Translate this page into:
Spesolimab for treatment of severe hidradenitis suppurativa in the real world
Corresponding author: Dr. Hong Liu, Department of Dermatology, Dermatology Hospital of Shandong First Medical University. Jinan, Shandong, China. hongyue2519@hotmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Wang N, Liu W, Zhu L, Yu C, Yan X, Shan X, et al. Spesolimab for treatment of severe hidradenitis suppurativa in the real world. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_1788_2024
Dear Editor,
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, recurrent inflammatory disease involving dysregulated tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) and interleukin (IL)-17.1 Current treatments are limited, thus highlighting an urgent need for effective targeted therapies. Recent research has revealed elevated IL-36 in patients with HS, thereby indicating a link between HS and Th17 cytokines.2,3 This finding suggests the potential of IL-36R antagonists to serve as new treatments. Here, we present a case series indicating the efficacy and safety of spesolimab in four patients with severe HS (Hurley III) who were unresponsive to other treatments.
We report four such patients. The basic information is reported in Table 1. Dermatological assessments revealed painful inflammatory nodules, abscesses, malodorous draining tunnels (dTs), and hypertrophic scars in various areas [Figure 1a and Supplementary Figure 1]. Genetic testing via whole genome sequencing and IL36RN Sanger sequencing identified mutations in two patients (c.115+6T>C in patient 1 and c.C338T in patient 3). The other two patients were mutation-free.
| Patient No. | Patient | Age of onset | BMI | Smoking | Lesion location | Previous treatments and results | Hurley stage |
Results w0/w8/w12 |
Results w0/w8/w12 |
Results w0/w8/w12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex/age | IHS4 | NPRS | DLQI | |||||||
| 1 | F/32 | 15 | 25.5 | No | Axillae, gluteal and inguinal region | rifapentine 0.3 g/d, acitretin 30 mg/d, clarithromycin 0.5 g/d; unsatisfactory | III | 36/26/31 | 0/0/0 | 21/18/17 |
| 2 | M/35 | 30 | 29.3 | Yes | Axillae, buttocks, scalp, and lower jaw | prednisone (20-30 mg/d), isotretinoin 30 mg/d, minocycline 100 mg/d, adalimumab and ixekizumab; uncontrolled and unsatisfactory | III | 39/27/19 | 9/5/4 | 28/18/15 |
| 3 | M/23 | 19 | 25.9 | No | Axillae, face, head, neck, and back | Acitretin 30 mg/d, minocycline 100 mg/d, cefixime 200 mg/d; unsatisfactory | III | 29/10/1 | 6/3/1 | 23/10/4 |
| 4 | M/18 | 13 | 30.4 | Yes | Face, axillae, gluteal and inguinal region | Isotretinoin 30 mg/d, minocycline 100 mg/d, adalimumab and photodynamic therapy; effective but unsatisfactory | III | 36/16/12 | 5/2/1 | 19/12/8 |
BMI: Body mass index
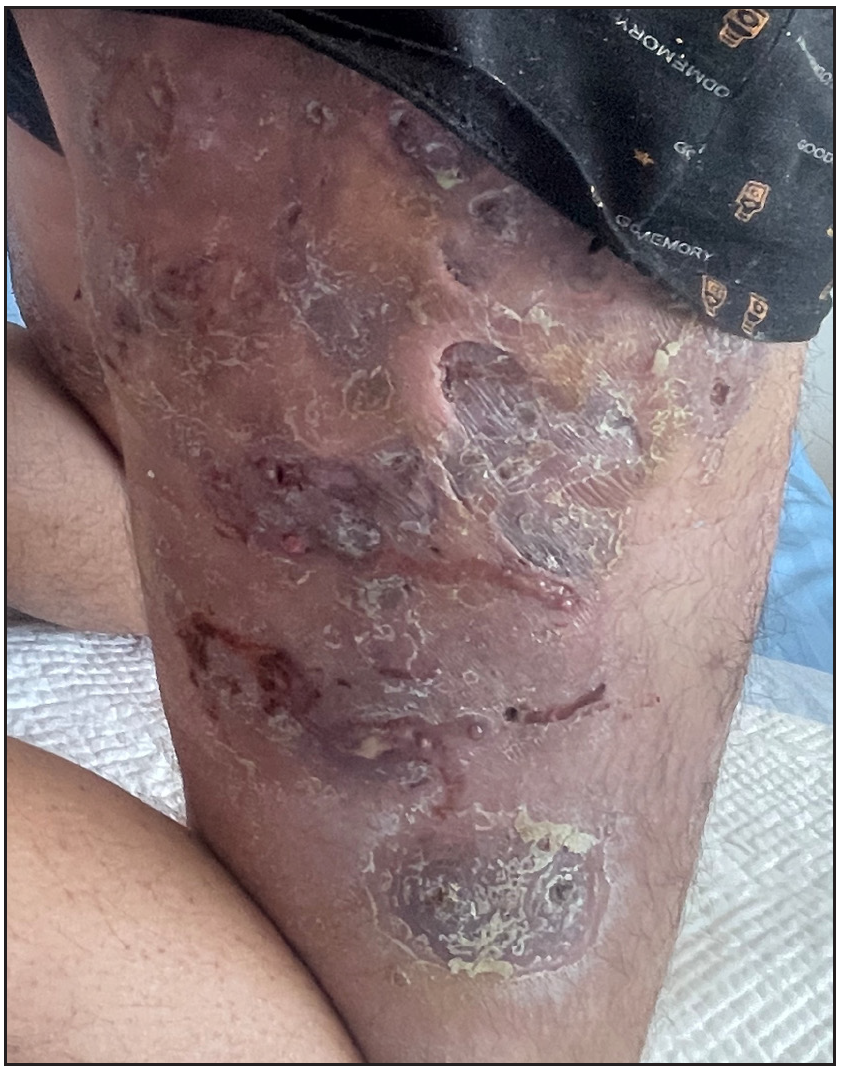
- Skin lesions before treatment in patient 2.
After evaluation and signed informed consent, all patients received a single dose of 900 mg spesolimab intravenously. Maintenance therapy included acitretin, minocycline, clarithromycin, rifapentine or other anti-inflammatory agents. Treatment efficacy was assessed pretreatment, at 8- and 12-week post-treatment with International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4), Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), and Numerical Pain Rating Scale (NPRS) [Table 1, Supplementary Fig 2]. Additionally, we measured the percentage of patients who achieved HiSCR50 and ISH4-55.4
After injection, all patients exhibited favourable responses at week 8. The abscess, inflammatory nodules, and dTs counts decreased, and no new flare occurred. Patients achieved an average of 44.9%, 44.4%, and 14.3% reduction in IHS4, NPRS, and DLQI separately [Supplementary Figure 2]. HiSCR50 and IHS4-55 were 25% and 50%, respectively, at week 8. By week 12, three patients showed marked improvement, with an average IHS4 reduction of 71.5%. NPRS and DLQI improved to 55.6% and 46.4%, respectively [Supplementary Figure 2], but only 2 patients showed improved HiSCR50 and ISH4-55 (patient 3 and 4). Notably, patient 1 experienced recurrence at week 12 because of discontinuation of the medication, and the IHS4 scores were 19.2% higher than in week 8.
Remarkably, three patients showed early skin lesion improvement or pain relief post-injection. By day 3, the neck nodules and abscesses in patient 3 had slightly decreased. By day 12, inflammatory nodules and abscesses had significantly decreased in patient 1 [Supplementary Figure 1]. By day 15, the pain subsided, and the lesions diminished in patient 2. After 30 days, isotretinoin was discontinued for patient 2 and the dosage of prednisolone was reduced from 20 mg daily to 10 mg daily. Although stability was achieved, the fistula and abscesses persisted [Figure 1b], and the same patient received a second dose of 900 mg spesolimab on day 50.
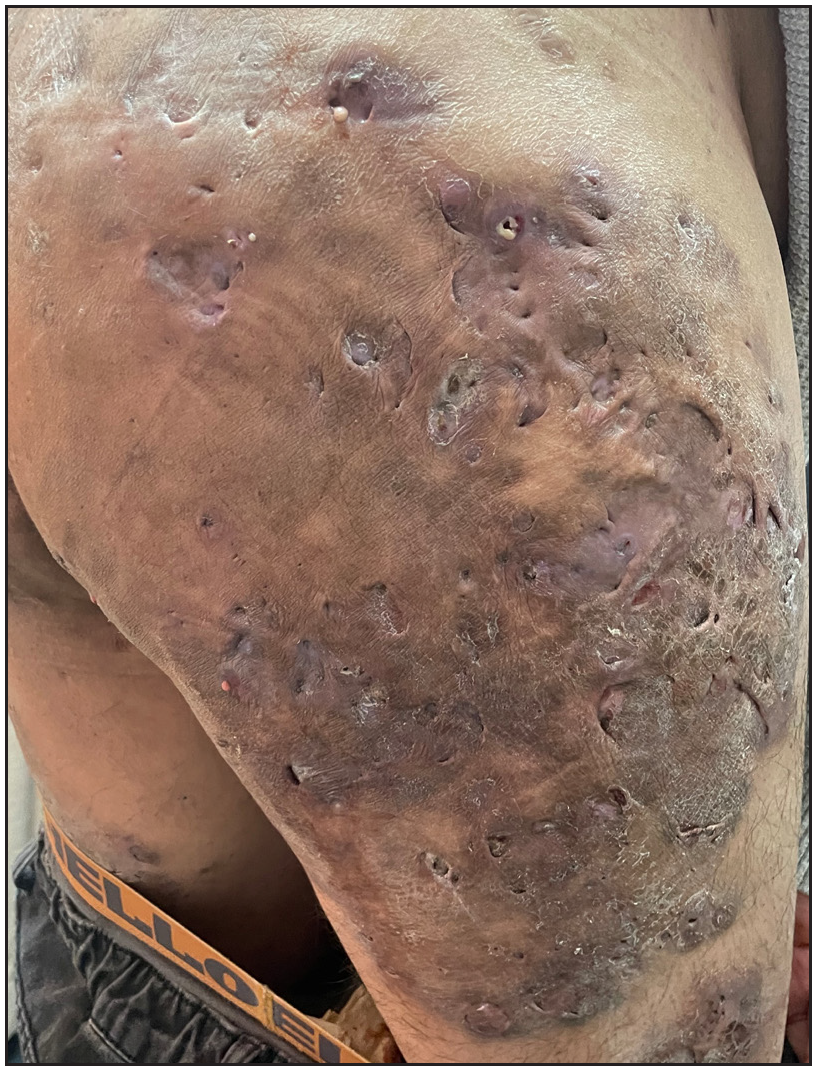
- Skin lesions after treatment in patient 2.
HS, a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by recurrent nodules, abscesses, dTs, and scarring, disproportionately affects young women.1 Herein, we present four cases of patients with HS treated with spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor). Remarkably, all four patients exhibited a favourable response to one or two doses of 900 mg spesolimab in combination with other therapies, achieving a 71.5% reduction in IHS4, and 2 patients reaching HiSCR50 and ISH4-55 at week 12. These results were more favourable than the clinical trial5 using 1200 mg spesolimab for a total of six times, which achieved a 54.3% reduction in ISH4 at week 12, possibly because of the use of combined treatment. Therefore, combined treatment might enable spesolimab dose reduction and potentially enhance treatment tolerability and cost-effectiveness. Among our patients, spesolimab exhibited an early therapeutic response and appeared to be efficacious in targeting superficial nodules, abscesses, and dTs. A recent preclinical study has revealed higher IL-36 expression within HS tunnels than in non-tunnel HS skin;6 consequently, spesolimab has shown clear advantages for dTs in our four patients.
Notably, patient 1 experienced recurrence within 4 weeks after discontinuing all medications, thus emphasising the need for long-term treatment to maintain remission in HS. Furthermore, patient 2 exhibited a relatively severe phenotype requiring additional therapeutic intervention, indicating heterogeneity in disease presentation and responsiveness to spesolimab. Moreover, a single dose of spesolimab was not sufficient for the treatment of severe HS. Therefore, our report underscores the critical importance of initiating early treatment with spesolimab or a combination of other effective drugs and maintaining therapy for the effective management of HS.
This report indicated the potential of IL-36 receptor antagonists as a viable treatment option for severe HS. However, evaluation of treatment efficacy in the presence of acitretin and systemic antibiotic use poses a challenge. Given the small sample size herein, further research is warranted to confirm and validate these findings.
Ethical approval
The research/study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Hospital for Skin Diseases, Shandong First Medical University, number 20231216KYKTKS001, dated 20231216.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Hidradenitis suppurativa: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1045-58.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical implementation of biologics and small molecules in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Drugs. 2021;81:1397-410.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- IL-36 cytokines are increased in acne and hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309:673-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adalimumab in conjunction with surgery compared with adalimumab monotherapy for hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized controlled trial in a real-world setting. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:677-84.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proof-of-concept study exploring the effect of spesolimab in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:508-18.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunnels in hidradenitis suppurativa: active inflammatory entities with specific molecular and genetic profiles–a narrative review. Dermatology. 2023;239:323-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





