Translate this page into:
Residents Page
doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.93650
PMID: 22421663
Named cells in dermatology
Fiona F Sequeira1 , Suneil Gandhi2 , Usha Kini3 , Ishwar Bhat1
1 Department of Dermatology, St John's Medical College and Hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
2 Department of Dermatology, JN Medical College, Belgaum, India
3 Department of Pathology, St John's Medical College and Hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Correspondence Address:
Fiona F Sequeira
Department of Dermatology, St John's Medical College and Hospital, Koramangala, Bangalore, Karnataka - 560 034
India
2 Department of Dermatology, JN Medical College, Belgaum, India
3 Department of Pathology, St John's Medical College and Hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Correspondence Address:
Fiona F Sequeira
Department of Dermatology, St John's Medical College and Hospital, Koramangala, Bangalore, Karnataka - 560 034
India
| How to cite this article: Sequeira FF, Gandhi S, Kini U, Bhat I. Named cells in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2012;78:207-216 |
Copyright: (C)2012 Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology
Introduction
This article briefly describes the named cells in dermatology. It′s purpose is to serve as a ready reckoner to the postgraduates during their quiz preparations. They include the following:
- General category
- Normal cutaneous anatomy: Langerhans cells, Glomus cells, Veil cells, Mast cells
- Bullous disorders: Tzanck cells
- Eczematous disorders: Tadpole cells
- Metabolic and storage disorders: Gargoyle cells, Gaucher′s cell, Xanthoma cells
- Tumors: Basalioma cells, Basophilic and shadow cells, Doughnut cells, Flower cells, Granular cells, Halo cells, Hibernoma cells, Paget cells, Sezary cells, Signet ring cells, Spider web cells, Strap cells, Reed Sternberg cells, Vulvar Clear Cells of Toker, Floret giant cells
- Histiocytic disorders: Touton giant cells
- Collagen vascular disorders: LE cells, Tart cells
- Drug induced: Podophyllin cells
- Keratinization disorders: Mantle cells, Half and half cells
- Disorders of the panniculus: Bean bag cells
- Disorders of photoimmunology: Sunburn cells
- Benign pigmented lesions: Balloon cells
- Papulosquamous disorders: Pekin cells
- Infectious disorders
- Bacterial: Clue cells, Downey cells, Greenblatt and Pund cells, Lepra cells, Mikulicz cells, Von Hansemann cells, Langhan giant cells
- Protozoal: Wright cells
- Viral: Koilocytes, Warthin Finkeldey cells, Mitosoid cells
[SUPPORTING:1]
[Figure - 1], [Figure - 2], [Figure - 3], [Figure - 4], [Figure - 5] and [Figure - 6].
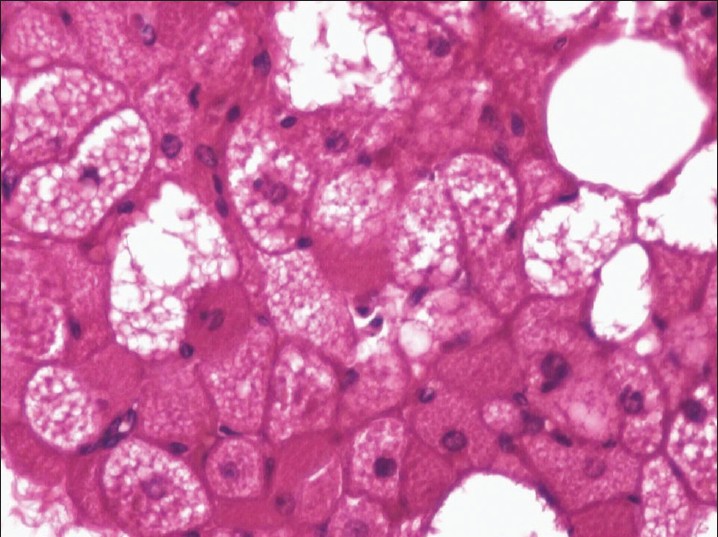 |
| Figure 1: Hibernoma. Large polyhedral fat cells containing eosinophilic granular cytoplasm (×200) |
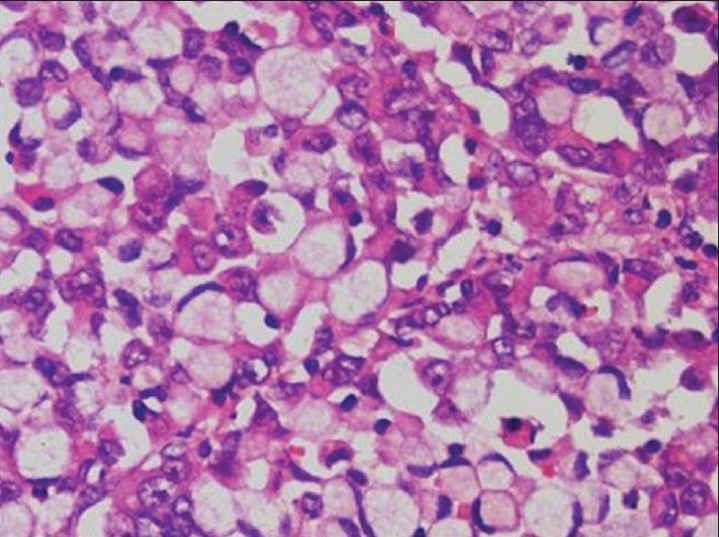 |
| Figure 2: Signet ring cells in an adenocarcinoma. Sheet of large cells with vacuolated cytoplasm pushing the single hyperchromatic nucleus to the periphery (×400) |
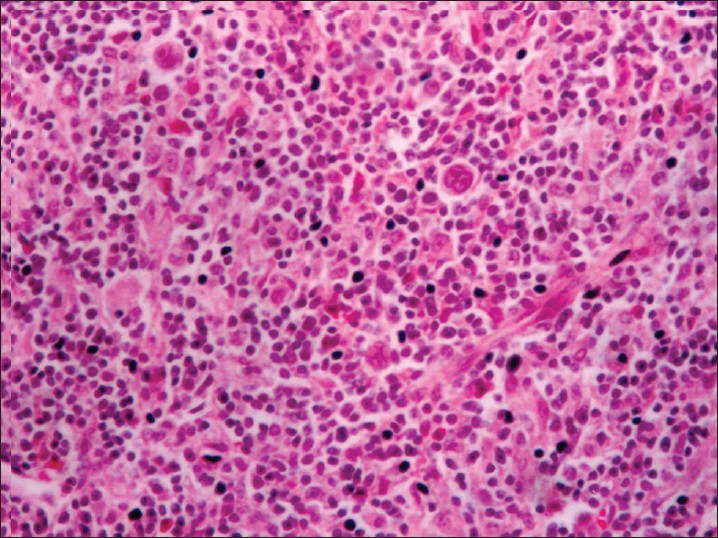 |
| Figure 3: Reed Sternberg cells in a case of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Note the bilobed nucleus with a resemblance to an "owl's eye" with prominent eosinophilic inclusion-like nucleoli (×200) |
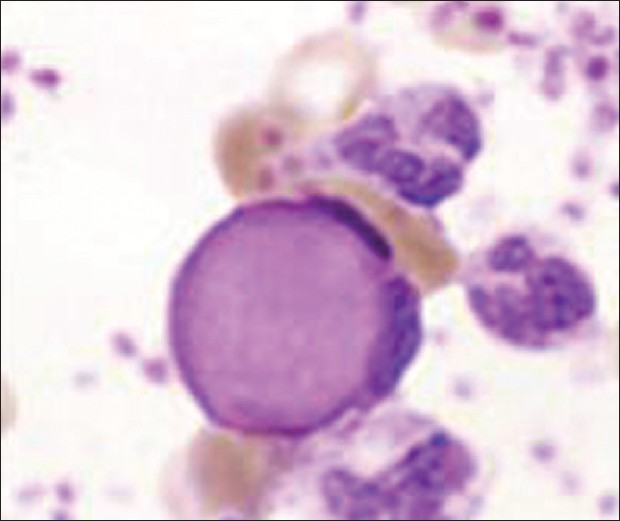 |
| Figure 4: LE cells. Distorted nuclear material in the cytoplasm of a polymorphonuclear leukocyte causing the nucleus to be compressed and pushed to the periphery (×1000) |
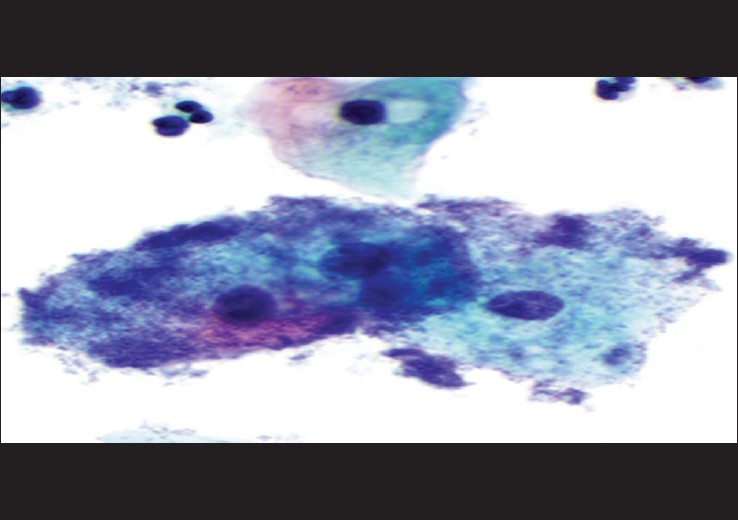 |
| Figure 5: Clue cells. Squamous epithelial cells with a large number of coccobacillary organisms, Gardnerella vaginalis and other anaerobic bacteria densely attached in clusters to their surfaces give them a granular appearance (×400) |
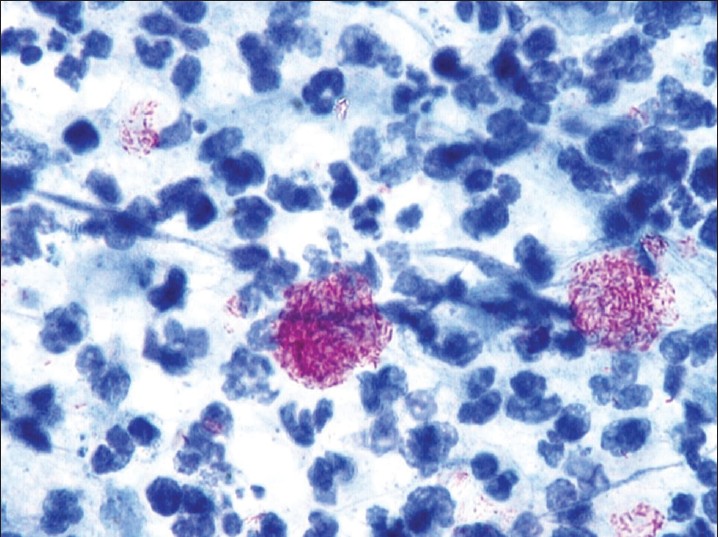 |
| Figure 6: Lepra cells. Large cells with their abundant cytoplasm, occupying the greater part of the cell and filled with mycobacteria leprae bacilli, highlighted by modified Fite Faraco (MFF stain, x1000) |
References
| 1. |
Haake AR, Holbrook K. The structure and development of skin. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz S, Fitzpatrick TB, editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology In General medicine. 5 th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 1-109.
th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 1-109.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Grevelink SV, Mulliken JB. Vascular anomalies. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz S, Fitzpatrick TB, editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology In General medicine. 5 th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 1-35.
th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 1-35.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Braverman IM. Ultrastructure and organization of the cutaneous microvasculature in normal and pathologic states. J Invest Dermatol 1989;93:2S-9S.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Braverman IM. The dermal microvascular unit: Relationship to immunological processes and dermal dendrocytes. In: Nickoloff BJ, editor. Dermal Immune System. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1993. p. 91.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Bingham CO, Austen KF. The molecular and cellular biology of the mast cell. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz S, Fitzpatrick TB, editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology In General medicine. 5 th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 1-33.
th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 1-33.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 6. |
Tang CK, Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Cancer 1978;42:2311.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 7. |
Gupta LK, Singhi MK. Tzanck smear: A useful diagnostic tool. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2005;71:295-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 8. |
Pariser RJ. Diagnosis of spongiotic vesicular dermatitis by Tzanck smear: The "tadpole cell". J Am Acad Dermatol 1983;8:519-22.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 9. |
Durdu M, Baba M, Seçkin D. The value of Tzanck smear test in diagnosis of erosive, vesicular, bullous, and pustular skin lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol 2008;59:958.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 10. |
Lagunoff D, Ross R, Benditt EP. Histochemical and electron microscopic study in a case of Hurler's disease. Am J Pathol 1962;41:273-86.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 11. |
Hammerschmidt, Dale E, Parkin, Janet L, Brunning, Richard. Gaucher cell. J Lab Clin Med 1996;4:410.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 12. |
Naito M. Macrophage differentiation and function in health and disease. Pathol Int 2008;58:143-55.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 13. |
Braun-Falco O, Eckert F. Macroscopic and microscopic structure of xanthomatous eruptions. Curr Probl Dermatol 1991;20:54.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 14. |
Klein W, Chan E, Seykora J. Tumors of the epidermal appendages. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 874.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 874.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 15. |
Rivet J, Rogez C, Wechsler J. Trichoepithelioma with "monster" stromal cells. J Cutan Pathol 2001;28:379-82.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 16. |
Klein W, Chan E, Seykora J. Tumors of the epidermal appendages. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 879-80.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 879-80.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 17. |
Jaffes ES. Post-thymic T cell lymphomas. In: Jaffes ES, editors. Surgical pathology of the lymphnodes and related organs. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1995. p. 360.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 18. |
Das P, Iyer VK, Mathur SR, Ray R. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A critical evaluation of cytomorphological features in seven cases. Cytopathology 2010;21:251-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 19. |
Dahmoush L, Hijazi Y, Barnes E, Stetler-Stevenson M, Abati A. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: A cytopathologic, immunocytochemical, and flow cytometric study. Cancer 2002;25:110-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 20. |
Santos JB, Farré L, Batista ES, Santos HH, Vieira MD, Bittencourt AL. The importance of flower cells for the early diagnosis of acute adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with skin involvement. Acta Oncol 2010;49:265-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 21. |
Tsukasaki K, Hermine O, Bazarbachi A, Ratner L, Ramos JC, Harrington W, et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A proposal from an international consensus meeting. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:453-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 22. |
Stock D, McKee P, Donley B, Lakin R, Goldblum J, Howard M. Granular cell tumor of the toe: A case report. J Foot Ankle Surg 2009;48:358-61.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 23. |
Scarisbrick J, Whittacker S. Cutaneous lymphoma. In: Marcus R, John W, Sweetenham, Williams ME, editors. Lymphoma: Pathology, diagnosis and treatment. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2007. p. 235.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 24. |
Ragsdale B. Tumors with fatty, muscular, osseous and cartilagenous differentiation. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 1065.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 1065.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 25. |
Matanza-Rodriguez MI, Alvarez-Cañas MC, Gomez-Ortega JM, Fernandez F, Blanco C, Garijo F, et al. Hibernoma: A new case in the submandibular region. Ann Saudi Med 1996;16:670-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 26. |
Kirkham N. Tumors and cysts of the epidermis. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 853.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 853.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 27. |
Vonderheid EC, Bernengo MG, Burg G, Duvic M, Heald P, Laroche L, et al. Update on erythrodermic cutaneous T cell lymphoma: Report of the international Society for cutaneous lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002;46:95-106.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 28. |
Murphy G, Schwarting R. Cutaneous Lymphomas and leukemias. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 958.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 958.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 29. |
Ragsdale B. Tumors with fatty, muscular, osseous and cartilagenous differentiation. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 1075.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 1075.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 30. |
Verdolini R, Goteri G, Brancorsini D, Collina G, Simonetti O, Offidani A.Adult rhabdomyoma: Report of two cases of rhabdomyoma of the lip and of the eyelid. Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:264-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 31. |
Veziroglu F, Uc-kan S, Sengüven B. Adult type rhabdomyoma in a child. Oral Oncol 2006;42:213-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 32. |
Agamanolis DP, Dasu S, Krill CE Jr. Tumors of skeletal muscle. Hum Pathol 1986;17:778.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 33. |
Stein H. Hodgkins lymphoma: Introduction. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours series. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues: Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2001. p. 239.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 34. |
Hayes TG, Rabin VR, Rosen T, Zubler MA. Hodgkin's disease presenting in the skin: Case report and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol 1990;22:944-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 35. |
Willman JH, Golitz LE, Fitzpatrick JE. Vulvar clear cells of Toker: Precursors of extramammary Paget's disease. Am J Dermatopathol 2005;27:185-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 36. |
Toker C. Clear cells of the nipple epidermis. Cancer 1970;25:601-10.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 37. |
Shaktawat SS, Golka D. Floret-like multinucleated giant cells in neurofibroma. Diagn Pathol 2007;2:47.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 38. |
Aterman K, Remmele W, Smith M. Karl Touton and his "xanthelasmatic giant cell": A selective review of multinucleated giant cells. Am J Dermatopathol 1988;10:257-69.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 39. |
Guillou L, Calonge E, Speight P, Rosai J, Fletcher CDM. Hobnail hemangioma: A pseudomalignant vascular lesion with a reappraisal of targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma. Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:97-105.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 40. |
Hepburn AL. The LE cell. Rheumatology 2001;40:826-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 41. |
Tan EM. The LE cell and its legacy. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1998;16:652-8
[Google Scholar]
|
| 42. |
Hargraves MM, Richmond H, Morton R. Presentation of two bone marrow elements; the "tart" cell and "LE" cell. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin 1948;23:25-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 43. |
Fisher A. Severe systemic and local reactions to topical podophyllin resin. Cutis 1981;28:233-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 44. |
Eady RA, Cowen T. Half-and-half cells in lichen planus. A possible clue to the origin and early formation of colloid bodies. Br J Dermatol 1978;98:417-23.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 45. |
Winkelmann RK, Bowie EJ. Hemorrhagic diathesis associated with benign histiocytic cytophagic panniculitis and systemic histiocytosis. Arch Intern Med 1980;140:1460-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 46. |
Sheehan JM, Young AR. The sunburn cell revisited: An update on mechanistic aspects. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2002;1:365-77.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 47. |
Mardi K, Sharma J. Metastatic balloon cell melanoma: A rare differential in the diagnosis of clear cell tumors. Internet J Pathol 2009;8:16.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 48. |
Bachner FL, Ng B, Sudilovsky D. Metastatic balloon cell melanoma: A case report. Acta Cytol 2005;49:543-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 49. |
Pekin TJ, Malinin TI, Zvaifler NJ. Unusual synovial fluid findings in Reiter's syndrome. Ann Intern Med 1967;66:677-84.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 50. |
Sachdeva S. Clue cell. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2006;72:392-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 51. |
Downey H, McKinlay CA. Acute lymphadenosis compared with acute lymphatic leukemia. Arch Intern Med 1923;32:82-112.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 52. |
Auwaerter PG. Infectious mononucleosis in middle age. JAMA 1999;5:454-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 53. |
Edwin O, Wheeler, John D, Turner, Scannell J. Fever, splenomegaly and atypical lymphocytes: A syndrome observed after cardiac surgery utilizing a pump oxygenator. N Engl J Med 1962;266:454-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 54. |
Pund ER, Greenblatt RB. Specific histology of granuloma inguinale. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1937;23:224-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 55. |
Hart G. Donovanosis. Clin Infect Dis 1997;25:24-32.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 56. |
Oliver J. Origin of the lepra cells. J Exp Med 1926;43:233-9.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 57. |
Lucas S. Bacterial diseases. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 572.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 572.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 58. |
Hoffman E, Loose LD, Harkin JC. The mickulicz cell in rhinoscleroma. Am J Pathol 1973;73:47.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 59. |
An T, Ferenczy A, Wilens SL, Melicow M. Observations on the formation of Michaelis-Gutmann bodies. Hum Pathol 1974;5:753-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 60. |
Pritchard J, Foley P, Wong H. "Langerhans and Langhans: What's misleading in a name?" Lancet 2003;362:922.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 61. |
Ramírez JR, Agudelo S, Muskus C, Alzate JF, Berberich C, Barker D, et al. Diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Colombia: the sampling site within lesions influences the sensitivity of parasitologic diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:3768-73.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 62. |
Licona H, Bonthius DJ. Measles. In: Biller J, editor. The Interface of Neurology and Internal Medicine. Kluwer, Lippincott; 2007. p. 879.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 63. |
Xu X, Erickson L, Elder D. Diseases caused by viruses. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Johnson B, Murphy G, editors. Lever's Histopathology of the skin. 9 th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 664.
th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 2005. p. 664.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 64. |
Carlos R, Sedano HO. Multifocal papilloma virus epithelial hyperplasia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1994;77:631-5.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
13,532
PDF downloads
6,868





