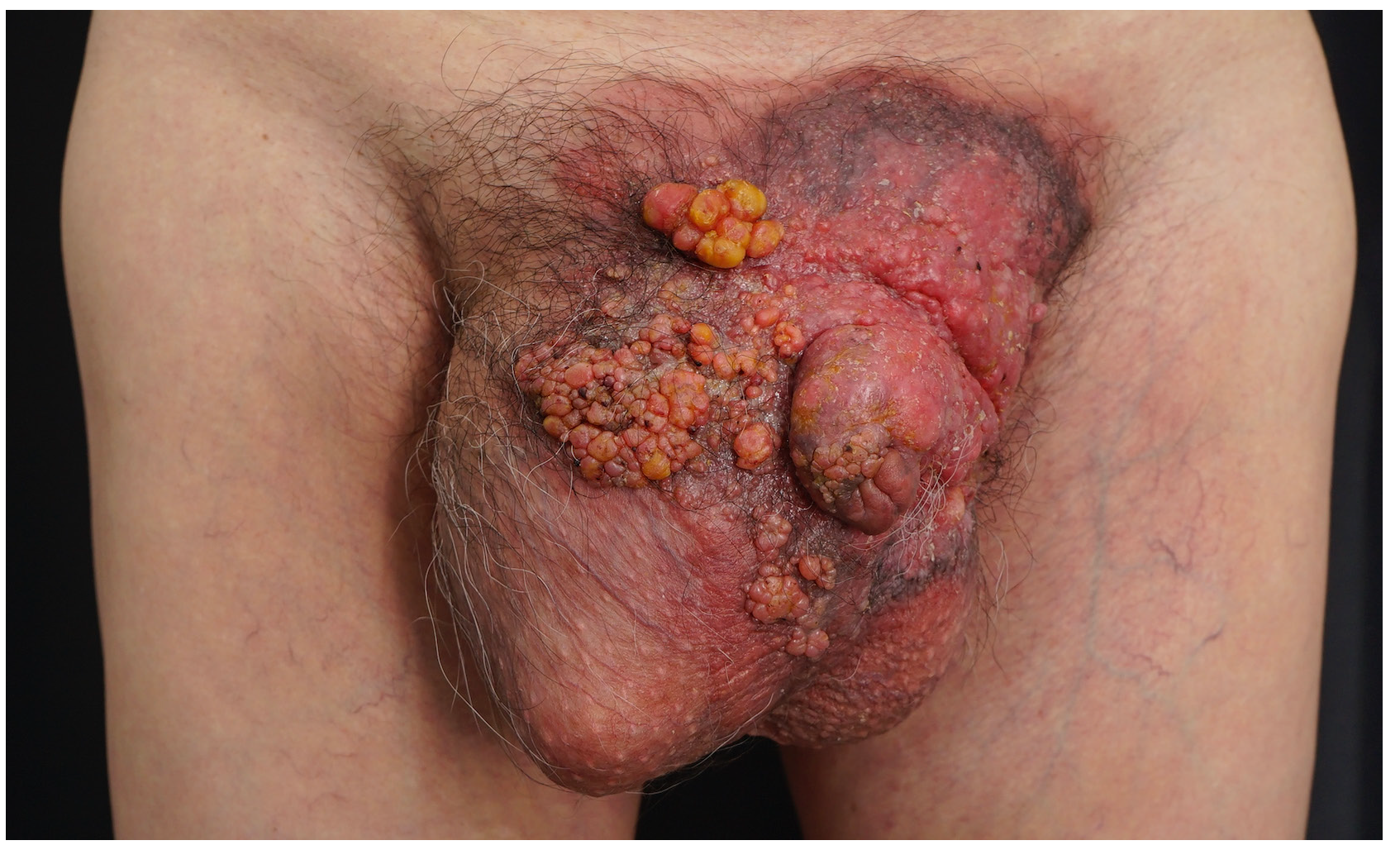
- Erythematous coalescing papules and nodules on the scrotum and penis.
Extramammary Paget’s disease, generally presenting as an intraepithelial adenocarcinoma, typically appears as erosive, crusted, or eczematous plaques. Differential diagnoses for multiple nodules on the scrotum include condyloma acuminatum, squamous cell carcinoma, and sebaceous carcinoma, necessitating histopathological examination for confirmation. The nodules in this patient probably resulted from the lymphatic stasis secondary to the invasion of lymphatic vessels by Paget cells.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of AI-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.





