Translate this page into:
Ribociclib induced vitiligo-like lesions
Corresponding author: Dr. Rohit Kothari, Department of Dermatology, Command Hospital Air Force, Bangalore, India. rohitkothari3422@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Kothari R, Darling HS, Bhatnagar A, Janney M, Mohan S, Kumar R. Ribociclib induced vitiligo-like lesions. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2025;91:396-7. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_239_2024
Dear Editor,
Ribociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK 4/6) inhibitor that is used in metastatic breast cancer treatment. We herein report a rare case of ribociclib-induced vitiligo-like lesions and a comprehensive literature review of this uncommon adverse effect which summarises the features of 25 reported cases till date.1-6 Considering the increasing use of this medication and the social stigma associated with vitiligo, it is crucial to be aware of this adverse effect and counsel the patients prior to starting the therapy.
A 51-year-old female with metastatic breast carcinoma was started on injection ribociclib 400 mg/day for 3-weeks/month with letrozole 2.5 mg/day, following which she developed depigmented macules over the face, neck and forearms, ten months after therapy initiation [Figure 1a]. There was no prior history of an autoimmune condition in the patient or family. Dermoscopy revealed ill-defined white structureless areas, reduced pigment-network, scaling, reticulated telangiectasias, coiled-hairs (likely secondary to chemotherapy) and leukotrichia [Figure 1b]. A skin biopsy showed significant loss of melanocytes and focal melanin pigment incontinence favouring vitiligo [Figure 1c]. She was treated with 0.1% mometasone cream and 0.1% tacrolimus ointment. Follow-up at 6-months revealed a stable disease with minimal repigmentation.

- Multiple depigmented macules over face, neck and forearms.
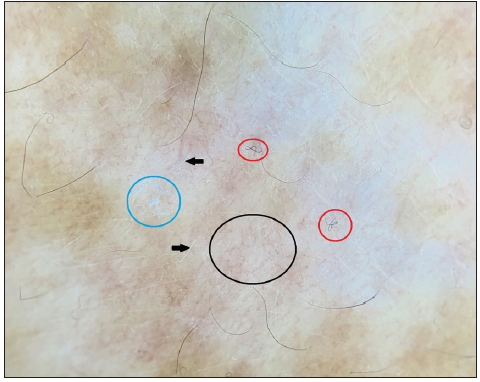
- Dermoscopy showing ill-defined white structureless areas due to pigment loss, reduced pigment network, reticulated telangiectasias (black circle), scaling (blue circle), coiled hairs (red circles) likely due to chemotherapy and leukotrichia (black arrows). (Illuco IDS-1100, Polarised 10x).
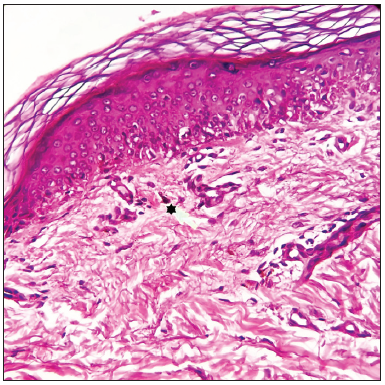
- Histopathology from the forearm showing significantly reduced melanocytes in the basal layer and focal melanin pigment incontinence (five-point star) favouring vitiligo (Haematoxylin and eosin, 400x).
CDK4/6 inhibitors are associated with a wide range of cutaneous adverse-effects, the most common of which is alopecia, followed by rash and pruritus, usually reported within 1–4 months of treatment initiation. Other rare side-effects include trichorrhexis, onychoclasis, erythema multiforme, bullous dermatitis and vitiligo.1 Ribociclib-induced vitiligo-like lesions are reported more commonly in the 4th–7th decade, a common age-group for breast cancer. It predominantly involves the photo-exposed areas; however, it may also involve the trunk and extremities. The interval between ribociclib initiation and the development of vitiligo varies between 3 and 10 months and the lesions are commonly pruritic. There are no treatment guidelines; however, topical steroids/calcineurin inhibitors, emollients, and antihistamines may be used. In extensive cases, oral steroids and phototherapy may be tried. The response to therapy is discouraging in almost all the cases and the aim should be to halt the disease progression rather than aiming for repigmentation.1-6 The depigmentation may lessen over several months after stopping the drug; however, a few areas may remain depigmented.4 None of the reported cases, except one, had a history of vitiligo.6 The characteristics of all the reported cases are summarised in Table 1. The exact cause of these lesions is not known. It is hypothesised that apoptosis of the melanocytes secondary to CDK4/6 inhibitors and keratinocyte precursors with altered proliferation may be responsible. We also hypothesise that there may be a role of ultraviolet radiation (UVB) due to the characteristic distribution of the lesions. UVB radiation induces DNA damage, which may be more pronounced in the background of CDK 4/6 inhibition. There is scanty data to assign any prognostic significance to these lesions and it may be considered a class-specific adverse-effect.
| Study | No. of patients | Patient’s age | Latency of vitiligo lesions | Distribution of lesions | Symptoms | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raschi E et al.1 | 6 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Silvestre-Torner et al.2 | 1 | 70 years | 8 months | Face, neck, with affectation of hair follicle | Asymptomatic | - | - |
| Anjaneyan et al.3 | 1 | 78 years | 7 months | Face, hands, forearms, arms, thighs, legs, feet, chest, abdomen | Pruritus | Betamethasone (5 mg two consecutive days/week), levocetrizine (5 mg at night) & moisturisers | Lesions didn’t progress & mild improvement. |
| Chan et al.4 | 2 | 71 years; & 54 years | 7 months; & 3 months | Legs, arms, V of neck, cheeks, posterior neck, back; & Face, arms, and trunk | - | - | No repigmentation at the 12-month follow-up; & depigmentation lessened over several months but some remain over her arms and upper chest. |
| Sharaf et al.5 | 1 | 78 years | 5 months | Face, hands, feet | - | Topical steroids | Little improvement |
| Sollena et al.6 | 14 | 40–79 years | - | Face, hands, and chest, trunk, extremities | Pruritus | Topical calcineurin inhibitors ± topical/systemic steroids ± UVB | Partial response |
| Present case | 1 | 51 years | 10 months | Face, neck, & forearms | Asymptomatic | Topical calcineurin inhibitors + topical steroids | Lesions did not progress & showed little improvement |
The increasing use of ribociclib and the possibility of underreporting vitiligo due to social stigma associated with the condition, emphasise the importance of awareness of this adverse-effect and counselling the patients prior to initiation of chemotherapy, as it is usually resistant to treatment.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Skin toxicities with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: Signals from disproportionality analysis of the FDA adverse event reporting system. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:247-55.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribociclib-induced vitiligo: A case report. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12:e2022045.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribociclib-induced extensive vitiligo-like lesions: Possible pathomechanisms with clinical, dermoscopic and histological correlation. BMJ Case Rep. 2022;15:e248782.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Drug induced vitiligo-like depigmentation from a CDK 4/6 inhibitor. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2022;18:e154-e156.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitiligo-like lesions in a patient with metastatic breast cancer treated with cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor: A case report and literature review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:5-10.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- European Network for cutaneous adverse event of oncologic drugs (ENCADO) group. Vitiligo-like lesions in patients with advanced breast cancer treated with cycline-dependent kinases 4 and 6 inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021;185:247-53.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]





