Translate this page into:
Lung cancer skin metastasis
Corresponding author: Dr. Songmei Geng, Department of Dermatology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xincheng District, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China. gsm312@yahoo.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Zhu L, Wang Y, Geng S. Lung cancer skin metastasis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2025;91:131. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_132_2024
A 38-year-old man presented with multiple asymptomatic red nodules on his right chest wall for six-months duration [Figure 1]. Three years ago, a bronchoscopic biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma. He received chemotherapy eight times and responded poorly. Chest computed tomography (CT) scan revealed metastasis in the lungs and bone. The pathology of the nodule displayed the eosinophilic cytoplasmic tumour cell clusters in the dermis, with mitosis and glandular differentiation, similar to the primary lung tumour [Figure 2a]. Immunohistochemical staining showed that the tumour cells were positive for CK7, P63 while negative for CK20 [Figure 2b–2d]. Finally, the diagnosis of lung cancer skin metastasis was made.
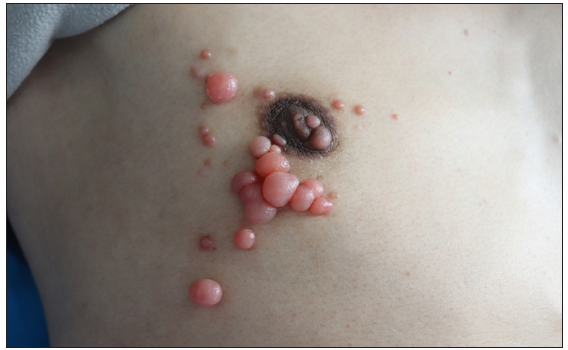
- Multiple red nodules on the right chest wall.
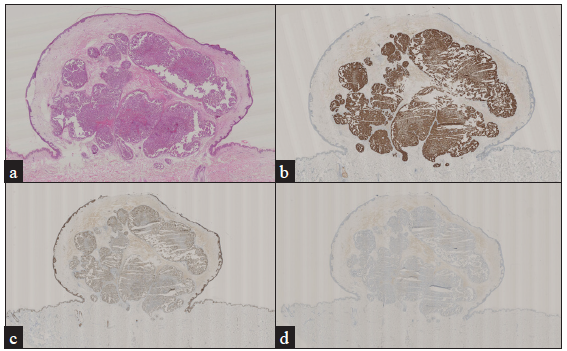
- (a) Eosinophilic cytoplasmic tumour cell clusters in the dermis (Haematoxylin and eosin, 15x), (b) Positive immunohistochemical staining for CK7 (15x), (c) Positive immunohistochemical staining for p63 (15x), (d) Negative immunohistochemical staining for CK20 (15x).
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
The Open Funds for Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Infection and Immune Diseases.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of AI-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.





